[ad_1]
Vertically aligned carbon nanotube (VaCNT) membranes can be utilized to wash or desalinate water with a excessive move price and low stress. Not too long ago, researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Know-how (KIT) and collaborators performed steroid hormone adsorption experiments to analyze the interplay of forces in microscopic pores.
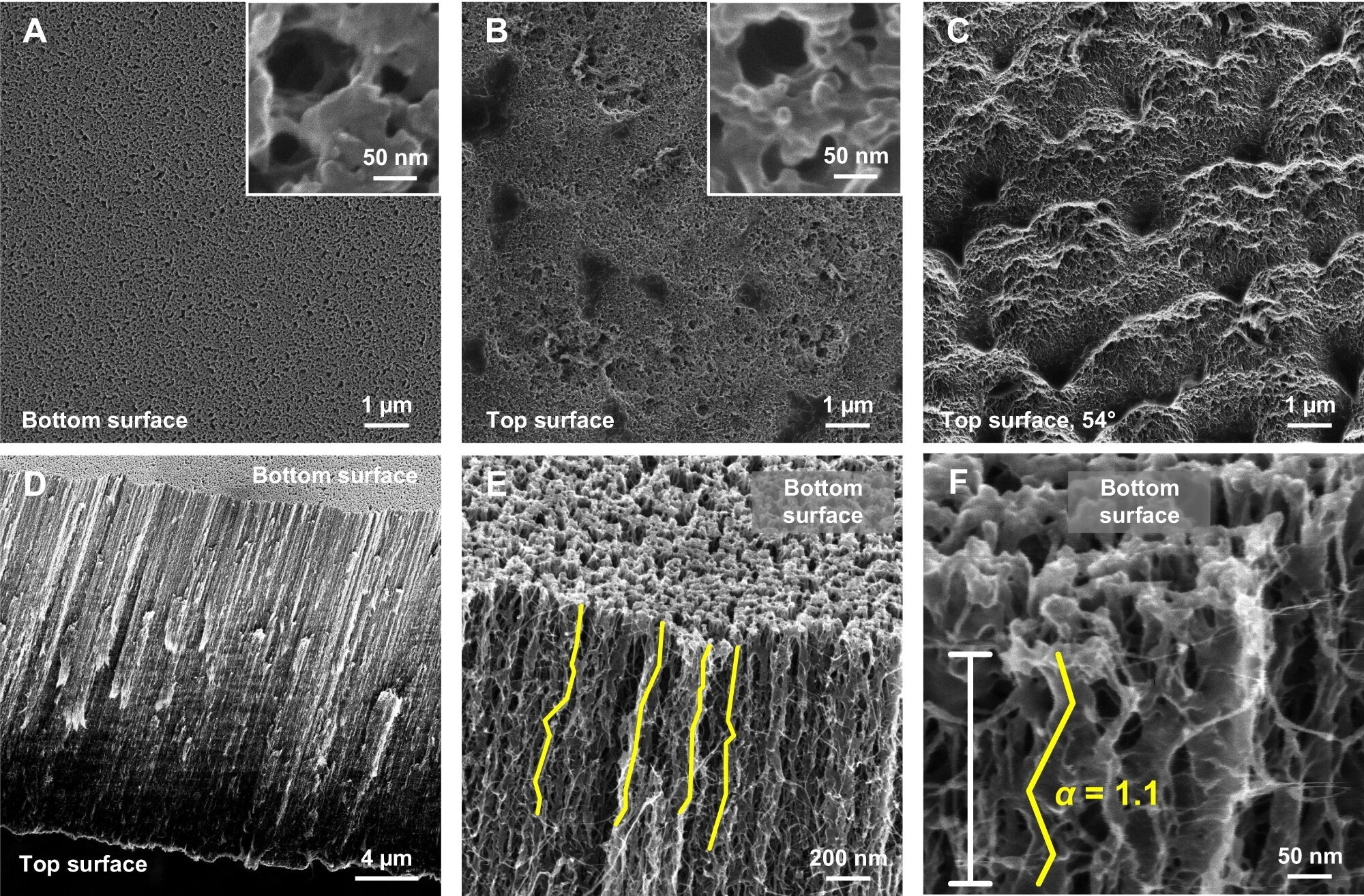
Floor and pore morphology of VaCNT membranes. A, B Prime and backside floor of the VaCNT membrane (the insets resolve the membrane ‘pores’ on each surfaces). C View of the highest floor at a tilt angle of 54° exhibiting the roughness of this floor. D, E, F Rising zooms of the VaCNT membrane cross-section at a tilt angle of 54°. The attainable move paths highlighted in E and F offers an estimate of the pore tortuosity. Picture Credit score: Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44883-2
They found that VaCNTs with sure pore geometry and floor construction are appropriate for utilization as extremely selective membranes. The research was revealed in Nature Communications.
Everybody on the planet requires entry to protected consuming water. Membranes are utilized to effectively take away micropollutants, corresponding to steroid hormones, that are hazardous to human well being and the setting. A extremely potential membrane materials is constructed of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes (VaCNT).
This materials is superb—with small pores of 1.7 to three.3 nanometers in diameter, an almost good cylindrical form, and small torsion. The nanotubes ought to have a extremely adsorbing impact, however have a really low friction solely.
Andrea Iris Schäfer, Professor, Institute for Superior Membrane Know-how, Karlsruhe Institute of Know-how
Pores are at the moment too giant for environment friendly retention, but smaller pores should not technically sensible.
Interaction of Forces
In research utilizing steroid micropollutants, IAMT researchers investigated why VaCNT membranes make wonderful water filters. They utilized membranes made by the Lawrence Livermore Nationwide Laboratory (LLNL) in Livermore, California. The discovering: VaCNT’s low adsorption, or floor deposition, is helpful for extremely selective membranes that concentrate on particular molecules.
The research demonstrates that adsorption in membrane nanopores relies not solely on the adsorption floor and restricted mass switch, but additionally on the interplay of hydrodynamic forces, friction, and attraction and repulsion forces on the liquid-wall interface. On account of their low friction and fast move velocity, extremely water-permeable nanopores have little contact.
Schäfer added, “When the molecules should not retained due to their dimension, interplay with the fabric will usually decide what occurs. The molecules will bounce by way of the membrane just like a climber climbing a wall. That is a lot simpler when there are lots of good climbing holds.”
Pore geometry and floor construction are specifically designed with the assistance of research such because the one carried out by IAMT.
Ten Years to Flip the Concept into an Experiment
At LLNL, Dr. Francesco Fornasiero and his colleagues created the membranes. The newest analytical tools at IAMT was used to conduct and assess the micropollutant checks.
“It took about 10 years to show the concept right into a profitable experiment that has met with the large curiosity of the membrane know-how group,” Schäfer added.
It’s fairly difficult to provide membranes which are so almost flawless. In bigger areas up to some sq. centimeters, there’s a very excessive probability of defects. And defects would have an effect on the result. LLNL has been profitable in creating membranes in bigger areas in recent times. To maintain hint contaminants on two sq. centimeters for research, IAMT researchers concurrently constructed minuscule filtration gadgets.
“Downscaling is extraordinarily tough. Having managed this collectively is an enormous success. Now, we’re ready for the event of membranes with even smaller pores,” Schäfer additional added.
The analysis was the primary to have a look at how hydrodynamic forces, friction, and attraction and repulsion interacted. It presents elementary outcomes on water dealing with. These would possibly assist ultra- and nanofiltration processes managed by nanopores.
Journal Reference:
Nguyen, M. N., et. al. (2024) Interaction of the forces governing steroid hormone micropollutant adsorption in vertically-aligned carbon nanotube membrane nanopores. Nature Communications. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-44883-2.
Supply: https://www.equipment.edu/english/
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




