[ad_1]
Researchers from KTH Royal Institute of Expertise and Stockholm College have launched a novel technique that streamlines the manufacturing of electrochemical transistors, using an ordinary Nanoscribe 3D microprinter.
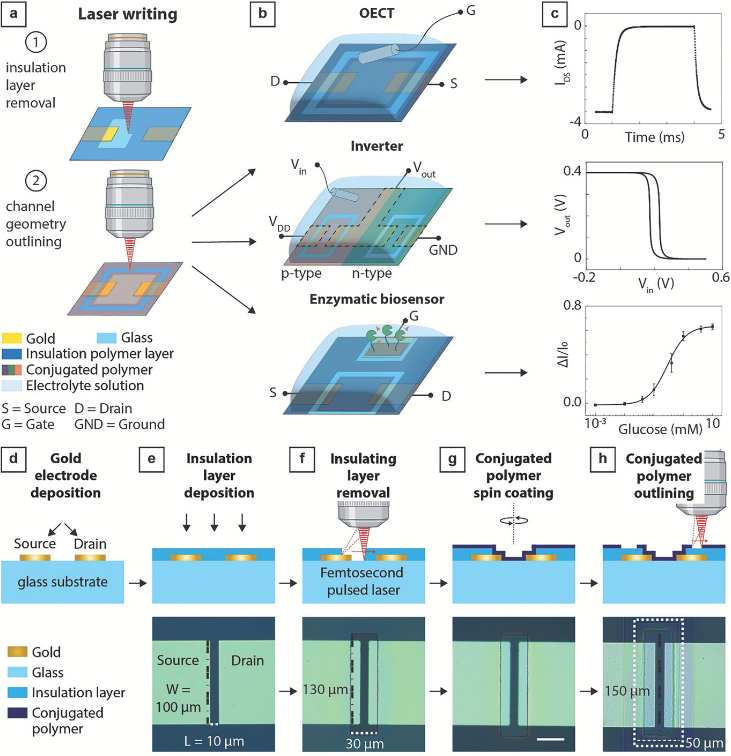
By hacking the 3D printer, the researchers had been in a position to streamline the method by eliminating the necessity for specialised cleanroom environments and the usage of solvents or chemical compounds, addressing key limitations related to conventional fabrication processes. Professor Anna Herland, specializing in Micro- and Nanosystems at KTH, underscores the importance of this strategy in expediting the prototyping of important elements for medical implants, wearable electronics, and biosensors.
Rushing up sustainable bioelectronic system fabrication
Printed within the journal Superior Science, the analysis showcases the profitable fabrication of complementary inverters and enzymatic glucose sensors utilizing the brand new technique. In response to Erica Zeglio, a co-author of the research and researcher at Digital Futures, this strategy not solely accelerates manufacturing but in addition presents a extra sustainable different to traditional practices.
Polymers play a central position in varied bioelectronic functions, from monitoring dwelling tissues to facilitating illness analysis. The analysis crew’s strategy demonstrates enhanced effectivity and accessibility of those gadgets, probably paving the way in which for broader adoption and utilization.
KTH Professor Frank Niklaus, one other co-author of the research, highlighted the flexibility of the strategy, which extends past electrochemical transistors to embody different smooth digital gadgets. The profitable software of ultrafast laser pulses permits speedy prototyping and scaling of microscale gadgets, presenting alternatives for additional innovation within the area.
Professor Herland foresees a shortened time-to-market for bioelectronic gadgets and the incorporation of sustainable elements, marking progress in direction of an environmentally aware future in digital system manufacturing. This imaginative and prescient signifies a optimistic step in direction of enhanced effectivity and environmental duty within the manufacturing of digital gadgets.

Modern 3D printed bioelectronics
Bioelectronics merges biology and electronics, creating gadgets that work together with organic programs. It spans medical implants, wearable screens, neural interfaces, and biosensors, aiming to observe, diagnose, or deal with circumstances whereas advancing our understanding of biology.
Away from KTH Royal Institute of Expertise and Stockholm College, 3D printed bioelectronics developed by different entities have hit the headlines earlier than. One instance consists of that of College of Houston scientists who developed a novel technique of 3D printing bio-sensors utilizing multiphoton lithography (MPL) to create biocompatible circuit boards layer-by-layer, paving the way in which for implantable bio-electronic gadgets. As per the researchers, MPL is hailed as “state-of-the-art” as a consequence of its excessive materials versatility and accuracy.
The crew developed a customized MPL resin, enabling exact 3D printing of bio-circuit boards with homogeneous properties. Testing demonstrated enhanced cell survival and attachment. The bio-sensors exhibited excessive stability and precision in detecting glucose ranges, with ten instances greater sensitivity than present screens, probably accelerating the event of cybernetic implants.
Again in 2020, Joshua Uzarski from the CCDC Soldier Middle revealed to 3D Printing Business that the U.S. Military was actively engaged in growing Cyberpunk-style bio-sensors. Discussing the potential of conformal 3D printing, Uzarski highlighted its software for quickly fabricating microfluidic gadgets on organic surfaces like human pores and skin. Paying homage to these in Cyberpunk 2077, these gadgets aimed for battlefield deployment providing enhanced situational consciousness and potential detection of organic threats. The strategy devised by Uzarski’s crew allowed for versatile, contamination-free microfluidic constructions and speedy prototyping.
What 3D printing traits do the business leaders anticipate this yr?
What does the Way forward for 3D printing maintain for the following 10 years?
To remain updated with the most recent 3D printing information, don’t neglect to subscribe to the 3D Printing Business publication or observe us on Twitter, or like our web page on Fb.
Whilst you’re right here, why not subscribe to our Youtube channel? That includes dialogue, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Are you on the lookout for a job within the additive manufacturing business? Go to 3D Printing Jobs for a collection of roles within the business.
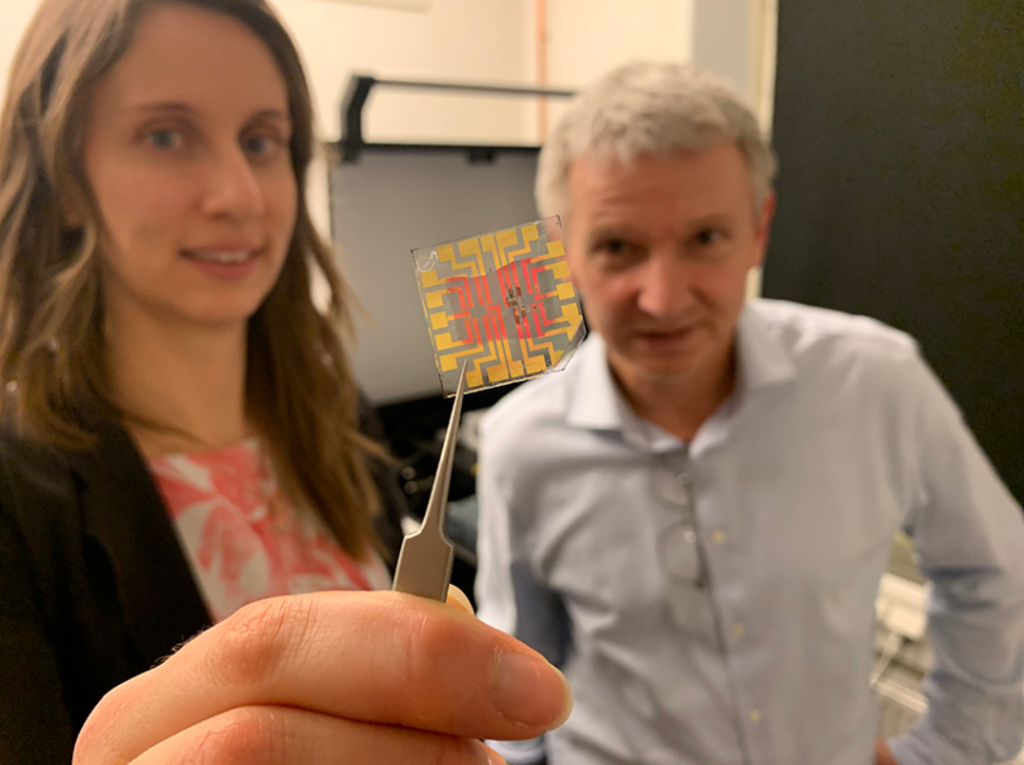
Featured picture reveals researchers Erica Zeglio, left, and Frank Niklaus present a transistor which they printed utilizing a 3D microprinter. Photograph by way of KTH Royal Institute of Expertise.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




