[ad_1]
Mar 19, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Tiny chips could equal a giant breakthrough for a staff of scientists led by Brown College engineers.
Writing in Nature Electronics (“An asynchronous wi-fi community for capturing event-driven information from massive populations of autonomous sensors”), the analysis staff describes a novel method for a wi-fi communication community that may effectively transmit, obtain and decode information from hundreds of microelectronic chips which can be every no bigger than a grain of salt.
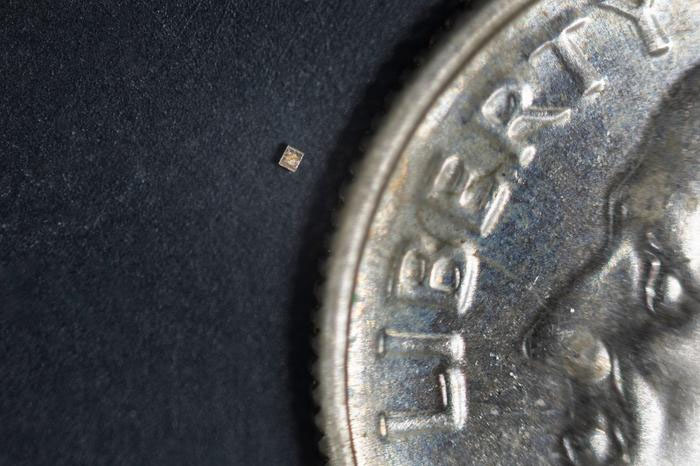

The sensor community is designed so the chips may be implanted into the physique or built-in into wearable units. Every submillimeter-sized silicon sensor mimics how neurons within the mind talk by spikes {of electrical} exercise. (Picture: Nick Dentamaro, Brown College)
The sensor community is designed so the chips may be implanted into the physique or built-in into wearable units. Every submillimeter-sized silicon sensor mimics how neurons within the mind talk by spikes {of electrical} exercise. The sensors detect particular occasions as spikes after which transmit that information wirelessly in actual time utilizing radio waves, saving each vitality and bandwidth.
“Our mind works in a really sparse method,” mentioned Jihun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Brown and research lead writer. “Neurons don’t hearth on a regular basis. They compress information and hearth sparsely in order that they’re very environment friendly. We’re mimicking that construction right here in our wi-fi telecommunication method. The sensors wouldn’t be sending out information on a regular basis — they’d simply be sending related information as wanted as brief bursts {of electrical} spikes, and they might give you the chance to take action independently of the opposite sensors and with out coordinating with a central receiver. By doing this, we’d handle to save lots of plenty of vitality and keep away from flooding our central receiver hub with much less significant information.”
This radiofrequency transmission scheme additionally makes the system scalable and tackles a standard downside with present sensor communication networks: all of them must be completely synced to work effectively.
The researchers say the work marks a big step ahead in large-scale wi-fi sensor know-how and will in the future assist form how scientists gather and interpret info from these little silicon units, particularly since digital sensors have change into ubiquitous because of fashionable know-how.
“We stay in a world of sensors,” mentioned Arto Nurmikko, a professor in Brown’s Faculty of Engineering and the research’s senior writer. “They’re far and wide. They’re actually in our cars, they’re in so many locations of labor and more and more entering into our houses. Essentially the most demanding atmosphere for these sensors will at all times be contained in the human physique.”
That’s why the researchers imagine the system may also help lay the inspiration for the following technology of implantable and wearable biomedical sensors. There’s a rising want in drugs for microdevices which can be environment friendly, unobtrusive and unnoticeable however that additionally function as half of a big ensembles to map physiological exercise throughout a complete space of curiosity.
The analysis staff describes a novel method for a wi-fi communication community that may effectively transmit, obtain and decode information from hundreds of microelectronic chips which can be every no bigger than a grain of salt. (Picture: Nick Dentamaro, Brown College)
“This can be a milestone when it comes to really creating such a spike-based wi-fi microsensor,” Lee mentioned. “If we proceed to make use of typical strategies, we can’t gather the excessive channel information these purposes would require in these sorts of next-generation techniques.”
The occasions the sensors establish and transmit may be particular occurrences resembling adjustments within the atmosphere they’re monitoring, together with temperature fluctuations or the presence of sure substances.
The sensors are ready to make use of as little vitality as they do as a result of exterior transceivers provide wi-fi energy to the sensors as they transmit their information — which means they only must be inside vary of the vitality waves despatched out by the transceiver to get a cost. This capability to function while not having to be plugged into an influence supply or battery make them handy and versatile to be used in many alternative conditions.
The staff designed and simulated the advanced electronics on a pc and has labored by a number of fabrication iterations to create the sensors. The work builds on earlier analysis from Nurmikko’s lab at Brown that launched a brand new type of neural interface system referred to as “neurograins.” This technique used a coordinated community of tiny wi-fi sensors to report and stimulate mind exercise.
“These chips are fairly refined as miniature microelectronic units, and it took us some time to get right here,” mentioned Nurmikko, who can be affiliated with Brown’s Carney Institute for Mind Science. “The quantity of labor and energy that’s required in customizing the a number of totally different features in manipulating the digital nature of those sensors — that being principally squeezed to a fraction of a millimeter house of silicon — will not be trivial.”
The researchers demonstrated the effectivity of their system in addition to simply how a lot it may probably be scaled up. They examined the system utilizing 78 sensors within the lab and located they had been in a position to gather and ship information with few errors, even when the sensors had been transmitting at totally different occasions. By way of simulations, they had been in a position to present the best way to decode information collected from the brains of primates utilizing about 8,000 hypothetically implanted sensors.
The researchers say subsequent steps embody optimizing the system for diminished energy consumption and exploring broader purposes past neurotechnology.
“The present work offers a strategy we are able to additional construct on,” Lee mentioned.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




