[ad_1]
Mar 21, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Along with their fundamental parts, the properties of crystalline and nanoporous supplies usually rely crucially on visitor atoms or ions which can be embedded within the tiny pores of their lattice construction. This is applicable to high-tech supplies utilized in sensor or separation expertise in addition to to pure supplies.
The bluish gemstone aquamarine, for instance, can be colourless with out such visitor parts. Figuring out the sort and place of visitor parts is troublesome, as many supplies react sensitively to the radiation emissions from electron microscopes.
Due to a brand new technique developed by a group led by Daniel Knez and Ferdinand Hofer on the Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis at Graz College of Expertise (TU Graz), this may now be completed with much less radiation and is due to this fact a lot simpler.
“The distinctiveness of our technique lies in the truth that we will decide the three-dimensional distribution of ions in crystal channels or nanopores based mostly on a single electron microscope picture,” says Daniel Knez.
The findings have been revealed in Communications Supplies (“Three-dimensional distribution of particular person atoms within the channels of beryl”).
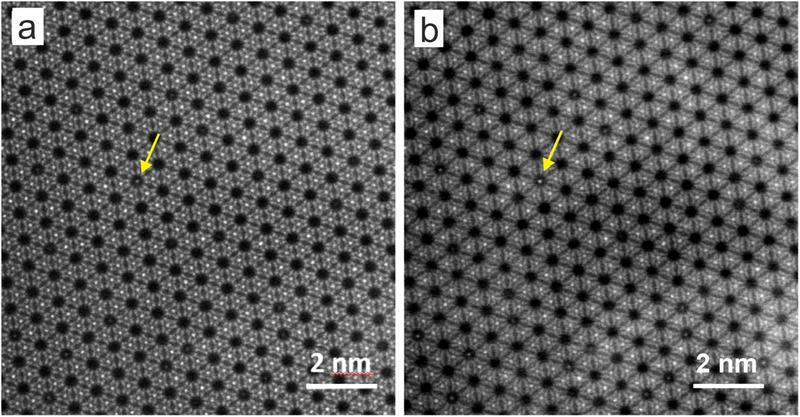
An electron microscope picture of an aquamarine. The yellow arrows mark caesium ions within the crystal pores. (Picture: FELMI-ZFE)
The mysterious blue color of aquamarine
The researchers developed their technique whereas analysing the gemstone aquamarine. Till now, it was not recognized the place precisely the iron that lends the stone its blue color is positioned within the crystal. One speculation was that particular person iron atoms are caught within the pores and create this impact from there. However this has now been refuted.
Of their experiments, the researchers have established past doubt that there isn’t a iron within the pores, however as a substitute caesium ions. The color-conferring iron atoms are positioned in shut proximity to the caesium ions, however are built-in into the columns of the crystal lattice.
A single picture with atomic decision as a foundation
For his or her experiments, the researchers recorded a so-called Z-contrast picture of the aquamarine crystal at atomic decision utilizing the ASTEM microscope, a scanning transmission electron microscope.
The electron beam of the ASTEM microscope is targeted on the floor of the crystal pattern, additionally penetrating into the pores of the fabric. If it hits ions saved there, they seem as shiny dots within the picture. Based mostly on the energy of the distinction with empty pores and the neighbouring lattice constructions, the researchers can decide the kind of embedded ions and likewise estimate how deep they’re positioned within the pores. These information had been statistically analysed and in contrast with a lot of simulations of the crystal construction so as to have the ability to estimate the varied components influencing the measured sign.
Modern technique opens up new potentialities for supplies science
Along with fundamental analysis, the brand new technique can also be appropriate for the focused improvement of recent supplies. “Our technique can be utilized to exactly decide the place of doping components, i.e. focused function-controlling components, in nanoporous supplies equivalent to zeolites or metal-organic framework compounds,” says Ferdinand Hofer. This facilitates the optimisation of (single-atom) catalysts and solid-state electrolytes in future batteries or the event of biomedical purposes for controlling drug uptake.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




