[ad_1]

China desires to make use of and manufacture extra of its personal medical tools.Credit score: VCG by way of Getty Photographs
As a sinology scholar within the early Nineties at Nanjing College, Elisabeth Staudinger “received a flavour of what well being care felt like for the individuals in China”. As a part of her research, she needed to enterprise greater than 2,000 kilometres to Yunnan in China’s southwest nook. Again then, components of the province had been so distant that individuals who wanted medical consideration would usually have to attend for Mondays to roll round, when visiting retailers, physicians and dentists would arrange store in a weekly market.
“Quick ahead to at this time, you’ve got very affordable hospitals and health-care infrastructures throughout the nation” alongside near-universal well being protection, says Staudinger, who’s now a managing board member of the worldwide medical expertise firm Siemens Healthineers in Erlangen, Germany. “Issues are massively higher than it was,” she says. “However there’s nonetheless a variety of work to do.”

Nature Highlight: Medical units in China
China has a inhabitants of round 1.4 billion individuals, one-fifth of whom are over the age of 60. A burgeoning center class and the accompanying rise in medical circumstances linked to affluence, corresponding to kind 2 diabetes and hypertension, has meant that China has embraced preventive care, alongside remedy, says Jeroen Groenewegen-Lau, an analyst who research science, expertise and innovation on the Mercator Institute for China Research (MERICS), a assume tank in Berlin. However this has meant opening up the market to costly remedies and expertise, he says.
Conscious of the prices, the Chinese language authorities started a drive round a decade in the past to supply and use extra regionally manufactured medical units, says analyst Alexander Brown, additionally at MERICS. Particularly, the main focus has been on high-end tools corresponding to X-ray scanners, which may help early illness detection. The push intensified additional in 2021, within the hope of slashing prices and assembly the evolving health-care wants of an ageing inhabitants, whereas additionally boosting innovation and enhancing nationwide safety by curbing imports.
The technique is affecting each China’s medical-device sector and the medical-technology trade as a complete. Medical expertise consists of units that use info expertise to detect, gather and add knowledge. Hospitals in China have been instructed to acquire merchandise made within the nation when attainable, and home and overseas producers have altered their enterprise operations and focus. In 2021, the latest 12 months for which knowledge had been accessible, China held 20% of the medical-device market share, second solely to the USA.
Gathering momentum
The Chinese language authorities promotes its ‘make native, purchase native’ technique in a wide range of methods: devoted innovation parks, subsidies and analysis funding for home medical-technology corporations, and centralized volume-based buying for public hospitals.
“However technically there is just one regulation on the books that’s explicitly round Chinese language-product procurement,” says Helen Chen, a managing companion based mostly in Shanghai on the international agency L.E.Ok. Consulting. In Could 2021, the Ministry of Trade and Info Expertise, and the Ministry of Finance launched Order 551, which includes a listing of 315 merchandise. Round half of those are medical tools corresponding to ophthalmic lenses and medical lasers, whereas the remaining consists of gadgets corresponding to these utilized in marine, geological and geophysical work — ground-based radars, for instance. State-owned companies seeking to procure such gadgets should make sure that the tools is manufactured from 25–100% of regionally manufactured components.

Unleashing the ability of massive knowledge to information precision medication in China
Order 551 should be seen within the broader context, says Chen, “which is that China, usually, is attempting to be far more self-sufficient in its health-care merchandise”. The directive got here only a month after the Chinese language authorities outlined a five-year plan aimed toward propelling six or extra Chinese language corporations into the world’s prime 50 medical-device companies — up from the 4 that had been within the prime 100 in 2021. The nation’s ambition for its medical-device sector might be traced again additional, nevertheless. In 2010, medical units had been recognized as one in every of 20 Strategic Rising Industries — alongside biotechnology, renewable vitality, and the Web of Issues — and the central authorities started dedicating five-year plans to the sector.
In 2014, Chinese language President Xi Jinping highlighted the trigger additional, saying: “It’s essential to speed up the localization of high-end medical units to lower manufacturing prices and to advertise the continual improvement of nationwide enterprises.” The pivot to producing merchandise corresponding to high-value imaging, diagnostic and remedy tools — together with computed tomography (CT) scanners, ultrasound and dialysis machines, in addition to implantables corresponding to pacemakers — is especially notable as a result of up till that time, medical manufacturing had centred primarily on producing syringes, gloves, gauzes and different low-end disposables (see ‘Medical machines’).
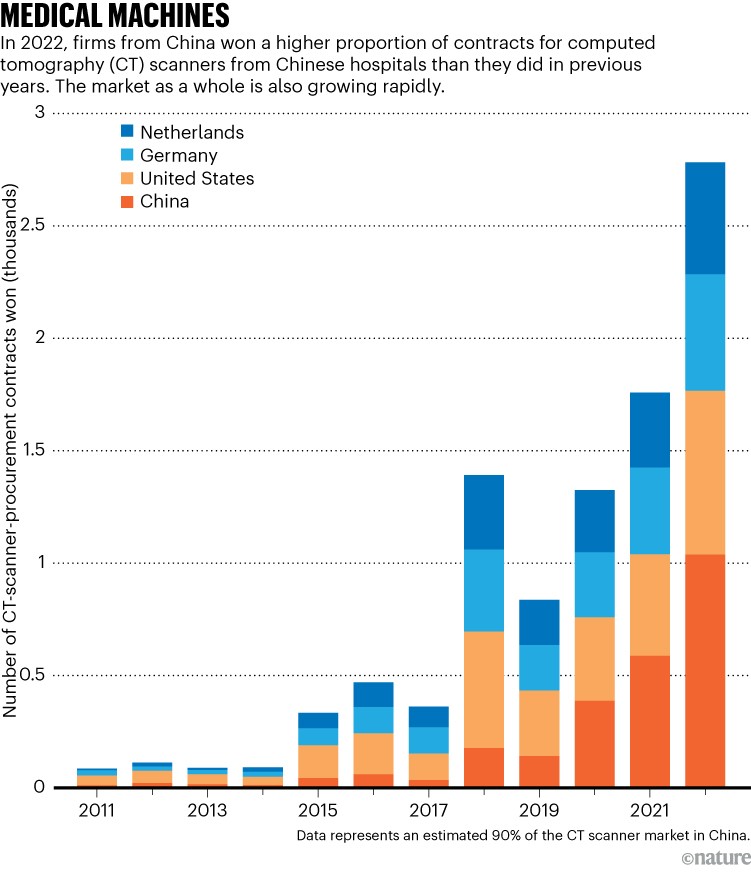
Supply: Alexander Brown/Merics
However for trade watchers corresponding to Chen, the actual game-changer occurred in 2015, when the federal government introduced its Made in China 2025 (MIC2025) initiative. The strategic plan boldly declared the nation aimed to develop into a world manufacturing powerhouse for ten industries — together with robotics, electrical automobiles and medical units — by 2025. China hopes to realize this by boosting native industrial capabilities in analysis and improvement, design, and the procurement of essential parts, in addition to by transferring meeting processes into the nation.
Amongst different targets, MIC2025 requires 70% of mid-to-high-end medical units to be produced domestically by 2025, and for this to rise to 95% by 2030.
With solely a 12 months to the primary deadline, Brown says: “I believe they nonetheless have a strategy to go. They haven’t been capable of catch up as a lot as they might have preferred in distinction to one thing like new-energy automobiles.”
“But it surely’s not for the dearth of effort — China has been funnelling some huge cash into the sector. I believe the hurdles are partly to do with the extremely specialised nature of medical units,” Brown provides. “Nonetheless, Made in China has had the best affect by way of build up native industrial capability.”

How paediatrician researchers are advancing youngster well being
And it’s a tried-and-tested strategy. The nation has gained dominance in industries corresponding to prescribed drugs, photo voltaic panels and machine instruments, in line with a report by Brussels-based assume tank, the European Centre for Worldwide Political Economic system. Policymakers first establish sectors and applied sciences that they assume are essential to the nation’s financial improvement and safety. The federal government then initiates insurance policies to develop home industries that may problem international companies (see go.nature.com/49rlyhv).
China’s ambitions for its medical-device trade look no completely different. A profusion of coverage and monetary initiatives to spice up native manufacturing and use of medical units appeared after MIC2025. In April 2022, for example, provincial governments in Anhui, Hubei and Shanxi informed hospitals to restrict their use of medical and testing tools to these produced domestically.
The federal government additionally started providing incentives, corresponding to diminished hire, to entice companies to maneuver or arrange places of work in 4 medical-device industrial zones — the Bohai Financial Rim together with Beijing; the Yangtze River Delta encompassing Shanghai; the Pearl River Delta, made up of Guangdong, Shenzhen and a handful of different cities; and Central China, which incorporates Wuhan, Chengdu and Chongqing. It additionally elevated tax advantages for analysis and improvement investments: rising from 1.7 billion yuan (US$236 million) in 2017 to 11.4 billion yuan in 2022, in line with a MERICS evaluation of 122 medical-technology companies listed on the Shanghai, Shenzhen and Beijing inventory exchanges (see go.nature.com/3urvdkn).
In July 2023, the Shenzhen Institute of Superior Expertise started mass producing a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) instrument it had developed. And firstly of the COVID-19 pandemic, United Imaging Healthcare in Shanghai equipped greater than 100 domestically produced CT scanners and X-ray machines to hospitals together with these in Wuhan, Shanghai and Beijing.
In 2019, one in every of China’s largest medical-technology companies, MicroPort in Shanghai, reported that surgeons had accomplished the primary profitable surgical procedure, a prostatectomy, with its lacroscopic robotic Toumai. The four-armed Toumai can do advanced surgical procedures in slim areas within the physique, corresponding to urethral reconstructions. It might probably even be operated remotely.
Ripples far and extensive
In response to a 2021 evaluation by consultancy agency Deloitte (see go.nature.com/3uyujzw), the market income of China’s medical-device trade greater than doubled between 2015 and 2019, continuously outpacing the enlargement in gross home product with an annual development price of roughly 20% because the launch of MIC2025.
Some sectors have even begun to show the tide on commerce — producers of pacemakers, for example, noticed their international exports develop by 110% between 2015 and 2020. In the meantime, gross sales of pacemakers by overseas opponents to China rose by 2%.
General, the market share of home manufacturers producing high-end units has risen from 20% to 30% prior to now decade. US and European multinationals corresponding to Siemens, GE HealthCare and Medtronic proceed to dominate the sector, nevertheless, says Rohit Anand, an analyst on the consulting agency GlobalData in Hyderabad, India. This distinction in market share boils all the way down to “substantial disparity in product high quality, scale and effectivity”, he says.

Components of high-end units corresponding to computed tomography scanners are actually made in China.Credit score: Function China/Future Publishing by way of Getty
Brown observes that medical units are area of interest merchandise that require specialised information, and Chinese language companies have struggled to achieve a foothold.
Citing medical robotics for example, he provides: “There isn’t an enormous market in China as a result of they’re very costly. The typical Chinese language buyer simply can’t afford to pay for that, and those that may afford to would in all probability go for a number one American agency over some inexperienced Chinese language one.”
Attitudes amongst medical professionals are altering, nevertheless. A 2020 survey of Chinese language hospital staff, performed by the agency L.E.Ok. Consulting, discovered that 3% “use Chinese language supplies when attainable”. In a follow-up survey a 12 months later, after Order 551, round 30% stated they all the time use Chinese language supplies (see go.nature.com/3iba26v).
Usually, the choice comes all the way down to practicalities, says Deloitte analyst Alan MacCharles in Shanghai. “You may need two or three choices and the physician may say: ‘The Western gadget is barely higher however as a result of I haven’t had coaching on that system in awhile, I’m far more proficient with the Chinese language manufacturers.’”
Due to new buying laws, many worldwide producers have opted to determine native operations in China. Some companion with native companies, organising joint ventures, corresponding to those between Sinopharm Imaging in Beijing and US agency GE Healthcare, or between Shanghai Electrical and Siemens.

From tea to tofu: why Chinese language dietary staples are wealthy pickings for analysis
A handful of outstanding overseas companies have established their very own manufacturing vegetation within the nation. Sysmex in Kobe, Japan, now assembles its blood and urine testing tools in Shandong. Equally, Dutch agency Philips produces a handful of high-end scanners in China, corresponding to its EPIQ Elite ultrasound sequence, which incorporates an AI-powered cardiovascular machine. In 2020, Philips launched its Ingenia Ambition MRI, which is made in China and boasts a 50% discount in scan instances. It’s the first MRI to function with out helium fuel, a non-renewable useful resource that’s in scarce provide.
And at a world commerce truthful final Could, GE Healthcare displayed 23 medical units, 18 of which had been made and developed in China. One spotlight was the ultra-high-end Revolution CT scanner, which boasts the power to conduct a coronary examination “in a single heartbeat beneath any coronary heart price and rhythm circumstances”, in line with GE Healthcare. The agency started manufacturing the scanner at its Beijing manufacturing facility in 2020. Of the CT tools that the corporate ships to clients worldwide, 70% are made at that manufacturing facility.
Making the choice to begin manufacturing in China isn’t taken flippantly. “It’s not a simple course of as a result of the price of constructing these vegetation for high-end units is excessive,” says MacCharles. “You possibly can have native supply-chain and intellectual-property points, it takes years to get absolutely licensed and principally you possibly can’t produce something for fairly a while.”
US companies, specifically, face challenges, given the continuing tensions between the 2 nations, says Grace Fu Palma, founding father of China Med Machine in Beijing, a consultancy that gives regulatory and enterprise recommendation to overseas companies seeking to enter the Chinese language market. “The political state of affairs is unquestionably having a destructive affect on the entry of overseas companies.”
Staudinger says that China continues to be a precedence location for Siemens, which has been working there for greater than 30 years and has six analysis and improvement websites within the nation, regardless of growing pressures for customers to purchase from native companies. “The laws are generally projected as this factor the place they need to get overseas corporations in a foreign country,” she says. “However that isn’t what we’ve skilled.”
“So long as you’re a part of the journey and part of supporting the course of constructing a strong, high-quality health-care system in China,” says Staudinger, “you’ll really feel very welcome.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




