[ad_1]
Mar 06, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) The high-tech double-barrel nanopipette, developed by College of Leeds scientists, and utilized to the worldwide medical problem of most cancers, has – for the primary time – enabled researchers to see how particular person dwelling most cancers cells react to therapy and alter over time – offering very important understanding that might assist medical doctors develop more practical most cancers remedy.
The instrument has two nanoscopic needles, which means it might probably concurrently inject and extract a pattern from the identical cell, increasing its potential makes use of. And the platform’s excessive stage of semi-automation has sped up the method dramatically, enabling scientists to extract knowledge from many extra particular person cells, with far larger accuracy and effectivity than beforehand potential, the examine exhibits.
Presently, methods for learning single cells often destroy them, which means a cell may be studied both earlier than therapy, or after.
This machine can take a “biopsy” of a dwelling cell repeatedly throughout publicity to most cancers therapy, sampling tiny extracts of its contents with out killing it, enabling scientists to look at its response over time.
In the course of the examine, the multi-disciplinary group, that includes biologists and engineers, examined most cancers cells’ resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy utilizing glioblastoma (GBM) – the deadliest type of mind tumour – as a check case, due to its skill to adapt to therapy and survive.
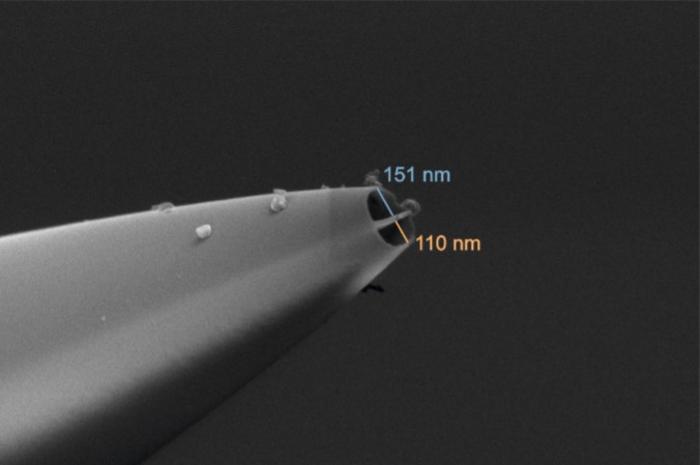
Electron microscopy picture of a nanopipette (picture acquired utilizing a scanning electron microscope (SEM)). (Picture: Dr Alexander Kulak)
Their findings are printed within the journal Science Advances (“Single-cell nanobiopsy allows multigenerational longitudinal transcriptomics of most cancers cells”).
Important breakthrough
One of many paper’s corresponding authors, Dr Lucy Stead, Affiliate Professor of Mind Most cancers Biology within the College of Leeds’ College of Medication, mentioned: “It is a vital breakthrough. It’s the first time that we’ve got a expertise the place we will truly monitor the adjustments going down after therapy, relatively than simply assume them.
“Any such expertise goes to offer a layer of understanding that we’ve got merely by no means had earlier than. And that new understanding and perception will result in new weapons in our armoury in opposition to all forms of most cancers.”
She added: “GBM is the most cancers in most want of these new weapons as a result of in 20 years there was no enchancment in survival on this illness.
“It’s lagging behind a lot and we predict that’s due to the extremely ‘plastic’ nature of those tumours – their skill to adapt to therapy and survive it.
“That’s the reason it’s so essential that we will dynamically observe and characterise these cells as they modify, so we will map out the journey these cells can take, and subsequently discover methods to cease them at each flip. We merely couldn’t try this with the applied sciences that we had.”
Transformative
Dr Stead leads the Glioma Genomics analysis group on the Leeds Institute of Medical Analysis at St James’s Hospital, which is targeted on attempting to treatment GBM mind tumours. She added: “This expertise might be transformative for this specific most cancers, serving to us lastly establish efficient remedies for this terrible, incurable illness.”
The analysis was primarily funded by The Mind Tumour Charity, which counts former Leeds footballer Dominic Matteo as one in every of its high-profile supporters. Matteo didn’t have GBM however underwent surgical procedure to take away a mind tumour in 2019.
Dr Simon Newman, Chief Scientific Officer at The Mind Tumour Charity, mentioned: “We all know glioblastoma cells reply in a different way to therapy, usually creating therapy resistance which results in recurrence. The event of this novel expertise, which might extract samples from tumour cells grown within the lab earlier than and after therapy, will give a singular perception into how drug resistance might develop and result in tumours rising again.
“We hope that this essential work, funded by The Mind Tumour Charity, will enhance our information of those advanced mind tumours and permit us to search out new, more practical remedies – one thing so urgently wanted for these confronted with this devastating illness.”
Collaborative
The examine was a collaboration between researchers from Leeds’ Bragg Centre for Supplies Analysis; Leeds’ College of Digital and Electrical Engineering; Leeds Institute of Medical Analysis, and the Earlham Institute, Norwich, who studied single GBM cells over a interval of 72hrs.
They used the nanosurgical platform, which is much too small to be manipulated by hand. The miniscule needles are exactly managed by robotic software program to manoeuvre them into place, into the cells within the petri dish. The nanopipette’s second needle performs a basic function in controlling the tools.
The machine permits scientists to take samples repeatedly, to check the development of illness in a person cell. A lot analysis on molecular biology is carried out on populations of cells, giving a median outcome that ignores the truth that each cell is completely different.
Some cells die throughout therapy, however others survive. The important thing to discovering a treatment is knowing what permits one cell to outlive and what’s occurring to those that die.
Unprecedented precision
Lead creator Dr Fabio Marcuccio, Analysis Affiliate within the College of Medication at Imperial Faculty London, who carried out the analysis whereas at Leeds, mentioned: “Our machine permits the examine of the way in which mind most cancers cells adapt to therapy over time, with unprecedented precision. This instrument will present knowledge that might result in vital enhancements in most cancers therapy and prognoses.”
He added: “This work is the results of a collaborative effort with my colleagues and co-leads Dr Chalmers Chau, Analysis Fellow in Bionanotechnology in Leeds’ College of Digital and Electrical Engineering, and Dr Georgette Tanner, previously of Leeds, now Bioinformatician at Oxford Nanopore Applied sciences, whose contributions have been basic to the experimental design and knowledge evaluation. This demonstrates the significance of making an interdisciplinary group to sort out the most important challenges of our time.”
Most cancers cell plasticity – the flexibility of cells to alter their behaviours – is without doubt one of the greatest challenges in most cancers therapy because it stays poorly understood. GBM most cancers cells are significantly “plastic”: they’ll adapt in a short time, and that is thought to assist them develop resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Studying how these cells adapt, and subsequently how we will block them, may stop most cancers from recurring, one thing which just about at all times occurs with GBM.
Camilla Hawkins, an occupational therapist from London, was identified with GBM in August 2022. The 55-year-old mentioned: “Any findings, reminiscent of these, that might assist inform new remedies, has acquired to be welcomed. Prolonged good high quality of life is value dwelling, even the place the prognosis is terminal.”
Crucially essential
The opposite corresponding creator and co-lead Dr Paolo Actis, Affiliate Professor of Bio-Nanotechnology in Leeds’ College of Digital and Electrical Engineering, has been engaged on the nanobiopsy instrument for round 15 years and mentioned its new capabilities, in comparison with its authentic scope, offered “exceptional benefits”.
He added: “Most cancers cells that aren’t killed by chemotherapy are those that make the most cancers develop again and result in demise.
“Our instrument can pinpoint these cells and we will now carry out biopsies on them so we will particularly examine how those that survive therapy have modified.
“That is crucially essential because the extra we will perceive how the cells change, the extra medicine we will develop to cease them from adapting.”
Dr Stead mentioned additional analysis wanted to be carried out, utilizing this expertise on many extra samples within the lab and in people, however that it had already yielded vastly precious info.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




