[ad_1]
Apr 03, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Neutrons are subatomic particles that don’t have any electrical cost, in contrast to protons and electrons. That implies that whereas the electromagnetic pressure is chargeable for a lot of the interactions between radiation and supplies, neutrons are basically resistant to that pressure.
As a substitute, neutrons are held collectively inside an atom’s nucleus solely by one thing known as the sturdy pressure, one of many 4 elementary forces of nature. As its identify implies, the pressure is certainly very sturdy, however solely at very shut vary — it drops off so quickly as to be negligible past 1/10,000 the scale of an atom. However now, researchers at MIT have discovered that neutrons can really be made to cling to particles known as quantum dots, that are made up of tens of 1000’s of atomic nuclei, held there simply by the sturdy pressure.
The brand new discovering might result in helpful new instruments for probing the fundamental properties of supplies on the quantum degree, together with these arising from the sturdy pressure, in addition to exploring new sorts of quantum info processing units. The work is reported within the journal ACS Nano (“µeV-Deep Neutron Certain States in Nanocrystals”), in a paper by MIT graduate college students Hao Tang and Guoqing Wang and MIT professors Ju Li and Paola Cappellaro of the Division of Nuclear Science and Engineering.
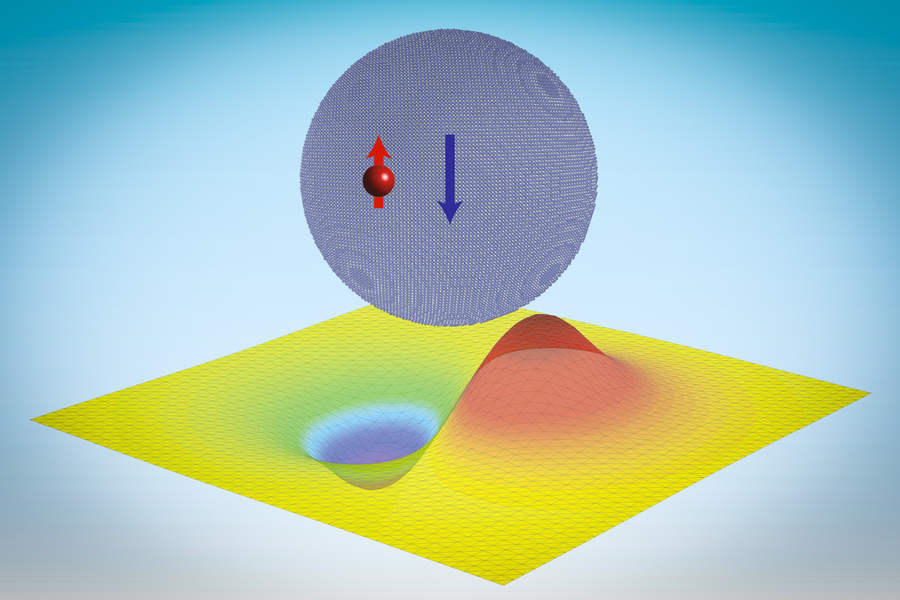
MIT researchers found “neutronic” molecules, by which neutrons will be made to cling to quantum dots, held simply by the sturdy pressure. The discovering might result in new instruments for probing materials properties on the quantum degree and exploring new sorts of quantum info processing units. Right here, the purple merchandise represents a sure neutron, the sphere is a hydride nanoparticle, and the yellow subject represents a neutron wavefunction. (Picture: Courtesy of the researchers)
Neutrons are extensively used to probe materials properties utilizing a technique known as neutron scattering, by which a beam of neutrons is concentrated on a pattern, and the neutrons that bounce off the fabric’s atoms will be detected to disclose the fabric’s inside construction and dynamics.
However till this new work, no person thought that these neutrons would possibly really persist with the supplies they had been probing. “The truth that [the neutrons] will be trapped by the supplies, no person appears to find out about that,” says Li, who can also be a professor of supplies science and engineering. “We had been shocked that this exists, and that no person had talked about it earlier than, among the many consultants we had checked with,” he says.
The explanation this new discovering is so shocking, Li explains, is as a result of neutrons don’t work together with electromagnetic forces. Of the 4 elementary forces, gravity and the weak pressure “are usually not vital for supplies,” he says. “Just about the whole lot is electromagnetic interplay, however on this case, for the reason that neutron doesn’t have a cost, the interplay right here is thru the sturdy interplay, and we all know that could be very short-range. It’s efficient at a variety of 10 to the minus 15 energy,” or one quadrillionth, of a meter.
“It’s very small, but it surely’s very intense,” he says of this pressure that holds the nuclei of atoms collectively. “However what’s attention-grabbing is we’ve obtained these many 1000’s of nuclei on this neutronic quantum dot, and that’s in a position to stabilize these sure states, which have way more diffuse wavefunctions at tens of nanometers. These neutronic sure states in a quantum dot are literally fairly akin to Thomson’s plum pudding mannequin of an atom, after his discovery of the electron.”
It was so sudden, Li calls it “a fairly loopy resolution to a quantum mechanical drawback.” The staff calls the newly found state a synthetic “neutronic molecule.”
These neutronic molecules are created from quantum dots, that are tiny crystalline particles, collections of atoms so small that their properties are ruled extra by the precise dimension and form of the particles than by their composition. The invention and managed manufacturing of quantum dots had been the topic of the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, awarded to MIT Professor Moungi Bawendi and two others.
“In standard quantum dots, an electron is trapped by the electromagnetic potential created by a macroscopic variety of atoms, thus its wavefunction extends to about 10 nanometers, a lot bigger than a typical atomic radius,” says Cappellaro. “Equally, in these nucleonic quantum dots, a single neutron will be trapped by a nanocrystal, with a dimension nicely past the vary of the nuclear pressure, and show comparable quantized energies.” Whereas these vitality jumps give quantum dots their colours, the neutronic quantum dots could possibly be used for storing quantum info.
This work relies on theoretical calculations and computational simulations. “We did it analytically in two alternative ways, and ultimately additionally verified it numerically,” Li says. Though the impact had by no means been described earlier than, he says, in precept there’s no cause it couldn’t have been discovered a lot sooner: “Conceptually, individuals ought to have already thought of it,” he says, however so far as the staff has been in a position to decide, no person did.
A part of the issue in doing the computations is the very completely different scales concerned: The binding vitality of a neutron to the quantum dots they had been attaching to is about one-trillionth that of beforehand identified situations the place the neutron is sure to a small group of nuclei. For this work, the staff used an analytical device known as Inexperienced’s operate to exhibit that the sturdy pressure was adequate to seize neutrons with a quantum dot with a minimal radius of 13 nanometers.
Then, the researchers did detailed simulations of particular instances, akin to using a lithium hydride nanocrystal, a cloth being studied as a potential storage medium for hydrogen. They confirmed that the binding vitality of the neutrons to the nanocrystal depends on the precise dimensions and form of the crystal, in addition to the nuclear spin polarizations of the nuclei in comparison with that of the neutron. In addition they calculated comparable results for skinny movies and wires of the fabric versus particles.
However Li says that really creating such neutronic molecules within the lab, which amongst different issues requires specialised gear to keep up temperatures within the vary of some thousandths of a Kelvin above absolute zero, is one thing that different researchers with the suitable experience must undertake.
Li notes that “synthetic atoms” made up of assemblages of atoms that share properties and might behave in some ways like a single atom have been used to probe many properties of actual atoms. Equally, he says, these synthetic molecules present “an attention-grabbing mannequin system” that is perhaps used to check “attention-grabbing quantum mechanical issues that one can take into consideration,” akin to whether or not these neutronic molecules could have a shell construction that mimics the electron shell construction of atoms.
“One potential software,” he says, “is possibly we will exactly management the neutron state. By altering the best way the quantum dot oscillates, possibly we will shoot the neutron off in a specific route.” Neutrons are highly effective instruments for things like triggering each fission and fusion reactions, however to date it has been troublesome to manage particular person neutrons. These new sure states may present a lot higher levels of management over particular person neutrons, which may play a task within the growth of latest quantum info techniques, he says.
“One concept is to make use of it to control the neutron, after which the neutron will be capable of have an effect on different nuclear spins,” Li says. In that sense, he says, the neutronic molecule may function a mediator between the nuclear spins of separate nuclei — and this nuclear spin is a property that’s already getting used as a fundamental storage unit, or qubit, in growing quantum laptop techniques.
“The nuclear spin is sort of a stationary qubit, and the neutron is sort of a flying qubit,” he says. “That’s one potential software.” He provides that that is “fairly completely different from electromagnetics-based quantum info processing, which is to date the dominant paradigm. So, no matter whether or not it’s superconducting qubits or it’s trapped ions or nitrogen emptiness facilities, most of those are based mostly on electromagnetic interactions.” On this new system, as a substitute, “we now have neutrons and nuclear spin. We’re simply beginning to discover what we will do with it now.”
One other potential software, he says, is for a type of imaging, utilizing impartial activation evaluation. “Neutron imaging enhances X-ray imaging as a result of neutrons are way more strongly interacting with gentle components,” Li says. It can be used for supplies evaluation, which might present info not solely about elemental composition however even concerning the completely different isotopes of these components. “A number of the chemical imaging and spectroscopy doesn’t inform us concerning the isotopes,” whereas the neutron-based technique may accomplish that, he says.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

