[ad_1]
Mar 21, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) One of many large promoting factors of two-dimensional (2D) supplies is their self-passivated nature, which permits them to be deposited on any substrate and opens up new prospects for three-dimensional materials stacks.
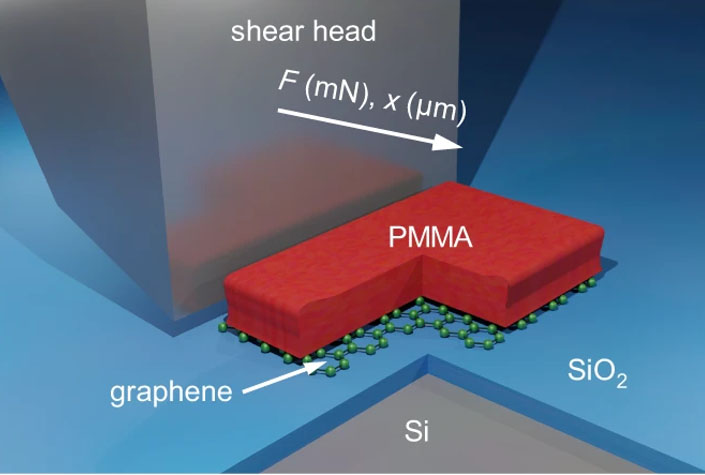
The draw back is their weak adhesion to the substrate, which could be a supply of system instability. Quantifying the adhesion of 2D supplies to three-dimensional surfaces is due to this fact an important step for the dependable integration of gadgets based mostly on 2D supplies. A staff of researchers round Max Lemme has now proven that the adhesion between 2D supplies and substrates may be effectively quantified utilizing button-shear testing.
Schematic illustration of the working precept of button shear testing. (Picture: AMO)
Though button shear testing is a well-established technique for adhesion measurement within the semiconductor trade, its applicability to quantifying the adhesion of 2D supplies remained to be confirmed. One of many challenges has been, for instance, to find out the dimensions of the buttons and the measurement routine required to acquire dependable outcomes.
The fundamental precept of button shear testing is kind of easy: a polymer button is fabricated on prime of the pattern and used as a “deal with” to maneuver the pattern itself by pulling on it with a metallic tip. Extra exactly, the pattern is moved at a relentless velocity towards a hard and fast shear head, whereas the place of the stage and the drive exerted on the pinnacle are concurrently recorded. The utmost drive recorded corresponds to the drive required to provoke the shear course of and supplies info on the adhesion between the pattern and the substrate.
If the precept is easy, the reliability of the strategy critically will depend on the main points – particularly on the properties of the buttons and on the velocity of the measurements – which must be fastidiously examined and optimized for the supplies beneath investigation.
The outcomes of such a scientific examine targeted on 2D supplies have been now reported in Nature Communications (“Button shear testing for adhesion measurements of 2D supplies”). The examine is the results of a collaboration between the Chair of Digital Units (ELD) at RWTH Aachen College, Infineon Applied sciences AG and AIXTRON SE. Concerned within the examine have been additionally AMO GmbH and different tutorial companions.
The publication in Nature Communications not solely reviews the main points of the fabrication of the polymer button and the methodology developed per measuring the adhesion of 2D supplies – particularly graphene, hexagonal boron nitride, in addition to molybdenum disulfide, and tungsten diselenide on silicon dioxide and silicon nitride substrates – but it surely additionally exhibits that the strategy permits to guage the results of various pattern remedies on adhesion, offering essential insights for additional optimization.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




