[ad_1]
Mar 21, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) A synthetic intelligence (AI) picture recognition algorithm can predict whether or not a mouse is transferring or not based mostly on mind useful imaging information. The Kobe College researchers additionally developed a technique to establish which enter information is related, shining mild into the AI black field with the potential to contribute to brain-machine interface know-how.
For the manufacturing of brain-machine interfaces, it’s mandatory to know how mind alerts and affected actions relate to one another. That is referred to as “neural decoding,” and most analysis on this discipline is completed on the mind cells’ electrical exercise, which is measured by electrodes implanted into the mind.
Alternatively, useful imaging applied sciences, corresponding to fMRI or calcium imaging, can monitor the entire mind and may make lively mind areas seen by proxy information. Out of the 2, calcium imaging is quicker and presents higher spatial decision. However these information sources stay untapped for neural decoding efforts.
One specific impediment is the necessity to preprocess the info corresponding to by eradicating noise or figuring out a area of curiosity, making it tough to plot a generalized process for neural decoding of many various sorts of habits.
Kobe College medical scholar AJIOKA Takehiro used the interdisciplinary experience of the crew led by neuroscientist TAKUMI Toru to deal with this difficulty.
“Our expertise with VR-based actual time imaging and movement monitoring programs for mice and deep studying methods allowed us to discover ‘end-to-end’ deep studying strategies, which signifies that they don’t require preprocessing or pre-specified options, and thus assess cortex-wide data for neural decoding,” says Ajioka.
They mixed two totally different deep studying algorithms, one for spatial and one for temporal patterns, to whole-cortex movie information from mice resting or working on a treadmill and educated their AI-model to precisely predict from the cortex picture information whether or not the mouse is transferring or resting.
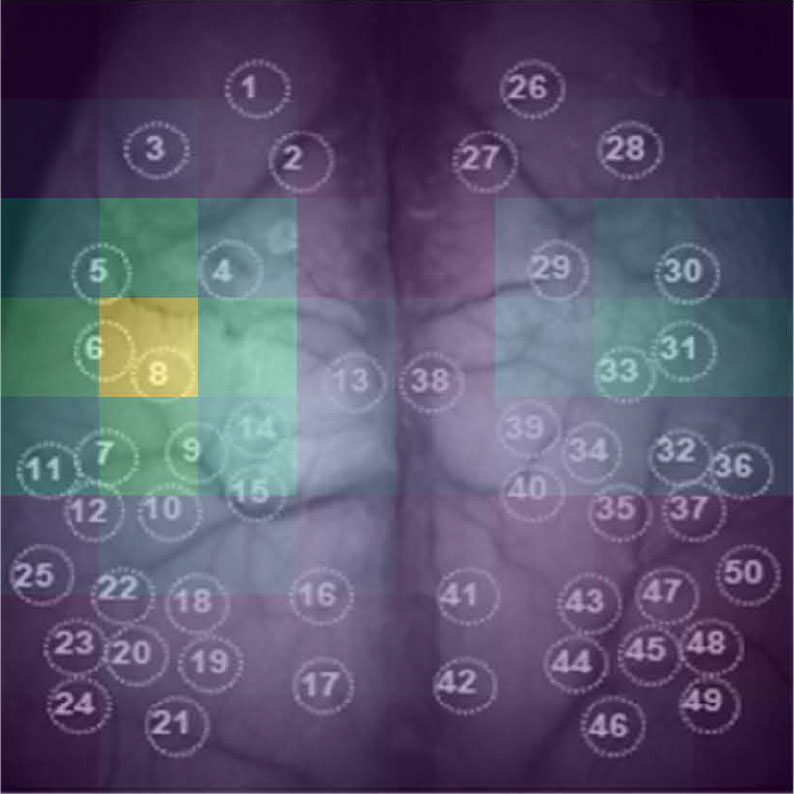
A brand new “end-to-end” deep studying technique for the prediction of behavioral states makes use of whole-cortex useful imaging that don’t require preprocessing or pre-specified options. Developed by medical scholar AJIOKA Takehiro and a crew led by Kobe College’s TAKUMI Toru, their strategy additionally permits them to establish which mind areas are most related for the algorithm (pictured). The power to extract this data lays the inspiration for future developments of brain-machine interfaces. (Picture: AJIOKA Takehiro)
Within the journal PLoS Computational Biology (“Finish-to-end deep studying strategy to mouse habits classification from cortex-wide calcium imaging”), the Kobe College researchers report that their mannequin has an accuracy of 95% in predicting the true behavioral state of the animal with out the necessity to take away noise or pre-define a area of curiosity. As well as, their mannequin made these correct predictions based mostly on simply 0.17 seconds of information, that means that they may obtain close to real-time speeds. Additionally, this labored throughout 5 totally different people, which exhibits that the mannequin may filter out particular person traits.
The neuroscientists then went on to establish which components of the picture information had been primarily chargeable for the prediction by deleting parts of the info and observing the efficiency of the mannequin in that state. The more serious the prediction grew to become, the extra necessary that information was. “This capacity of our mannequin to establish important cortical areas for behavioral classification is especially thrilling, because it opens the lid of the ‘black field’ facet of deep studying methods,” explains Ajioka.
Taken collectively, the Kobe College crew established a generalizable approach to establish behavioral states from whole-cortex useful imaging information and developed a way to establish which parts of the info the predictions are based mostly on. Ajioka explains why that is related. “This analysis establishes the inspiration for additional creating brain-machine interfaces able to close to real-time habits decoding utilizing non-invasive mind imaging.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




