[ad_1]
Researchers at São Paulo State College (UNESP) have created a revolutionary therapeutic method that has the potential to utterly change the way in which that visceral leishmaniasis, a uncared for tropical illness (NTD) unfold by sandflies, is handled. The World Well being Group (WHO) estimates that 12 million people worldwide undergo from the illness and that between 700,000 and 1 million new circumstances develop annually.
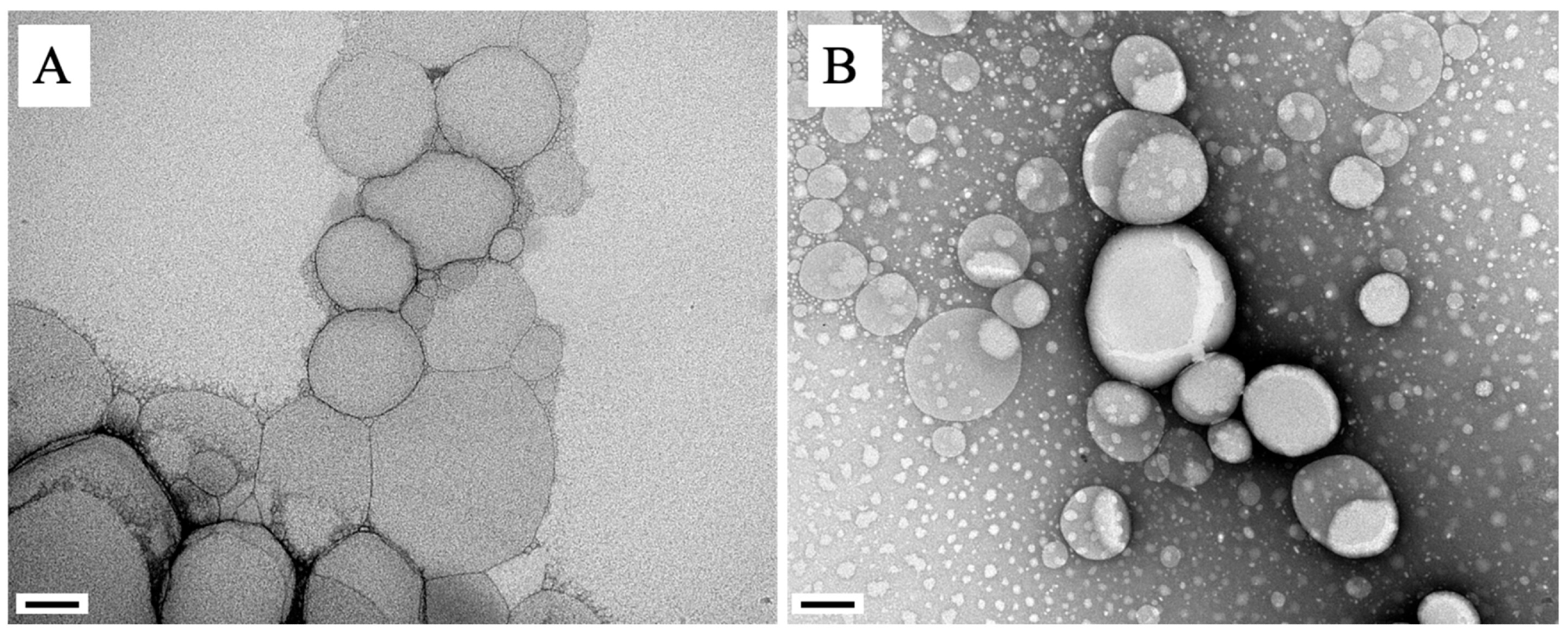
Lipid nanoparticles seen beneath a microscope, with out (A) and with (B) the encapsulated energetic precept. Picture Credit score: IB-CLP
The researchers’ technique consists of utilizing lipid nanoparticles to inject lupeol, a chemical compound identified to destroy the disease-causing Leishmania protozoan parasites. Lupeol is a triterpene present in a wide range of greens and fruits, corresponding to mangos, grapes, and strawberries, in addition to inexperienced peppers and olives.
In exams on animals, the approach successfully eradicated Leishmania from organs. The findings are detailed in a research revealed within the journal Prescribed drugs.
There are three varieties of leishmaniasis. The visceral kind is the deadliest, with a demise threat of as much as 95% if left untreated and as much as 10% even when handled, in accordance with WHO. The opposite two are cutaneous leishmaniasis (probably the most prevalent, leading to pores and skin ulcers) and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis (affecting the mouth, nostril, and throat).
The present therapies, which principally embrace the administration of pentavalent antimonials or amphotericin B, have severe hostile results, notably on the guts, liver, and kidneys. Some leishmaniasis medication are exceedingly costly, putting a major load on public well being techniques, and if administered incorrectly, they’ll set off drug resistance within the parasite.
In consequence, the researchers emphasize within the research the important necessity to find or create novel energetic compounds, a few of which have been present in crops.
Researchers from the Institute of Biosciences at UNESP’s Coastal Experiment Campus (IB-CLP) in São Vicente developed a brand new methodology to manage lupeol utilizing lipid nanoparticles.
Lupeol has been proven in vitro to be able to eliminating types of Leishmania, however it isn’t very soluble in physiological options, which limits its bioavailability in vivo.
Adriana de Jesus, Research First Writer and Postdoctoral Researcher, São Paulo State College
She added, “Placing it in lipid nanoparticles solves the issue by surmounting organic boundaries, maximizing therapeutic impact and delivering the treatment to the targets, which within the case of visceral leishmaniasis are the spleen, liver and bone marrow. The nanocarriers are merely the supply car. After they attain the goal web site, with the appropriate pH they open up and launch the treatment.”
First Time Ever
The analysis used 4 teams of hamsters contaminated with Leishmania infantum and handled for ten days. The primary group obtained solely lupeol, the second group obtained lupeol-containing nanoparticles, the third group obtained empty nanoparticles, and the fourth obtained merely a placebo.
Samples have been collected from the animals’ spleen, liver, blood, and plasma for biochemical, physiopathological, and parasite load investigation.
As predicted, lipid nanoparticles containing lupeol have been extra profitable than lupeol alone in eradicating visceral leishmaniasis parasites from the spleen and liver: administering the nanoparticles with lupeol for ten days decreased the parasite depend by 99.9%.
“As well as, the animals handled on this means exhibited minimal histopathological alterations within the spleen and liver. For the primary time ever, we proved that this mixture is very efficient in treating the illness and is a major formulation whose use ought to be thought of,” de Jesus added.
Lupeol nanoparticles have been injected intraperitoneally. The researchers now intend to create a nanocarrier for oral supply, permitting sufferers to take their treatment at house, in addition to variations for topical therapy of cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Journal Reference:
Jesus, J. A., et. al. (2024) Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Strong Methods for Lupeol Supply within the Remedy of Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis. Prescribed drugs. doi:10.3390/ph16121646.
Supply: https://fapesp.br/en
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink



