[ad_1]
Mar 21, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Autoimmune ailments are mysterious. It wasn’t till the Nineteen Fifties that scientists realized that the immune system may hurt the organs of its personal physique. Even at this time, the elemental causes and internal workings of most autoimmune ailments stay poorly understood, limiting the remedy choices for a lot of of those situations.
Over the previous a number of years, nonetheless, analysis has discovered clues for a way autoimmune ailments would possibly come up. This analysis has proven that DNA connected to small particles inside the bloodstream is a probable perpetrator concerned in lots of autoimmune ailments, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus, or simply lupus for brief, which primarily impacts younger ladies and may trigger kidney harm.
Nevertheless, because of the giant selection in sizes of each particles and DNA within the blood, testing to what extent and beneath what circumstances these DNA-particle combos play a task in illness has been extraordinarily tough.
Researchers at Duke College have now developed a option to systematically take a look at how these DNA-bound particles work together with the immune system. By utilizing tiny particles of particular sizes, attaching DNA strands of sure lengths and exposing the ensuing complexes to immune cells in a lab dish, the researchers present a greater elementary understanding of those ailments could also be doable.
The outcomes had been revealed within the journal Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy (“DNA Corona on Nanoparticles Results in an Enhanced Immunostimulatory Impact With Implications For Autoimmune Ailments”).
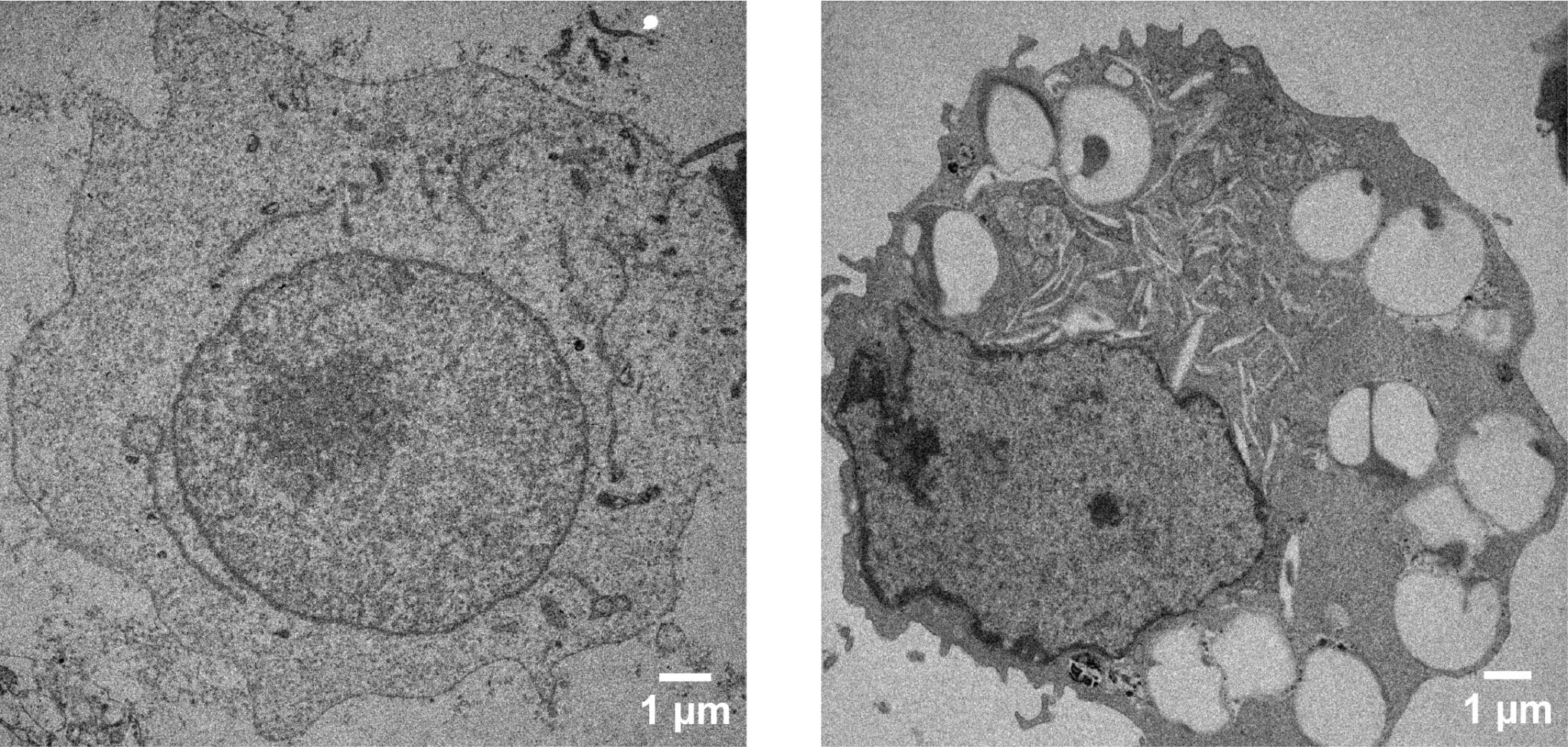
A wholesome cell’s inside construction (left) in comparison with a cell that has taken up nanoparticles coated with DNA (proper). The big cavities are the locations the place the nanoparticle was internalized, serving to researchers higher perceive what cell receptors are being activated. (Picture: Duke College)
“Our strategy recognized the mobile pathway that causes the dangerous response to those hybrid particles, and confirmed that DNA certain to the surfaces of nanoparticles is protected against being degraded by enzymes,” mentioned Christine Payne, the Yoh Household Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Supplies Science. “We expect these are extraordinarily vital outcomes that may kind the idea for future research with our novel system.”
Whereas DNA is normally locked away inside a cell’s nucleus, it usually will get into the bloodstream when cells die or are attacked by viruses and micro organism. Whereas most so-called “cell-free DNA” solely lasts minutes earlier than being damaged down by the physique, in some individuals and conditions, it could persist for for much longer. In current work, excessive ranges of cell-free DNA have been carefully associated to the severity of lupus signs, and plenty of docs at the moment are testing methods to make use of it to watch illness exercise.
Cell-free DNA could escape elimination largely by forming complexes with different molecules or attaching itself to naturally occurring particles. Relying on the origin of the DNA, it could vary in size from just a few hundred base pairs to a number of thousand. And the particles it could connect to vary from 100 to 1000 nanometers in diameter.
“Experimenting with the particles truly present in blood is tough as a result of they arrive in so many various sizes and combos,” mentioned Dr. David Pisetsky, professor of medication and integrative immunobiology on the Duke College College of Medication. “The place earlier work has targeted on utilizing nanoparticles for remedy, right here we’re exploring utilizing participles to grasp illness mechanisms, which could be very informative for vital medical questions.”
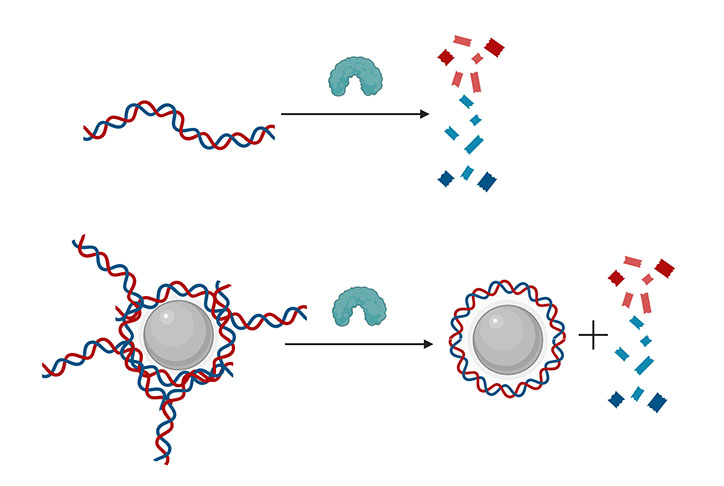
Usually, the enzyme DNase cuts cell-free DNA into tiny items (prime). However when DNA is connected to a nanoparticle, the enzyme can solely clip the ends, leaving a DNA “corona” across the nanoparticle. These complexes are believed to contribute to the signs of many autoimmune ailments. (Picture: Duke College)
Payne labored with members of her laboratory to manufacture tightly managed artificial particles at each ends of the naturally occurring measurement spectrum. They then connected DNA strands from E. Coli both just a few hundred base pairs lengthy or 10,000 base pairs lengthy to particles each giant and small. With a variety of artificial DNA-particle complexes in hand, they blended varied combos with human macrophages, a kind of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms, removes lifeless cells, and stimulates the motion of different immune cells.
“I joined the lab over a yr in the past and have been engaged on characterizing the nanoparticle coronas to grasp their measurement, quantity of DNA and the way the DNA degrades,” mentioned Diego Montoya, a third-year undergraduate pupil working in Payne’s lab and a co-author on the paper. “It’s been quite a lot of enjoyable and a privilege working with everybody on this analysis.”
The primary vital remark the crew made was that DNA connected to nanoparticles was protected against degrative enzymes, and that bigger nanoparticles supplied extra safety.
“We expect the enzymes may not be capable of entry the DNA to destroy it due to the form the DNA makes with the floor of the nanoparticle,” mentioned Faisal Anees, a Ph.D. pupil in Payne’s lab. “However there could be different results happening, in order that’s a query we’re attempting to reply extra definitively now.”
The outcomes confirmed that the macrophages responded to all kinds of DNA-particle complexes by producing inflammatory indicators for different cells to comply with, a trademark of many autoimmune ailments. In addition they demonstrated that this response is created via a particular signaling pathway known as cGAS-STING.
The researchers stress that the mixed outcomes don’t but present a smoking gun for the reason for lupus or different autoimmune ailments, that are seemingly diversified and nuanced.
“All of the methods the immune system assaults itself are actually complicated, exhausting to grasp and tough to deal with,” Payne mentioned. “This strategy provides researchers a option to drill down and pinpoint components that they wouldn’t be capable of with a purely organic system.”
“We now have a well-defined mannequin system that offers us the power to ask these questions on causation versus correlation,” added Pisetsky, who has been researching autoimmune ailments for nearly half a century. “It additionally provides us a brand new methodology for exploring potential therapies.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink



