[ad_1]
 “<robust>Spectral phase-contrast tomography</robust> Three-dimensional rendering of a contrast-perfused mouse pattern utilizing three decomposition channels: water (gentle tissues, blue), iodine (vasculature, purple) and calcium (bones, white). (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/<em>Phys. Med. Biol.</em> 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)”Spectral phase-contrast tomography Three-dimensional rendering of a contrast-perfused mouse pattern utilizing three decomposition channels: water (gentle tissues, blue), iodine (vasculature, purple) and calcium (bones, white). (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/Phys. Med. Biol. 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)
“<robust>Spectral phase-contrast tomography</robust> Three-dimensional rendering of a contrast-perfused mouse pattern utilizing three decomposition channels: water (gentle tissues, blue), iodine (vasculature, purple) and calcium (bones, white). (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/<em>Phys. Med. Biol.</em> 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)”Spectral phase-contrast tomography Three-dimensional rendering of a contrast-perfused mouse pattern utilizing three decomposition channels: water (gentle tissues, blue), iodine (vasculature, purple) and calcium (bones, white). (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/Phys. Med. Biol. 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)
The introduction of photon-counting detectors into CT scanners paved the way in which for the rise of spectral CT in medical settings. Such techniques make use of two or extra X-ray energies to create material-specific 3D maps. However since spectral CT is predicated on X-ray attenuation, it reveals low distinction when imaging weakly absorbing supplies similar to organic tissues. As such, high-Z distinction brokers are sometimes employed to spotlight constructions of curiosity.
In parallel, X-ray phase-contrast imaging is changing into extra extensively out there and gaining consideration for each pre-clinical and medical purposes. Section-contrast strategies, a lot of which may produce each attenuation and phase-shift maps, provide greater visibility of low-Z supplies similar to gentle tissues.
“Spectral CT has confirmed efficient in a spread of purposes, from materials quantification to image-artefact discount, whereas phase-contrast imaging boasts superior visualization of sentimental and microstructured tissues,” says Luca Brombal from the College of Trieste and INFN. “Constructing on these bases, we sought to leverage the mixed strengths of each strategies.”
Brombal and colleagues, additionally from College Faculty London, demonstrated the primary integration of spectral and phase-contrast CT utilizing a tomographic edge-illumination setup. The venture, described in Physics in Drugs & Biology, concerned growing an imaging setup that may purchase information with each spectral and phase-contrast properties, alongside the implementation of a fabric decomposition mannequin.
“The advantages of the mixed spectral phase-contrast method are the likelihood to concurrently produce three mass density maps of particular parts or compounds within the pattern, whereas enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio, particularly of the soft-tissue element, because of part sensitivity,” Brombal explains.
Materials decomposition
The crew used an edge-illumination phase-contrast set-up, during which masks positioned both facet of the pattern form the incident X-ray beam and selectively block the detector. A reference illumination curve is created with no pattern in place. As soon as the pattern is inserted, this curve is attenuated and laterally displaced, adjustments which might be then used to retrieve attenuation pictures and calculate the sample-induced part shift.
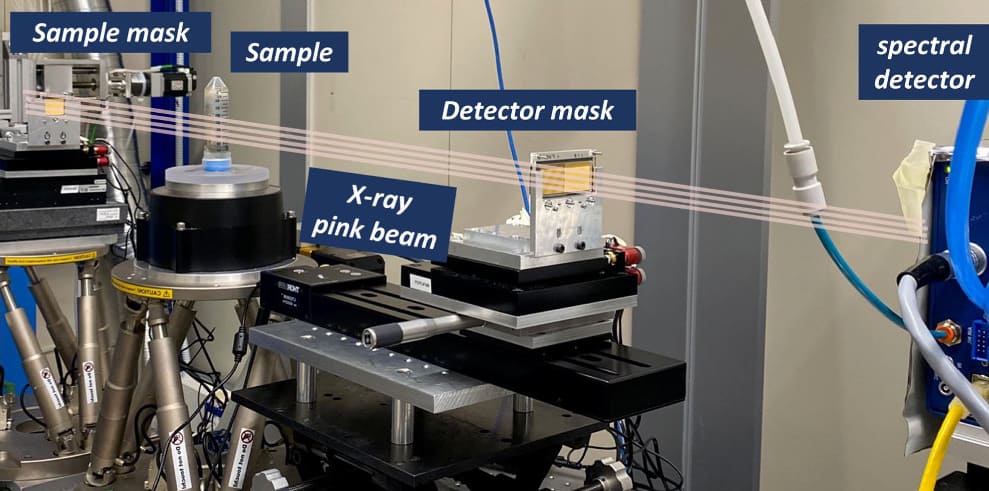 “<robust>Experimental setup</robust> The primary elements of the experiment on the Elettra synchrotron facility’s SYRMEP beamline. (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/<em>Phys. Med. Biol.</em> 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)”Experimental setup The primary elements of the experiment on the Elettra synchrotron facility’s SYRMEP beamline. (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/Phys. Med. Biol. 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)
“<robust>Experimental setup</robust> The primary elements of the experiment on the Elettra synchrotron facility’s SYRMEP beamline. (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/<em>Phys. Med. Biol.</em> 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)”Experimental setup The primary elements of the experiment on the Elettra synchrotron facility’s SYRMEP beamline. (Courtesy: CC BY 4.0/Phys. Med. Biol. 10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328)
For this research, the researchers employed synchrotron radiation from the Italian synchrotron facility Elettra. They notice, nevertheless, that translation to a laboratory setup utilizing standard X-ray tubes ought to be simple. They first scanned a take a look at phantom comprising plastic cuvettes crammed with 5 liquids: calcium chloride resolution (370 and 180 mg/ml); iodine resolution (50 and 10 mg/ml, just like concentrations utilized in iodine-based contrasts); and distilled water.
The imaging system is predicated on a photon-counting detector with a small-pixel (62 µm) cadmium telluride sensor, operated in two-colour mode to report incoming photons in low- and high-energy bins. The researchers acquired tomographic pictures of the phantom, recording 360 projections over 180°, with an publicity time of 1.2 s per step and a complete acquisition time of two.9 h.
After reconstructing 3D volumes from the attenuation and part projections, the crew carried out materials decomposition utilizing three algorithms: spectral decomposition, utilizing the low- and high-energy attenuation reconstructions as inputs; attenuation/part decomposition, utilized to part and attenuation reconstructions obtained by summing the vitality bins; and spectral/part decomposition, which makes use of low-energy, high-energy and part reconstructions.
The spectral/part decomposition algorithm exhibited the perfect efficiency of the three, appropriately figuring out all supplies with no sign contamination throughout channels and considerably much less noise than normal spectral decomposition, as a result of low noise of the enter part channel. This algorithm computed values closest to the nominal mass density, with RMS errors of 1.1%, 1.9% and three.5% for water, iodine and calcium chloride options, respectively.
Spectral/part decomposition additionally improved the signal-to-noise ratio of the photographs, by an element of 9 within the water channel and an element of 1.3 in iodine pictures, in contrast with spectral decomposition. As well as, solely the spectral/part decomposition enabled simultaneous quantification of all three materials densities.
Organic demonstration
To validate the approach utilizing a organic pattern, the researchers imaged ex vivo a laboratory mouse perfused autopsy with an iodine-based vascular distinction agent. They acquired 720 projections over 360°, with a complete publicity time of 5.8 h and a ensuing radiation dose of round 2 Gy. They notice that for future in vivo purposes the delivered dose could possibly be diminished to a whole lot of milligray, by optimizing the masks design, for instance, or utilizing extra dose-efficient acquisition schemes.
To protect high-resolution particulars, the researchers reconstructed attenuation and part pictures with a 20 µm3 voxel dimension. Spectral attenuation pictures confirmed sign from bones (calcium map) and vasculature (iodine map), however no soft-tissue sign. The part enter reconstruction, in the meantime, revealed soft-tissue constructions similar to cutaneous and subcutaneous layers and inside organs
Materials decomposition utilizing the spectral/part algorithm clearly separated the vasculature and bones, with no contamination sign, whereas the part channel offered good visibility of the formalin-fixed soft-tissue element.
The excessive decision of the iodine and calcium pictures demonstrated that the system can seize blood vessels smaller than 50 µm, in addition to the wonderful trabecular construction of the bone. The researchers additionally created a 3D rendering of the mouse pattern reconstruction after spectral/part decomposition, which concurrently visualizes gentle tissues, bones and vasculature.
The subsequent step, Brombal tells Physics World, shall be to translate this system from a proof-of-principle research to extra compelling scientific circumstances. “We not too long ago began a brand new venture targeted on the appliance of spectral phase-contrast to osteoarticular analysis, particularly within the context of detection of ailments similar to osteoarthritis, and to (quantitative) digital histology, doubtlessly offering complementary insights alongside standard pathological evaluation of surgical tissue specimens.”
The publish Spectral and phase-contrast CT mix strengths to boost X-ray imaging appeared first on Physics World.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

