[ad_1]
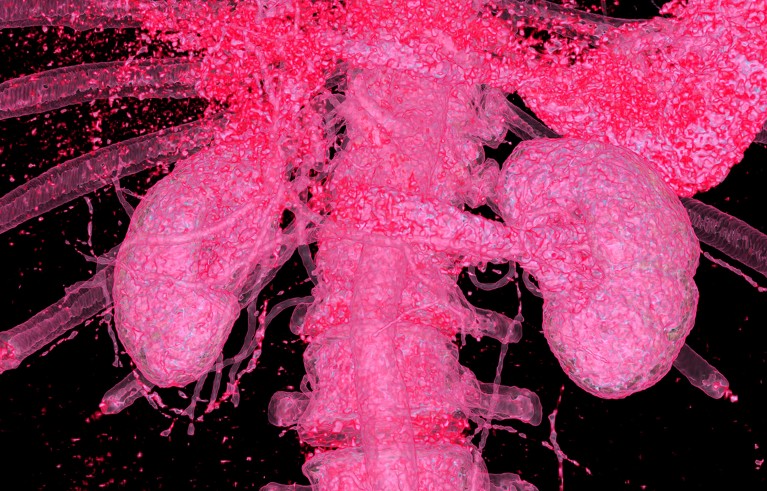
Kidney illness is rising worldwide. The secretariat of the World Well being Group has welcomed the decision to incorporate it as a non-communicable illness that causes untimely deaths.Credit score: Vsevolod Zviryk/SPL
A quiet epidemic is constructing world wide. It’s the third-fastest-growing reason for loss of life globally. By 2040, it’s anticipated to turn out to be the fifth-highest reason for years of life misplaced. Already, 850 million persons are affected, and treating them is draining public-health coffers: the US government-funded health-care plan Medicare alone spends US$130 billion to take action annually. The perpetrator is kidney illness, a situation by which injury to the kidneys prevents them from filtering the blood.
And but, in discussions of priorities for international public well being, the phrases ‘kidney illness’ don’t at all times function. One purpose for that is that kidney illness will not be on the World Well being Group (WHO) record of precedence non-communicable ailments (NCDs) that trigger untimely deaths. The roster of such NCDs consists of coronary heart illness, stroke, diabetes, most cancers and continual lung illness. With kidney illness lacking, consciousness of its rising affect stays low.
Continual kidney illness and the worldwide public well being agenda: a global consensus
The authors of an article in Nature Critiques Nephrology this week need to change that (A. Francis et al. Nature Rev. Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6; 2024). They’re led by the three largest skilled organizations working in kidney well being — the Worldwide Society of Nephrology, the American Society of Nephrology and the European Renal Affiliation — and so they’re urging the WHO to incorporate kidney illness on the precedence NCD record.
It will, the authors argue, deliver consideration to the rising menace, which is especially dire for individuals in low- and lower-middle-income international locations, who already bear two‑thirds of the world’s kidney-disease burden. Including kidney illness to the record can even imply that lowering deaths from it might turn out to be extra of a precedence for the United Nations Sustainable Growth Targets goal to cut back untimely deaths from NCDs by one-third by 2030.
As of now, charges of continual kidney illness are more likely to enhance in low- and lower-middle-income international locations because the proportion of older individuals of their populations will increase. Inclusion on the WHO record might present an incentive for well being authorities to prioritize remedies, knowledge assortment and different analysis, together with funding, as with different NCDs.
Kidney illness typically accompanies different situations that do seem on the NCD record, reminiscent of coronary heart illness, most cancers and diabetes — certainly, kidney-disease deaths prompted particularly by diabetes are on the record. However the article authors argue that “tackling diabetes and coronary heart illness alone is not going to goal the core drivers of a big proportion of kidney ailments”. Each acute and continual kidney illness can have many causes. They are often brought on by an infection or publicity to poisonous substances. More and more, the implications of worldwide local weather change, together with excessive temperatures and decreased availability of contemporary water, are regarded as contributing to the worldwide burden of kidney illness, as nicely.
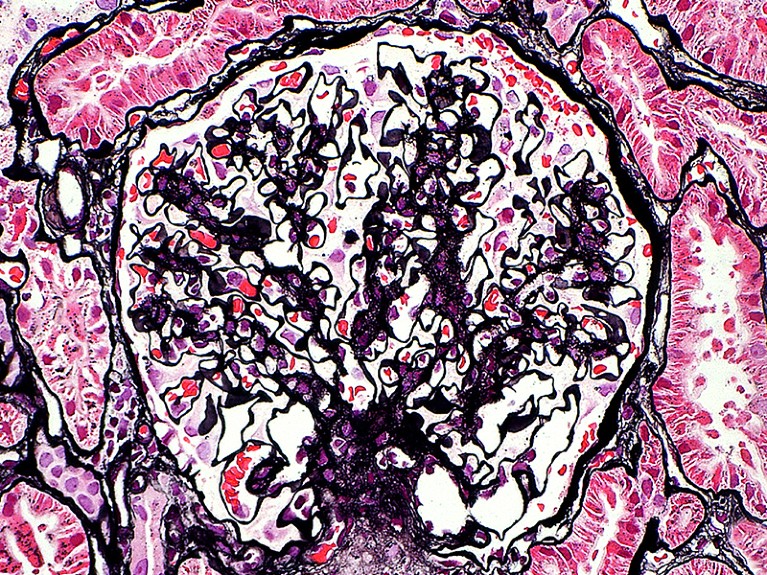
The kidney glomerulus filters waste merchandise from the blood. In individuals with broken kidneys, this occurs by dialysis.Credit score: Ziad M. El-Zaatari/SPL
The WHO secretariat, which works carefully with the nephrology group, welcomes the decision to incorporate kidney illness as an NCD that causes untimely deaths, says Slim Slama, who heads the NCD unit on the secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland. The information assist together with kidney illness as an NCD driver of untimely loss of life, he provides.
The choice to incorporate kidney illness together with different precedence NCDs isn’t solely all the way down to the WHO, nevertheless. There have to be conversations between the secretariat, WHO member states, the nephrology group, affected person advocates and others. WHO member states must instruct the company to take the steps to make it occur, together with offering acceptable funding for strategic and technical help.
Knowledge and funding gaps
Three studies based mostly on surveys by the Worldwide Society of Nephrology since 2016 spotlight the dimensions of information gaps (A. Okay. Bello et al. Lancet Glob. Well being 12, E382–E395; 2024). In lots of international locations, screening for kidney illness is troublesome to entry and a big proportion of instances go undetected and subsequently uncounted. For instance, it isn’t recognized exactly how many individuals with kidney failure die annually due to lack of entry to dialysis or transplantation: the numbers are someplace between two million and 7 million, in keeping with the WHO. Advocates should push public-health officers in additional international locations to gather the information wanted to observe kidney illness and the affect of prevention and remedy efforts.
Even with higher knowledge, remedies for kidney illness are sometimes prohibitively costly. They embrace dialysis, an intervention to filter the blood when kidneys can not. Dialysis is commonly required two or 3 times weekly for the rest of the recipient’s life, or till they will obtain a transplant, and it’s notoriously expensive. In Thailand, for instance, it accounted for 3% of the nation’s whole health-care expenditures in 2022, in keeping with the nation’s parliamentary price range workplace.
Finish continual kidney illness neglect
These prices might come down if individuals who have diabetes or hypertension, for instance, may very well be routinely screened for impaired kidney perform, as a result of they’re at excessive threat of creating continual kidney illness. This could allow kidney injury to be detected early, earlier than signs set in, opening the best way for remedies that don’t instantly require dialysis or transplant surgical procedure.
New medication that enhance weight reduction and deal with sort 2 diabetes might additionally assist to stop or scale back stress on the kidneys, however these, too, are too costly for many individuals in want. That’s the reason one thing must be finished to make medication extra inexpensive. The pharmaceutical business, which has turn out to be extraordinarily worthwhile, has a vital position. In Denmark, for instance, the business’s income helped to tip the nationwide economic system from recession into development in 2023, in keeping with the general public company Statistics Denmark. The COVID-19 pandemic confirmed that making income and making medication out there, and inexpensive, to a large inhabitants needn’t be mutually unique. Equally revolutionary considering is now wanted. “The entire world must reckon with this kidney downside,” says Valerie Luyckx, a biomedical ethicist on the College of Zurich in Switzerland.
The WHO including kidney illness to its precedence record might additionally appeal to funding for remedy, analysis and illness registries. That might jump-start the event of latest remedies and assist to make present remedies extra inexpensive and accessible.
NCDs are liable for 74% of deaths worldwide, however the world’s greatest donors to international well being presently commit lower than 2% of their budgets for worldwide well being help to NCD prevention and management, and never together with kidney illness. Drawing extra consideration to the quiet rampage of kidney illness amongst among the most susceptible individuals can be one necessary step in turning these statistics round.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

