[ad_1]
Apr 04, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson Faculty of Engineering and Utilized Sciences (SEAS) have developed a programmable metafluid with tunable springiness, optical properties, viscosity and even the power to transition between a Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluid.
The primary-of-its-kind metafluid makes use of a suspension of small, elastomer spheres — between 50 to 500 microns — that buckle beneath stress, radically altering the traits of the fluid. The metafluid could possibly be utilized in every thing from hydraulic actuators to program robots, to clever shock absorbers that may dissipate vitality relying on the depth of the impression, to optical gadgets that may transition from clear to opaque.
The analysis is printed in Nature (“Shell buckling for programmable metafluids”).
“We’re simply scratching the floor of what’s potential with this new class of fluid,” stated Adel Djellouli, a Analysis Affiliate in Supplies Science and Mechanical Engineering at SEAS and first writer of the paper. “With this one platform, you may accomplish that many various issues in so many various fields.”
Metamaterials — artificially engineered supplies whose properties are decided by their construction somewhat than composition — have been broadly utilized in a spread of purposes for years. However many of the supplies — such because the metalenses pioneered within the lab of Federico Capasso, Robert L. Wallace Professor of Utilized Physics and Vinton Hayes Senior Analysis Fellow in Electrical Engineering at SEAS — are strong.
“Not like strong metamaterials, metafluids have the distinctive capacity to movement and adapt to the form of their container,” stated Katia Bertoldi, William and Ami Kuan Danoff Professor of Utilized Mechanics at SEAS and senior writer of the paper. “Our purpose was to create a metafluid that not solely possesses these exceptional attributes but in addition supplies a platform for programmable viscosity, compressibility and optical properties.”
Utilizing a extremely scalable fabrication approach developed within the lab of David A. Weitz, Mallinckrodt Professor of Physics and of Utilized Physics at SEAS, the analysis group produced a whole lot of 1000’s of those highly-deformable spherical capsules full of air and suspended them in silicon oil. When the stress contained in the liquid will increase, the capsules collapse, forming a lens-like half sphere. When that stress is eliminated, the capsules pop again into their spherical form.
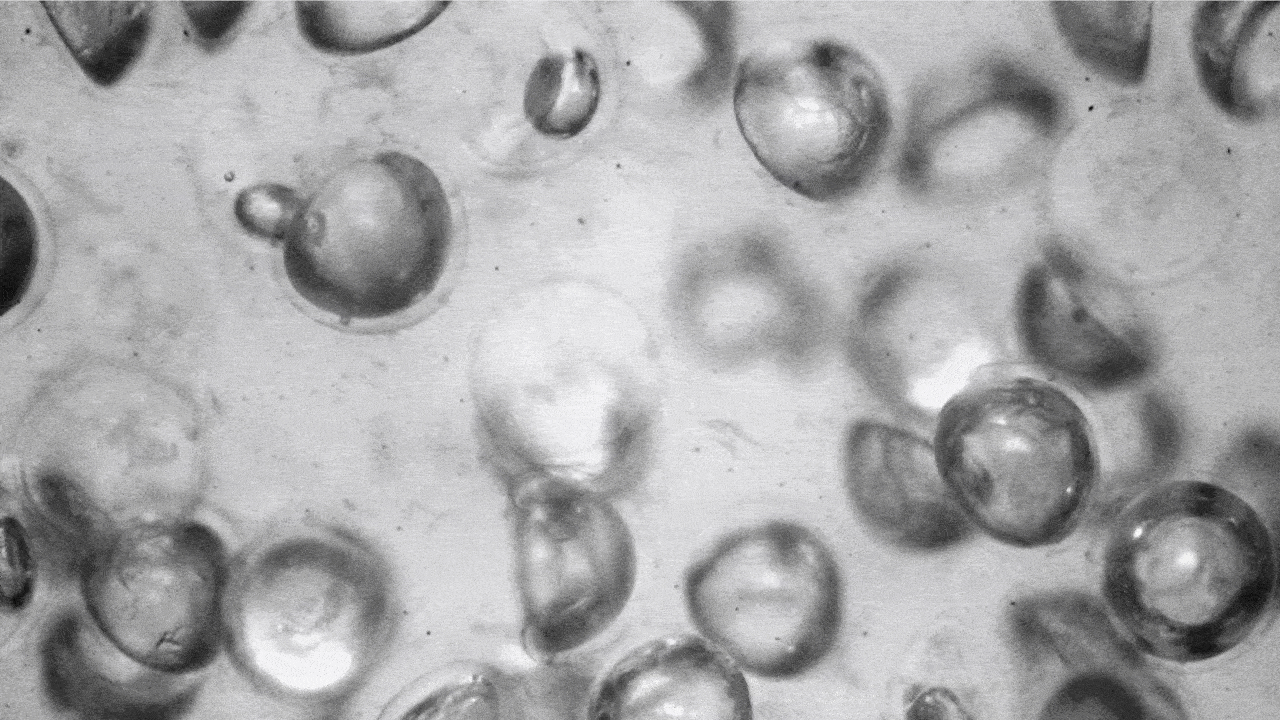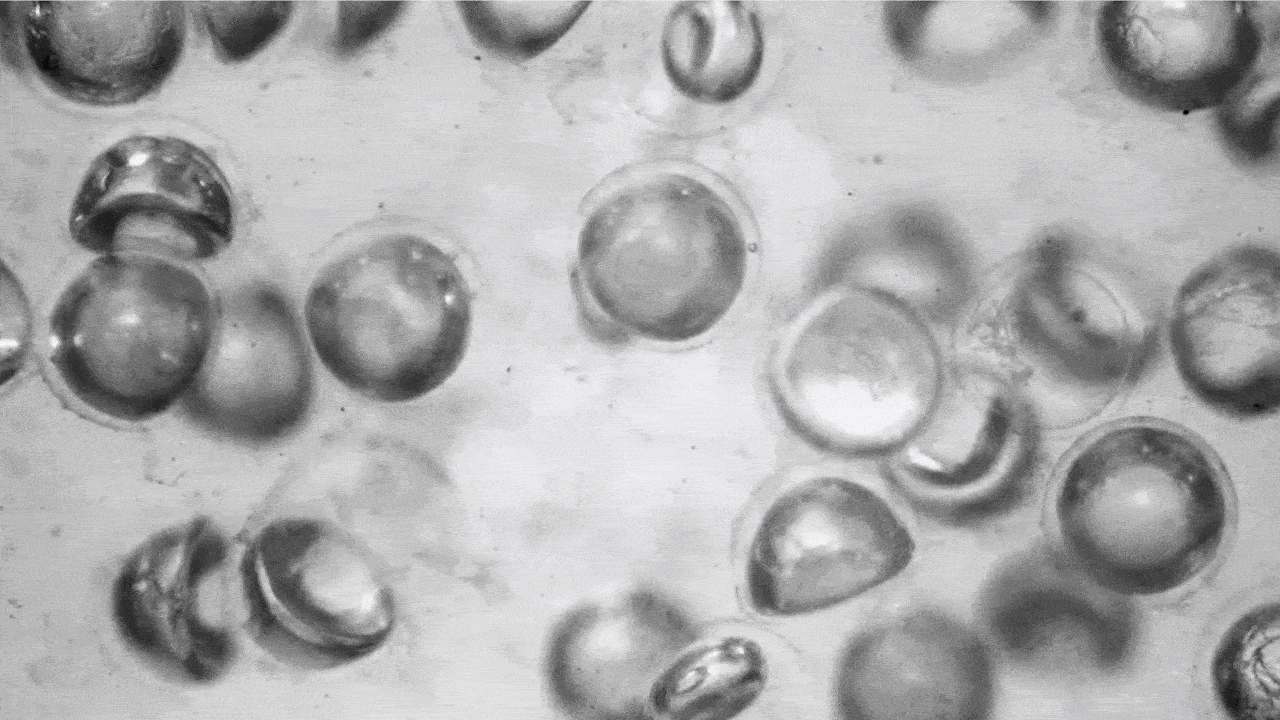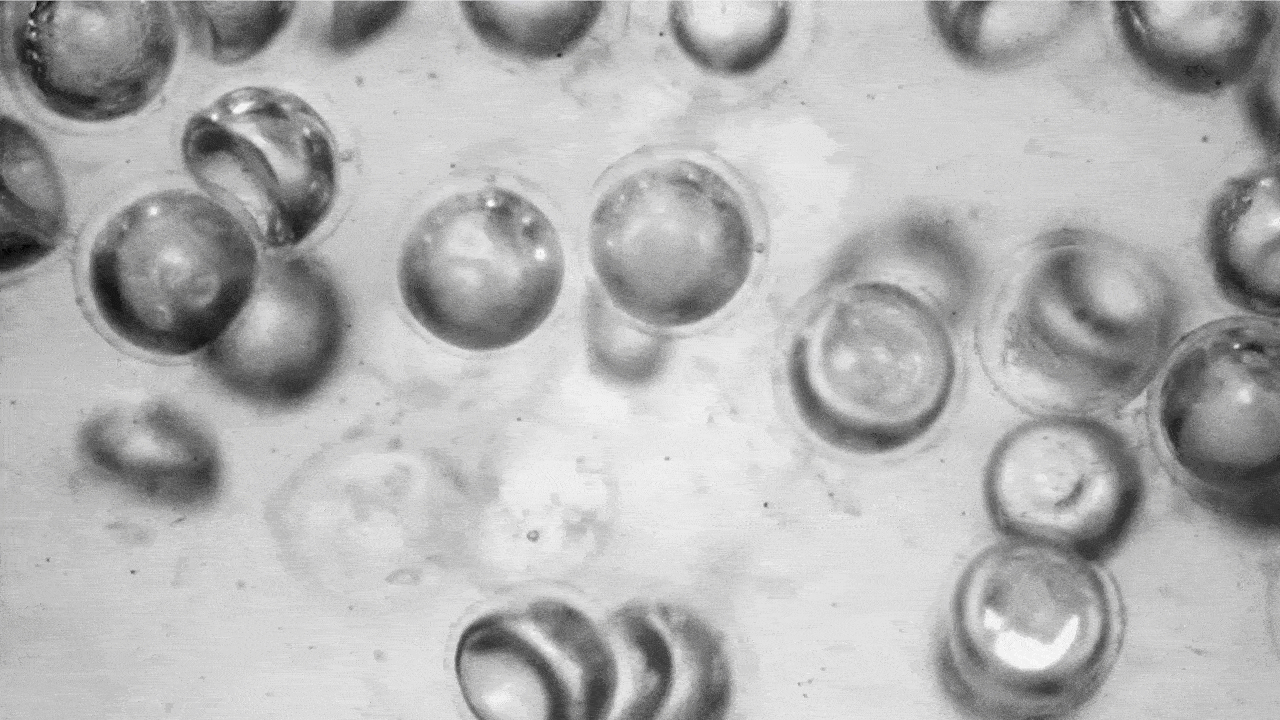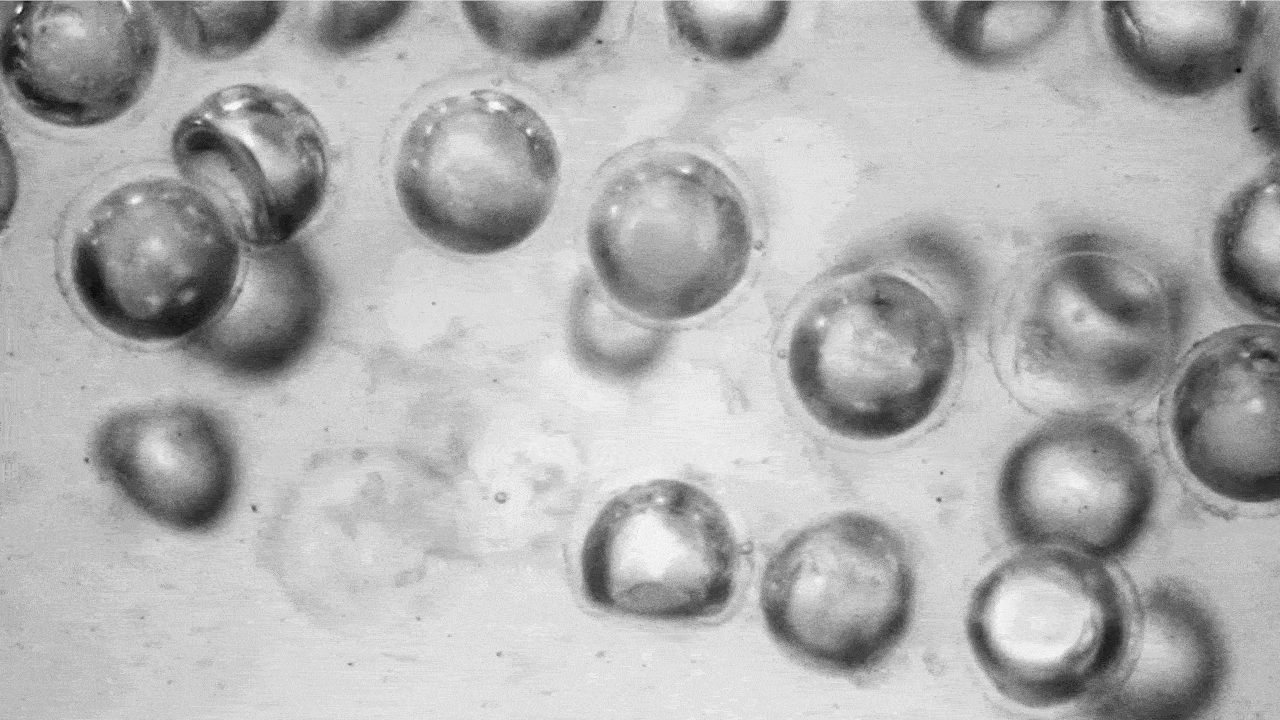
When stress is faraway from the fluid, the capsules pop again into their spherical form. (Picture: Adel Djellouli, Harvard SEAS)
That transition modifications most of the liquid’s properties, together with its viscosity and opacity. These properties could be tuned by altering the quantity, thickness and measurement of the capsules within the liquid.
The researchers demonstrated the programmability of the liquid by loading the metafluid right into a hydraulic robotic gripper and having the gripper choose up a glass bottle, an egg and a blueberry. In a standard hydraulic system powered by easy air or water, the robotic would wish some sort of sensing or exterior management to have the ability to modify its grip and choose up all three objects with out crushing them.
However with the metafluid, no sensing is required. The liquid itself responds to totally different pressures, altering its compliance to regulate the power of the gripper to have the ability to choose up a heavy bottle, a fragile egg and a small blueberry, with no extra programming.
“We present that we will use this fluid to endow intelligence right into a easy robotic,” stated Djellouli.
The group additionally demonstrated a fluidic logic gate that may be reprogrammed by altering the metafluid.
The metafluid additionally modifications its optical properties when uncovered to altering pressures.
When the capsules are spherical, they scatter gentle, making the liquid opaque, very similar to air bubbles make aerated water seem white. However when stress is utilized and the capsules collapse, they act like microlenses, focusing gentle and making the liquid clear. These optical properties could possibly be used for a spread of purposes, resembling e-inks that change shade based mostly on stress.
The researchers additionally confirmed that when the capsules are spherical, the metafluid behaves like a Newtonian fluid, that means its viscosity solely modifications in response to temperature. Nevertheless, when the capsules are collapsed, the suspension transforms right into a non-Newtonian fluid, that means that its viscosity will change in response to shear power — the larger the shear power, the extra fluid it turns into. That is the primary metafluid that has been proven to transition between Newtonian and non-Newtonian states.
Subsequent, the researchers goal to discover the acoustic and thermodynamic properties of the metafluid.
“The applying area for these scalable, easy-to-produce metafluids is large,” stated Bertoldi.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

