[ad_1]
Mar 13, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Physicists usually flip to the Rayleigh-Taylor instability to elucidate why fluid buildings kind in plasmas, however that is probably not the total story with regards to the ring of hydrogen clumps round supernova 1987A, analysis from the College of Michigan suggests.
In a examine printed in Bodily Assessment Letters (“Hydrodynamic mechanism for clumping alongside the equatorial rings of SN1987A and different stars”), the staff argues that the Crow instability does a greater job of explaining the “string of pearls” encircling the remnant of the star, shedding gentle on a longstanding astrophysical thriller.
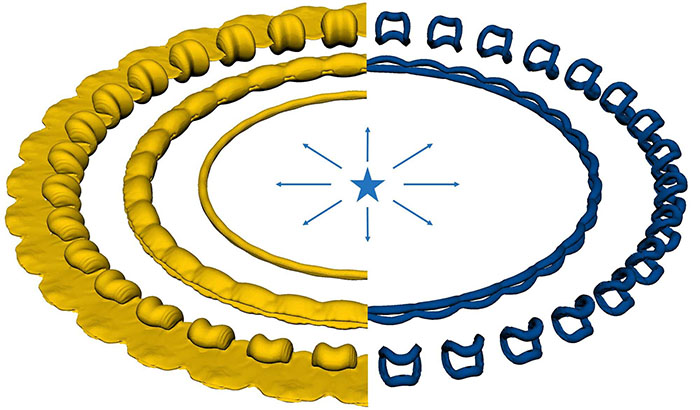
The simulation exhibits the form of the fuel cloud on the left and the vortices, or areas of quickly rotating circulate, on the appropriate. Every ring represents a later time within the evolution of the cloud. It exhibits how a fuel cloud that begins as an excellent ring with no rotation turns into a lumpy ring because the vortices develop. Ultimately the fuel breaks up into distinct clumps. (Picture: Michael Wadas, Scientific Computing and Circulation Laboratory)
“The fascinating half about that is that the identical mechanism that breaks up airplane wakes might be in play right here,” stated Michael Wadas, corresponding creator of the examine and a graduate pupil in mechanical engineering on the time of the work.
In jet contrails, the Crow instability creates breaks within the easy line of clouds due to the spiraling airflow coming off the tip of every wing, generally known as wingtip vortices. These vortices circulate into each other, creating gaps—one thing we are able to see due to the water vapor within the exhaust. And the Crow instability can do one thing that Rayleigh-Taylor couldn’t: predict the variety of clumps seen across the remnant.
“The Rayleigh-Taylor instability may let you know that there could be clumps, however it will be very tough to tug a quantity out of it,” stated Wadas, who’s now a postdoctoral scholar on the California Institute of Expertise.
On a black backdrop, dim or distant stars glow white, with three nearer or brighter stars producing hexagonal diffraction patterns like rainbow snowflakes. In the midst of the body, the supernova remnant resembles a reptilian eye, with a teal cloud within the heart ringed by vivid white dots which are the clumps of hydrogen lit up by the shockwave from the supernova. A pale haze surrounds the ring of dots, with different much less distinct dots inside.
Supernova 1987A is among the many most well-known stellar explosions as a result of it’s comparatively near Earth at 163,000 gentle years away, and its gentle reached Earth at a time when subtle observatories existed to witness its evolution. It’s the first supernova seen to the bare eye since Kepler’s supernova in 1604, making it an extremely uncommon astrophysical occasion that has performed an outsized position in shaping our understanding of stellar evolution.
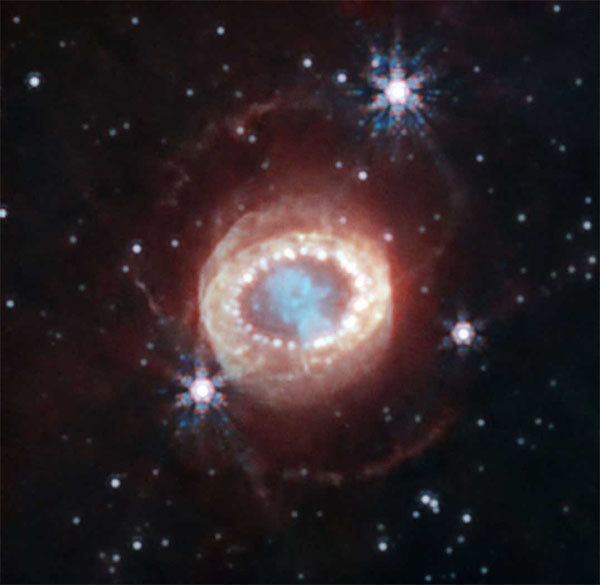

A near-infrared picture of the remnant left behind by supernova 1987A, taken by the James Webb Area Telescope. The hydrogen clumps generally known as the “string of pearls” seem as a hoop of white dots across the teal heart of the stellar remnant, nonetheless shining brightly as a result of vitality imparted by the supernova shockwave. The variety of clumps is in keeping with the Crow instability having brought about them to kind. (Picture: NASA, ESA, CSA, M. Matsuura (Cardiff College), R. Arendt (NASA’s Goddard Spaceflight Middle & College of Maryland, Baltimore County), C. Fransson (Stockholm College), J. Larsson (KTH Royal Institute of Expertise), A. Pagan (STScI))
Whereas a lot remains to be unknown in regards to the star that exploded, it’s believed that the ring of fuel surrounding the star forward of the explosion got here from the merger of two stars. These stars shed hydrogen into the house round them as they turned a blue big tens of hundreds of years earlier than the supernova. That ring-shaped cloud of fuel was then buffeted by the stream of high-speed charged particles coming off the blue big, generally known as a stellar wind. The clumps are believed to have shaped earlier than the star exploded.
The researchers simulated the way in which the wind pushed the cloud outward whereas additionally dragging on the floor, with the highest and backside of the cloud being pushed out quicker than the center. This brought about the cloud to curve in on itself, which triggered the Crow instability and brought about it to interrupt aside into pretty even clumps that turned the string of pearls. The prediction of 32 may be very near the noticed 30 to 40 clumps across the supernova 1987A remnant.
“That’s an enormous piece of why we expect that is the Crow instability,” stated Eric Johnsen, U-M professor of mechanical engineering and senior creator of the examine.
The staff noticed hints that the Crow instability would possibly predict the formation of extra beaded rings across the star, additional out from the ring that seems brightest in telescope photos. They had been happy to see that extra clumps appear to seem within the shot from the James Webb Area Telescope’s near-infrared digicam, launched in August final yr, Wadas defined.
The staff additionally steered that the Crow instability could be at play when the mud round a star settles into planets, though additional analysis is required to discover this chance.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




