[ad_1]
Mar 06, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Stanford researchers have unveiled a brand new sort of frequency comb, a high-precision measurement gadget, that’s innovatively small, ultra-energy environment friendly, and exceptionally correct. With continued improvement, this breakthrough “microcomb” – which is detailed in a examine revealed in Nature (“Built-in frequency-modulated optical parametric oscillator”) – might be the premise for mass-market adoption of the units in on a regular basis electronics.
Frequency combs are specialised lasers that generate evenly spaced-out strains of sunshine akin to the tooth of a comb or, extra aptly, the tick marks on a ruler. Within the roughly quarter-century of their improvement, these “rulers for gentle” have revolutionized many sorts of high-precision measurement, from timekeeping to molecular detection through spectroscopy. But as a result of frequency combs require cumbersome, pricey, and power-hungry tools, their deployment has been largely restricted to laboratory settings.
The researchers found a workaround for these points by integrating two totally different approaches for miniaturizing frequency combs into one easy, simply producible, microchip-style platform. Among the many many functions the researchers envision for his or her versatile expertise are highly effective handheld medical diagnostic units and widespread greenhouse gasoline monitoring sensors.
“The construction for our frequency comb brings the most effective components of rising microcomb expertise collectively into one gadget,” mentioned Hubert Stokowski, a postdoctoral scholar within the lab of Amir Safavi-Naeini, and lead writer of the examine. “We are able to doubtlessly scale our new frequency microcomb for compact, low-power, and cheap units that may be deployed virtually wherever.”
“We’re very enthusiastic about this new microcomb expertise that we’ve demonstrated for novel varieties of precision sensors which might be each small and environment friendly sufficient to be in somebody’s cellphone sometime,” mentioned Safavi-Naeini, affiliate professor within the Division of Utilized Physics at Stanford’s Faculty of Humanities and Sciences and senior writer of the examine.
Wrangling gentle
This new gadget is known as an Built-in Frequency-Modulated Optical Parametric Oscillator, or FM-OPO.
The device’s complicated title signifies that it combines two methods for creating the vary of distinct frequencies, or colours of sunshine, that represent a frequency comb. One technique, referred to as optical parametric oscillation, entails bouncing beams of laser gentle inside a crystal medium, whereby the generated gentle organizes itself into pulses of coherent, secure waves. The second technique facilities on sending laser gentle right into a cavity after which modulating the section of the sunshine – achieved by making use of radio-frequency indicators to the gadget – to in the end produce frequency repetitions that equally act as gentle pulses.
These two methods for microcombs haven’t been used broadly as a result of each include drawbacks. These points embrace vitality inefficiency, restricted potential to regulate optical parameters, and suboptimal comb “optical bandwidth” the place the comb-like strains fade as the space from the middle of the comb will increase.
The researchers approached the problem anew via their work on extremely promising optical circuit platform primarily based on a cloth referred to as skinny movie lithium niobate. The fabric has advantageous properties in comparison with silicon, the business commonplace materials. Two of those useful properties are “nonlinearity” (it permits gentle beams of various colours to work together with one another to generate new colours or wavelengths) and a broad vary of sunshine wavelengths can cross via it.
The researchers customary the parts on the coronary heart of the brand new frequency comb utilizing built-in lithium niobate photonics. These light-manipulating applied sciences construct upon advances within the associated, extra established discipline of silicon photonics, which entails fabricating optical and digital built-in circuits on silicon microchips. On this means, lithium niobate and silicon photonics have each expanded upon the semiconductors in standard pc chips, the roots of which attain again to the Nineteen Fifties.
“Lithium niobate has sure properties that silicon doesn’t, and we couldn’t have made our microcomb gadget with out it,” mentioned Safavi-Naeini.
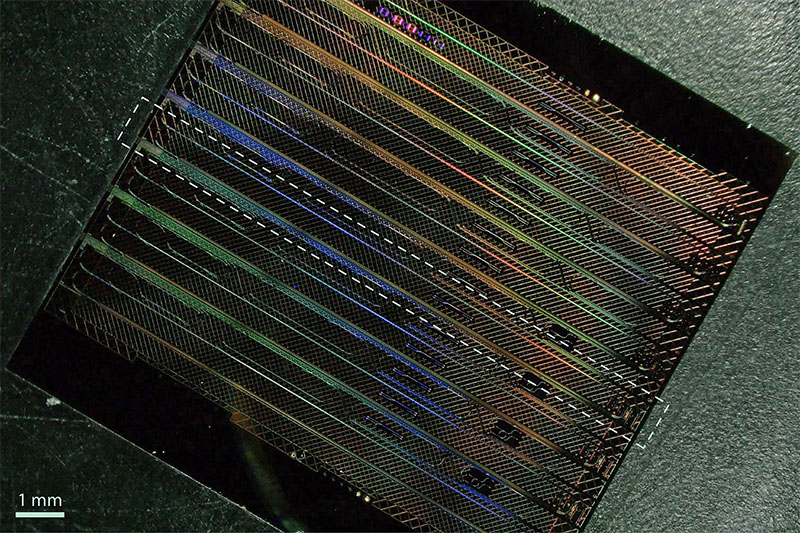
A microscope picture displaying a thin-film lithium niobate chip that comprises eight of the brand new “FM-OPO” units. One gadget has a footprint round 1×10 mm2 (highlighted right here with a dashed rectangle). (Picture: Kevin Multani and Hubert Stokowski)
Surprisingly glorious efficiency
Subsequent, the researchers introduced collectively components of each optical parametric amplification and section modulation methods. The workforce anticipated sure efficiency traits from the brand new frequency comb system on lithium niobate chips – however what they noticed proved much better than they anticipated.
Total, the comb produced a steady output fairly than gentle pulses, which enabled the researchers to cut back the required enter energy by roughly an order of magnitude. The gadget additionally yielded a conveniently “flat” comb, which means the comb strains farther in wavelength from the middle of the spectrum didn’t fade in depth, thus providing higher accuracy and broader utility in measurement functions.
“We had been actually stunned by this comb,” mentioned Safavi-Naeini. “Though we had some instinct that we’d get comb-like behaviors, we weren’t actually making an attempt to make precisely one of these comb, and it took us a number of months to develop the simulations and principle that defined its essential properties.”
For additional perception into their overperforming gadget, the researchers turned to Martin Fejer, the J. G. Jackson and C. J. Wooden Professor of Physics and a professor of utilized physics at Stanford. Together with different friends at Stanford, Fejer has helped advance fashionable skinny movie lithium niobate photonics applied sciences and the understanding of the fabric’s crystal properties.
Fejer, who can be a examine co-author, made the important thing connection between the bodily rules underlying the microcomb and concepts mentioned in scientific literature from the Seventies, notably ideas pioneered by Stephen Harris, emeritus professor of utilized physics and electrical engineering at Stanford.
The brand new microcombs, with additional honing, must be readily manufacturable at standard microchip foundries with many sensible functions akin to sensing, spectroscopy, medical diagnostics, fiber-optic communications, and wearable health-monitoring units.
“Our microcomb chip might be put into something, with the dimensions of the general gadget relying on the dimensions of the battery,” mentioned Stokowski. “The expertise we’ve demonstrated might go inside a low-powered private gadget, the dimensions of a cellphone and even smaller, and serve every kind of helpful functions.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink



