[ad_1]
Mar 18, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Astronomers have charted the largest-ever quantity of the universe with a brand new map of lively supermassive black holes dwelling on the facilities of galaxies. Known as quasars, the gas-gobbling black holes are, sarcastically, among the universe’s brightest objects.
The brand new map logs the situation of about 1.3 million quasars in area and time, the furthest of which shone shiny when the universe was only one.5 billion years outdated. (For comparability, the universe is now 13.7 billion years outdated.)
“This quasar catalog is totally different from all earlier catalogs in that it offers us a three-dimensional map of the largest-ever quantity of the universe,” says map co-creator David Hogg, a senior analysis scientist on the Flatiron Institute’s Middle for Computational Astrophysics in New York Metropolis and a professor of physics and information science at New York College. “It isn’t the catalog with essentially the most quasars, and it isn’t the catalog with the best-quality measurements of quasars, however it’s the catalog with the biggest whole quantity of the universe mapped.”
Hogg and his colleagues current the map in a paper revealed in The Astrophysical Journal (“Quaia, the Gaia-unWISE Quasar Catalog: An All-sky Spectroscopic Quasar Pattern”). The paper’s lead writer, Kate Storey-Fisher, is a postdoctoral researcher on the Donostia Worldwide Physics Middle in Spain.
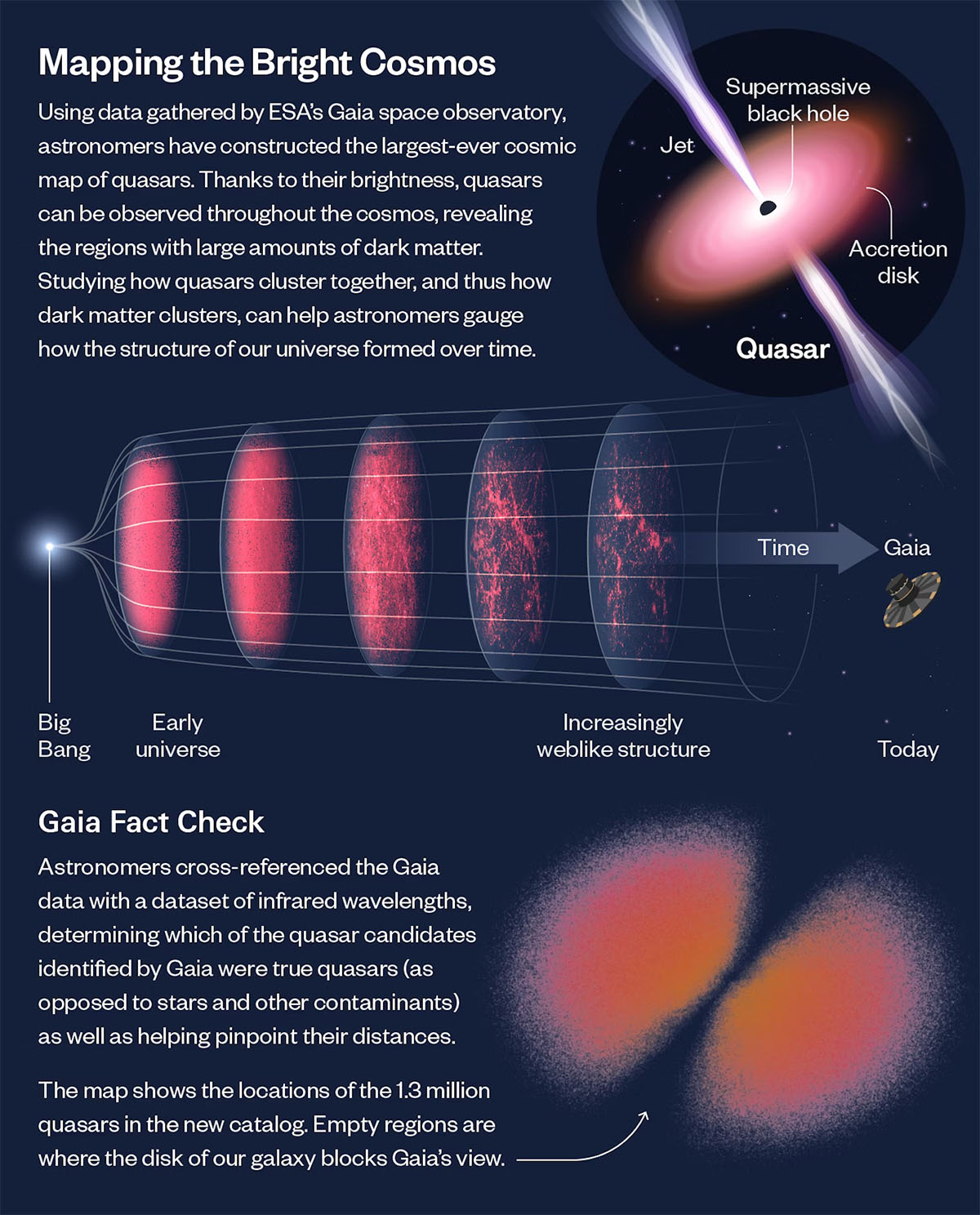
(Picture: ESA/Gaia/DPAC; Lucy Studying-Ikkanda/Simons Basis; Okay. Storey-Fisher et al. 2024) (click on on picture to enlarge)
The scientists constructed the brand new map utilizing information from the European House Company’s Gaia area telescope. Whereas Gaia’s major goal is to map the celebrities in our galaxy, it additionally inadvertently spots objects exterior the Milky Approach, corresponding to quasars and different galaxies, because it scans the sky.
“We had been in a position to make measurements of how matter clusters collectively within the early universe which might be as exact as a few of these from main worldwide survey initiatives — which is sort of outstanding on condition that we obtained our information as a ‘bonus’ from the Milky Approach–centered Gaia challenge,” Storey-Fisher says.
Quasars are powered by supermassive black holes on the facilities of galaxies and might be lots of of instances as shiny as a whole galaxy. Because the black gap’s gravitational pull spins up close by gasoline, the method generates a particularly shiny disk and typically jets of sunshine that telescopes can observe.
The galaxies that quasars inhabit are surrounded by huge halos of invisible materials known as darkish matter. By learning quasars, astronomers can be taught extra about darkish matter, corresponding to how a lot it clumps collectively.
Astronomers also can use the areas of distant quasars and their host galaxies to higher perceive how the cosmos expanded over time. For instance, scientists have already in contrast the brand new quasar map with the oldest gentle in our cosmos, the cosmic microwave background. As this gentle travels to us, it’s bent by the intervening net of darkish matter — the identical net mapped out by the quasars. By evaluating the 2, scientists can measure how strongly matter clumps collectively.
“It has been very thrilling to see this catalog spurring a lot new science,” Storey-Fisher says. “Researchers world wide are utilizing the quasar map to measure all the things from the preliminary density fluctuations that seeded the cosmic net to the distribution of cosmic voids to the movement of our photo voltaic system by means of the universe.”
The staff used information from Gaia’s third information launch, which contained 6.6 million quasar candidates, and information from NASA’s Broad-Area Infrared Survey Explorer and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. By combining the datasets, the staff eliminated contaminants corresponding to stars and galaxies from Gaia’s authentic dataset and extra exactly pinpointed the distances to the quasars. The staff additionally created a map exhibiting the place mud, stars and different nuisances are anticipated to dam our view of sure quasars, which is essential for decoding the quasar map.
“This quasar catalog is a good instance of how productive astronomical initiatives are,” says Hogg. “Gaia was designed to measure stars in our personal galaxy, nevertheless it additionally discovered tens of millions of quasars on the identical time, which give us a map of the complete universe.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




