[ad_1]
Mar 08, 2024
(Nanowerk Highlight) Think about a tiny bioelectronic gadget, implanted beneath your pores and skin, that would constantly monitor your very important indicators, exactly ship medicine, and even stimulate your muscle tissue and nerves to deal with a wide range of situations. Now think about if, after a pre-programmed time period, this gadget would merely dissolve away, its mission full, leaving no hint behind in your physique. No want for an extraction surgical procedure, no threat of long-term issues – only a short-term therapeutic answer that disappears when not wanted.
That is the tantalizing promise of bioresorbable electronics, a cutting-edge discipline that seeks to create medical implants from supplies that may harmlessly degrade and soak up into the physique after functioning for a helpful timeframe. By eliminating the necessity for surgical elimination, such “transient” units might revolutionize the remedy of situations starting from wound therapeutic to epilepsy. They might usher in a brand new period of precision medication the place the gadget itself is a type of “digital drug” that exists just for a desired period.
However designing units that may reliably function within the harsh atmosphere of the human physique after which vanish on cue is not any easy activity. A key problem has been growing an encapsulating materials that may defend the electronics from moisture and degradation for a controllable interval earlier than breaking down into benign byproducts. This packaging should act as an ideal moisture barrier for the gadget’s purposeful lifetime, but not linger within the physique indefinitely afterwards. Typical supplies have fallen in need of this very best.
Polymers, for instance, may be readily shaped into skinny movies however inherently permit water to slowly permeate by way of and degrade the electronics prematurely. Inorganic supplies like silicon dioxide are glorious limitations however are sometimes inflexible and require excessive temperatures to manufacture, limiting their versatility. Hybrid organic-inorganic approaches have proven promise however nonetheless battle to totally eradicate defects that quickly compromise the encapsulation. A completely new supplies technique is required to allow longer lasting and extra succesful bioresorbable units.
Now, a multi-disciplinary analysis group consisting of chemists, supplies scientists, and biomedical engineers might have discovered an answer. As reported in Superior Supplies (“Bioresorbable Multilayer Natural–Inorganic Movies for Bioelectronic Techniques”), they’ve devised an encapsulation technique that makes use of ultrathin alternating layers of silicon oxynitride (SiON) and a customized bioresorbable polymer known as polyanhydride (PA) to create a versatile, tunable, defect-tolerant moisture barrier. By stacking a number of layers of those supplies in an optimized configuration, they shaped a tortuous path that successfully impedes fluid penetration and prevents moisture from reaching the electronics, even when minor imperfections are current.
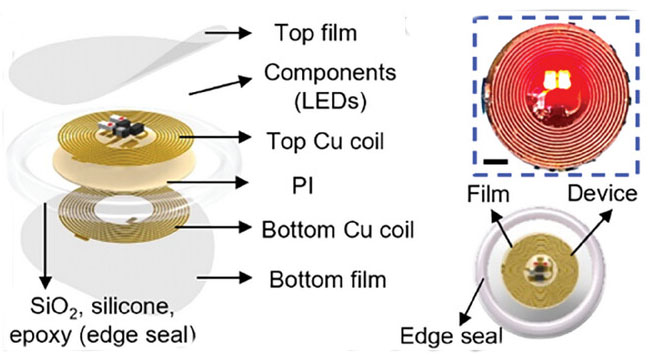
Optoelectronic gadget demonstration of water barrier efficiency of 3-layer SiON-PA movies. The picture exhibits an exploded view schematic diagram of the gadget and its encapsulation. Inset exhibits activated LEDs, indicating correct functioning of the gadget. (Reprinted with permission by Wiley-VCH Verlag)
To understand why it is a breakthrough, contemplate the weaknesses of single layer limitations. Even a nanoscopic pinhole in an inorganic barrier movie can quickly develop and permit moisture in. Polymers are extra forgiving of defects however are permeable over time. The group’s innovation was to create a multilayer construction the place many separate layers work collectively to “guard” one another. Any localized flaw is remoted and contained, unable to compromise the gadget.
Simply as crucially, the chemistry and variety of layers may be exactly tuned to manage how lengthy the gadget stays secure earlier than degrading. That is achieved by customizing the properties of the PA materials and the thickness of particular person layers within the stack. The result’s an unprecedented stage of management over a bioresorbable gadget’s purposeful lifetime, from days to months, whereas making certain a secure and predictable dissolution afterwards.
The potential of this know-how was vividly demonstrated by encapsulating wi-fi LED implants and testing them each in vitro and in dwell mice. Units protected by the multilayer SiON-PA movies remained secure and purposeful for over a month, whereas unprotected implants failed inside days within the physique. Imaging revealed the barrier held again any moisture penetration till the pre-programmed degradation started.
Intensive biocompatibility and degradation research had been additionally performed to make sure the protection and environmental influence of the barrier supplies. Each in vitro cell research and in vivo implantation experiments confirmed that the SiON-PA movies and their degradation merchandise had been non-toxic and didn’t set off any opposed inflammatory responses. The movies broke down into benign compounds that may very well be safely absorbed or excreted by the physique over time.
Whereas additional growth and testing are nonetheless wanted, this groundbreaking encapsulation technique opens the door to a brand new era of longer lasting and extra succesful bioresorbable medical units. By offering a tunable, defect-tolerant moisture barrier, it might allow implants for a a lot wider vary of situations, preprogrammed to final for a desired timeframe earlier than vanishing with no hint.
Nevertheless, challenges stay on the trail to scientific translation. Lengthy-term research will probably be wanted to totally characterize the in vivo degradation course of and any potential results of the byproducts. Scaling up the fabrication course of whereas sustaining exact management over layer properties would require additional engineering efforts. Regulatory hurdles should even be navigated to reveal the protection and efficacy of those novel units in people.
The event of this multilayer organic-inorganic moisture barrier represents a big leap ahead for the sphere of bioresorbable electronics. By offering a tunable, defect-tolerant encapsulation technique, this innovation might unlock a brand new period of long-lasting, transient medical units able to treating a variety of situations earlier than harmlessly dissolving away. The interdisciplinary method pioneered by this analysis group, combining the strengths of chemistry, supplies science, and biomedical engineering, showcases the ability of collaboration in pushing the boundaries of what’s doable.
Nevertheless, this groundbreaking work is only the start. Additional research are wanted to totally characterize the long-term in vivo efficiency and security of those supplies, in addition to to optimize and scale up the fabrication course of. Researchers should additionally navigate the advanced regulatory panorama to translate this know-how from the lab to the clinic. These challenges would require sustained effort and funding from each the scientific group and business companions.
However the potential societal influence of this know-how is immense. Think about a future the place sufferers with power situations like diabetes or coronary heart illness might obtain long-term, steady monitoring and remedy from a single, self-dissolving implant. Image a world the place most cancers sufferers might bear localized, sustained drug supply with out the necessity for repeated invasive procedures. Envision a time when mind problems like epilepsy or Parkinson’s may very well be managed with short-term, focused digital stimulation that leaves no lasting footprint. These potentialities are actually inside attain, because of advances like this bioresorbable moisture barrier.
Furthermore, the idea of “digital medication” – the place the gadget itself is a programmable, transient therapeutic – might essentially reshape the way in which we method medical remedy. By enabling exact, time-limited interventions tailor-made to every affected person’s wants, this paradigm shift might enhance outcomes, cut back unwanted effects, and decrease healthcare prices. It might additionally alleviate the environmental burden of medical waste, as single-use units would merely degrade into benign parts.
As for the timeline of scientific translation, specialists predict that the primary human trials of bioresorbable digital units might start inside the subsequent 5-10 years. As analysis continues to refine and optimize these applied sciences, we will count on to see an rising variety of purposes transfer from preclinical research to scientific testing. Throughout the subsequent twenty years, it’s fully believable that bioresorbable electronics might turn out to be a mainstream medical software, remodeling the usual of take care of a variety of situations.
After all, realizing this imaginative and prescient would require ongoing collaboration and funding from researchers, clinicians, business companions, and policymakers. It would demand a sustained dedication to interdisciplinary analysis, translational medication, and public-private partnerships.

By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is writer of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Expertise,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Abilities and Instruments Making Expertise Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
Nanowerk E-newsletter
Get our Nanotechnology Highlight updates to your inbox!
Thanks!
You’ve efficiently joined our subscriber record.
Develop into a Highlight visitor writer! Be a part of our giant and rising group of visitor contributors. Have you ever simply revealed a scientific paper or produce other thrilling developments to share with the nanotechnology group? Right here is how one can publish on nanowerk.com.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink



