[ad_1]
Researchers from the Air Drive Analysis Laboratory, Cornell College, and the Analysis & Expertise arm of aerospace producer Boeing have efficiently mapped the crystallization strategy of poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK) throughout 3D printing.
Excessive-performance polymers, corresponding to PEEK, are being more and more used to provide 3D printed elements that require demanding mechanical properties, corresponding to high-temperature resistance and lowered weight.
In response to the researchers, a larger understanding of how the inner constructions of those supplies develop throughout 3D printing is important to reaching larger management over the properties of 3D printed elements.
Within the research, the group used a specialised X-ray imaging course of to file how PEEK hardens right into a layered crystal construction when 3D printed – a course of also referred to as crystallization.
Reaching an “unprecedented degree” of element, the researchers have offered the primary full 2D map of the crystallization of a single layer throughout fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printing.
The findings, printed within the journal Macromolecules, may present designers and engineers with a larger understanding of how 3D printing parameters impression the mechanical properties of 3D printed elements. These parameters embrace materials deposition price, 3D print head pace, 3D print head temperature, 3D print mattress temperature, and nozzle diameter.
Mapping 3D printed PEEK crystallization
The researchers argue that the understanding of the correlation between 3D printing parameters and the properties of ultimate elements stays restricted. That is stated to be very true for extrusion-based additive manufacturing of polymers corresponding to PEEK, which possesses quick crystallization charges.
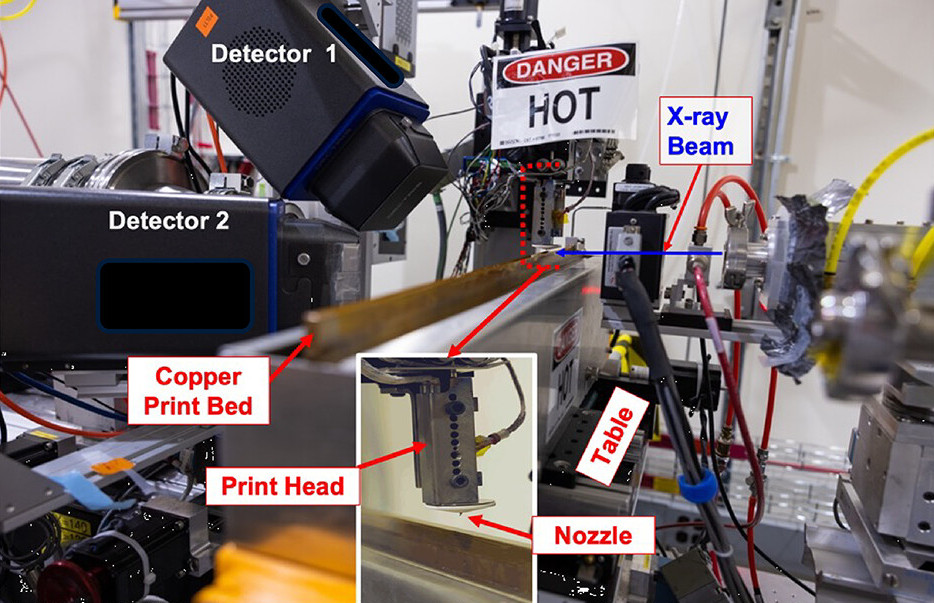
Throughout the research, the group used synchrotron-based microbeam wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) to file the crystal formation of the fabric throughout the FFF 3D printing course of.
When X-rays are directed at supplies, they arrive into contact with electrons and scatter in numerous instructions. In WAXS, the angles and depth at which this scattering happens are plotted and analyzed to find out key details about the inner crystalline construction of the fabric.
Utilizing this system, the researchers efficiently produced an in depth map of how PEEK crystallizes within the first few seconds following extrusion from the 3D printer’s nozzle. Throughout experimentation, a number of 3D print runs had been performed and measured with various print mattress temperatures of 145℃, 175℃, and 205℃. The 3D printing nozzle was saved at a constant temperature of 400℃.
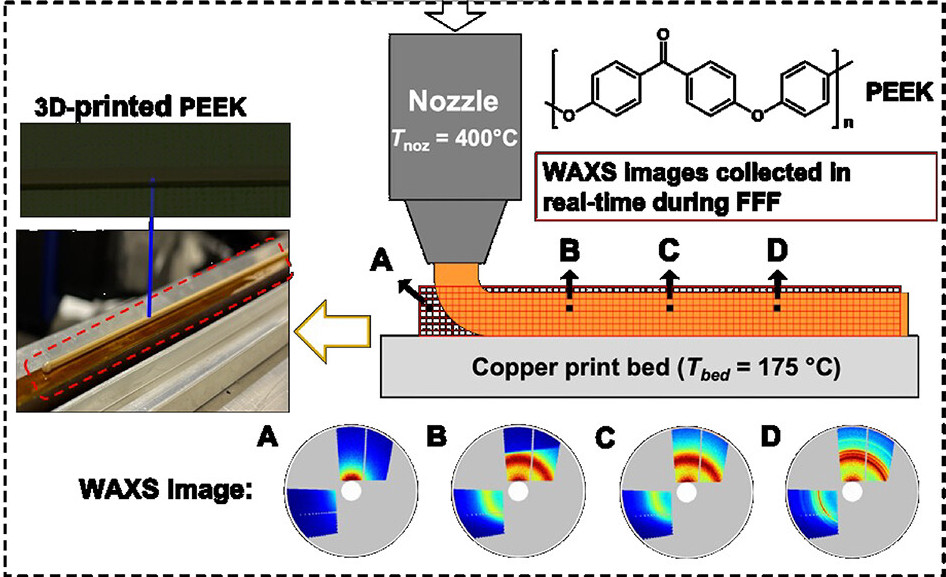
The information collected throughout this testing was collated into an in depth 2D map exhibiting how and the place the fabric crystallized over time.
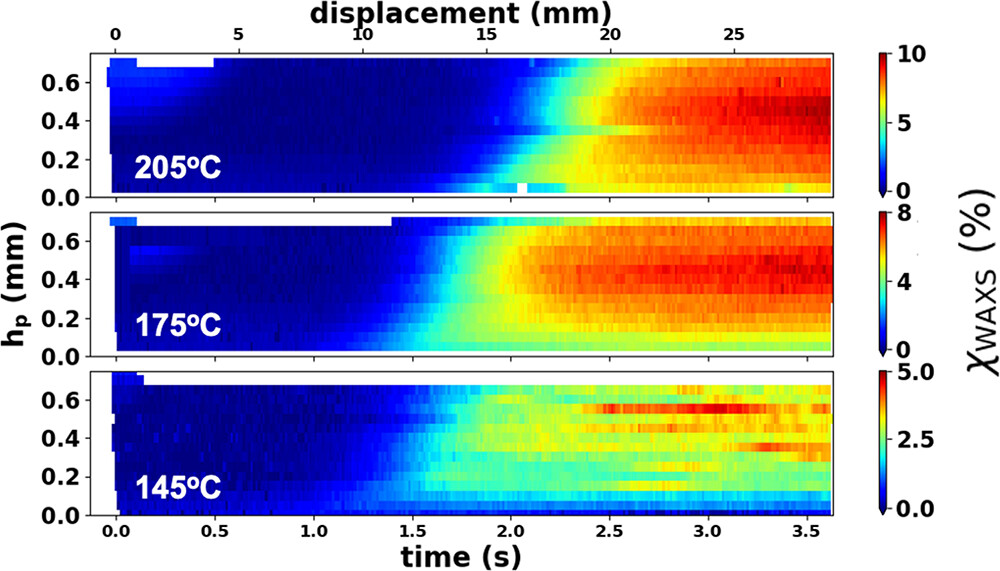
The findings point out that crystallization of PEEK happens first on the layers which might be closest to the 3D print mattress. This course of then steadily strikes vertically up the extruded materials, till it has utterly hardened.
The information additionally highlighted a transparent correlation between rising 3D print mattress temperatures and the onset of crystallization. In impact, when 3D printing at larger 3D print mattress temperatures, it takes longer for the fabric’s hardening course of to start.
What’s extra, the researchers discovered that supplies 3D printed at larger print mattress temperatures possessed the next remaining diploma of crystallization, translating to elevated hardness and density.
Finally, the researchers declare that these findings may permit these leveraging PEEK to higher management 3D printing parameters to precisely decide the mechanical efficiency of the 3D printed elements.
Controlling materials properties in 3D printing
This isn’t the primary time researchers have sought to realize larger management over half properties in 3D printing
Again in 2020, a group from the College of Nantes printed a research investigating the warmth switch and adhesion between layers in FFF 3D printing.
By this mission, the researchers sought to grasp, mannequin and quantify the warmth exchanges within the 3D printing course of. It was hoped that this is able to assist to find out the optimum 3D printing parameters wanted to maximise the mechanical properties of 3D printed elements.
All through their research, the Nantes researchers used a Creality CR-10 3D printer with ABS and carbon fiber-reinforced PEKK. Exact temperature measurements of warmth switch all through the 3D printing course of had been taken utilizing an infrared digicam, and in comparison with a predictive numerical mannequin.
Finally it was discovered that the numerical mannequin appropriately predicted warmth switch in 3D printing. Nonetheless, “poor data of the rheological properties” prevented the group from precisely predicting layer adhesion, a key consider figuring out remaining half properties.
Away from FFF, College of Colorado Boulder researchers have developed a novel course of for figuring out materials properties in inkjet 3D printing. Referred to as a “pantone for properties,” the research highlights how completely different resin supplies may be mixed in multi-material inkjet 3D printing to find out particular materials properties. These completely different supplies embrace a smooth elastomer, a inflexible plastic, and liquid constituents.
In response to the researchers, these findings provide potential for 3D printing mechanically-plausible artificial organic tissue utilized in medical functions.
What does the way forward for 3D printing maintain?
What near-term 3D printing traits have been highlighted by trade consultants?
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Business e-newsletter to maintain updated with the newest 3D printing information. It’s also possible to observe us on Twitter, like our Fb web page, and subscribe to the 3D Printing Business Youtube channel to entry extra unique content material.
Are you curious about working within the additive manufacturing trade? Go to 3D Printing Jobs to view a collection of obtainable roles and kickstart your profession.
Featured picture exhibits the researcher’s 3D printing experimental setup. Photograph through Macromolecules.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




