[ad_1]
Mar 13, 2024
(Nanowerk Highlight) Most cancers stays one of the crucial difficult ailments to deal with, regardless of a long time of analysis. Whereas focused therapies like epidermal development issue receptor (EGFR) inhibitors have proven promise, their effectiveness is usually restricted by poor bioavailability (the proportion of drug that reaches circulation after administration) and the event of drug resistance in most cancers cells.
Lately, nanoparticle-based drug carriers have emerged as a possible resolution to those challenges. These tiny particles, sometimes lower than 200 nanometers in dimension, can encapsulate medicine and ship them extra effectively to tumor websites. They will enhance drug solubility, delay circulation time, and even allow focused supply to most cancers cells whereas sparing wholesome tissue.
Among the many numerous supplies explored for nanoparticle fabrication, silk fibroin from silkworm cocoons has garnered curiosity as a result of its biocompatibility (not dangerous to dwelling tissues), biodegradability (will be damaged down naturally), and flexibility. Constructing on this basis, researchers from Wuhan College and Anhui Medical College in China have developed a novel drug supply system utilizing silk peptide nanoparticles.
As reported within the journal Nano Choose (“Enhancing focused most cancers remedy by way of a number of drug supply by silk peptide nanoparticles”), these nanoparticles can concurrently ship two medicine – the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib and the pure compound curcumin – leading to dramatically enhanced anti-cancer results. This co-delivery method represents a big development over current single-drug carriers.
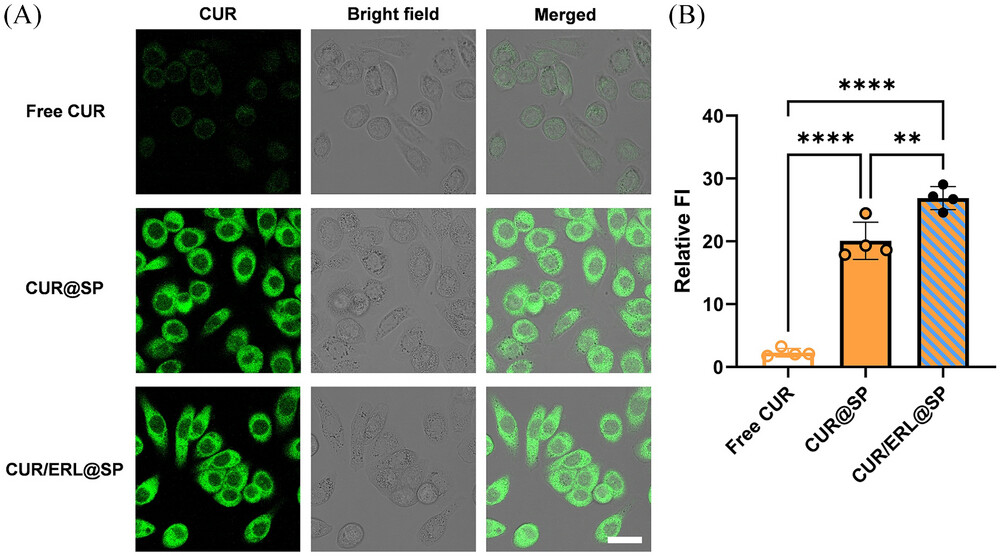
Remark on intracellular curcumin by confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging. A, CLSM photos of PC-9 cells incubated with the free drug and drug loaded nanoparticles with the CUR focus of 20 µg mL−1, respectively, for 4 hours. Scale bar: 30 µm. B, Relative fluorescence depth (FI) of PC-9 cells analyzed by ImageJ v1.8.0 software program. PC-9 cells had been incubated with the free drug and drug loaded nanoparticles with the CUR focus of 20 µg mL−1, respectively, for 4 hours. Information are imply ±SD, n = 4. The statistical significance between two units of knowledge was calculated utilizing Scholar’s t take a look at. **P <0.01 and ****P <0.0001.
The analysis workforce, led by Zi-Hao He and Li-Jin Qi, first extracted silk peptides from silkworm cocoons and fine-tuned the manufacturing course of to acquire nanoparticles smaller than 150 nanometers. Apparently, they found that curcumin performed a vital function in stabilizing the nanoparticles when co-loaded with erlotinib. This allowed them to beat previous challenges in creating erlotinib nanocarriers with constant dimension and good stability.
When examined on lung most cancers cells, the dual-drug silk nanoparticles confirmed outstanding outcomes. They had been taken up by the cells far more effectively in comparison with the free medicine, resulting in a 67% improve in intracellular drug accumulation. This enhanced supply translated into considerably stronger inhibition of most cancers cell development and elevated cell dying by apoptosis (programmed cell dying).
Investigating the underlying mechanisms, the researchers discovered that the nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery led to efficient suppression of EGFR and its activated kind (phosphorylated EGFR), that are key drivers of most cancers development. The therapy additionally favorably modulated apoptosis-regulating proteins, growing pro-apoptotic Bax whereas reducing anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and survivin.
Notably, the dual-drug silk nanoparticles demonstrated multi-faceted results towards most cancers development pathways. They hindered the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (a course of that permits most cancers cells to change into extra invasive and unfold), diminished the expression of immunosuppressive components like PD-L1 (which assist cancers evade immune assault), and inhibited cell fusion-promoting proteins (linked to tumor development). This means the potential for a complete anti-cancer affect.
To validate the scientific relevance of their findings, the workforce examined their nanoparticles on circulating tumor cells remoted from a lung most cancers affected person’s blood. The erlotinib-curcumin-loaded nanoparticles achieved a hanging discount in EGFR expression in these patient-derived cells, highlighting the translatability of this method.
Whereas these outcomes are promising, a number of challenges stay earlier than this expertise can attain scientific utility. Massive-scale manufacturing of the silk peptide nanoparticles must be optimized, and rigorous security and efficacy testing in animal fashions and human trials will probably be required. The long-term destiny of the nanoparticles within the physique and any potential negative effects additionally should be fastidiously evaluated.
Regardless of these hurdles, the modern work by He, Qi, and colleagues represents a big stride in nanomedicine for most cancers. By leveraging the distinctive properties of silk peptides and the synergistic potential of dual-drug supply, their platform opens new potentialities for simpler and focused most cancers therapies with fewer negative effects. With additional improvement and validation, this bio-inspired method may deliver us nearer to the objective of actually customized, exact most cancers medicines that may remodel affected person outcomes.

By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is writer of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Know-how,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Expertise and Instruments Making Know-how Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
Nanowerk Publication
Get our Nanotechnology Highlight updates to your inbox!
Thanks!
You will have efficiently joined our subscriber checklist.
Turn into a Highlight visitor writer! Be a part of our massive and rising group of visitor contributors. Have you ever simply revealed a scientific paper or produce other thrilling developments to share with the nanotechnology neighborhood? Right here is publish on nanowerk.com.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




