[ad_1]
Mar 13, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) If left to their very own gadgets, micro organism on our enamel or wounded pores and skin can encase themselves in a slimy scaffolding, turning into what is known as biofilm. These micro organism wreak havoc on our tissue and, being shielded from antibiotic medicine by the slime, are tough to dislodge. A brand new technique might provide a easy strategy to break up the muck and destroy the micro organism.
Researchers on the College of Pennsylvania and Stanford College have developed sugar-coated gold nanoparticles that they used to each picture and destroy biofilms. In a research printed within the Journal of Scientific Investigation (“Theranostic gold-in-gold cage nanoparticles allow photothermal ablation and photoacoustic imaging in biofilm-associated an infection fashions”), the authors demonstrated the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of the nanoparticles on the enamel and wounded pores and skin of rats and mice, eliminating the biofilms in as little as one minute and outperforming widespread antimicrobials.
“With this platform, you may bust biofilms with out surgically debriding infections, which could be vital when utilizing antibiotics. Plus, this methodology might deal with sufferers if they’re allergic to antibiotics or are contaminated by strains which are proof against medicine,” stated Luisa Russell, Ph.D., a program director within the Division of Discovery Science & Know-how at NIBIB. “The truth that this methodology is antibiotic-free is a big energy.”
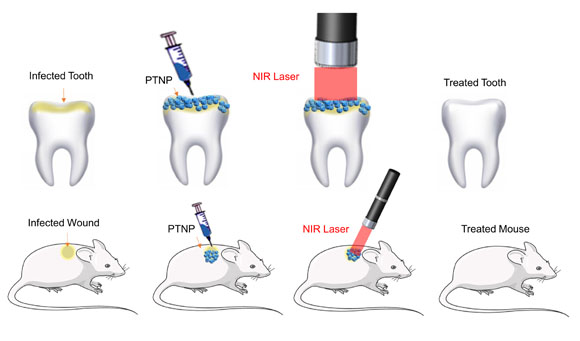
Within the research, gold nanoparticles delivered to contaminated enamel and pores and skin wounds are heated with close to infrared lasers to destroy biofilms. (Picture: Hajfathalian et al.)
Oral biofilms, also referred to as plaques, shaped by micro organism resembling Streptococcus mutans may cause important tooth decay. Wound infections, that are generally brought on by Staphylococcus micro organism, can significantly delay the therapeutic course of. In both case, the densely packed community of proteins and carbohydrates inside biofilms can stop antibiotics from reaching microbes all through the affected space.
However that isn’t the extent of the problem posed by biofilms. Not solely are they tough to take away, however they’re troublesome to discern within the first place.
This new analysis recognized an answer to knock out each issues with one stone: gold.
Gold is unhazardous and readily converts vitality from mild sources into warmth, making it a chief candidate for photothermal remedy, a technique that makes use of the warmth from nanoparticles to kill close by pathogens. Along with producing warmth, the nanoparticles emit detectable ultrasound waves in response to mild, which means that gold particles could be visualized utilizing a way known as photoacoustic imaging.
Within the new research, the authors encapsulated gold spheres inside bigger golden cage-shaped nanoparticles to optimize their response to mild for each therapeutic and imaging functions. To make the particles interesting to micro organism, they coated them in dextran, a carbohydrate that may be a widespread constructing block of biofilms.
The researchers assessed their technique by making use of the gold nanoparticles atop S. mutans-infected enamel from ex vivo rat jaws.
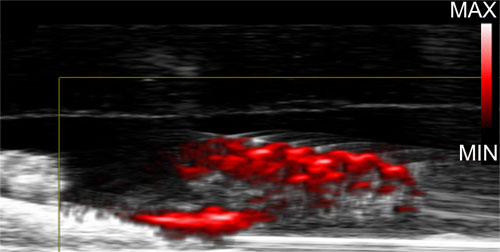
Researchers have been in a position to visualize biofilms in enamel handled with dextran-coated gold nanoparticles utilizing photoacoustic imaging. (Picture: Hajfathalian et al.)
In a photoacoustic imaging take a look at on the enamel, the nanoparticles emitted alerts that got here by loud and clear, permitting the crew to see exactly the place biofilms had taken up the dextran-coated particles on the enamel.
Then, to judge the particles’ therapeutic impact, they irradiated the enamel with a laser. For comparability, they handled different contaminated enamel samples with the topical antiseptic chlorhexidine.
The crew noticed a stark distinction within the outcomes of the 2 remedies, with the photothermal remedy being practically 100% efficient at killing biofilms, whereas chlorhexidine didn’t considerably diminish the viability of micro organism.
“The remedy methodology is very quick for the oral an infection. We utilized the laser for one minute, however actually in about 30 seconds we’re killing mainly all the micro organism,” stated research first creator Maryam Hajfathalian, Ph.D., a professor of biomedical engineering on the New Jersey Institute of Know-how, who carried out this research whereas a postdoctoral researcher at each the College of Pennsylvania and Stanford College.
Evaluations carried out on mice with open wounds of their pores and skin, contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus, have been equally profitable, as warmth generated by nanoparticles significantly outperformed one other antimicrobial agent known as gentamicin. Right here, the researchers additionally measured and famous an increase in temperature of 20 °C localized to the biofilm, not inflicting any obvious injury to surrounding tissue.
The authors point out that with additional checks they goal to point out whether or not the technique can stop cavities or pace up therapeutic.
“I believe it is essential to see how cheap, easy, and quick this course of is. Since we’re restricted in utilizing antibiotics, we’d like novel remedies like this as a substitute,” Hajfathalian stated.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




