[ad_1]
On this article, we’ll dive into CSS logical properties. We’ll take a look at what they’re, how they work, and what they’re helpful for. We’ll additionally present a useful cheat sheet so you possibly can simply evaluate CSS logical properties with their bodily equivalents.
Even in case you select to not use logical properties your self, it’s a good suggestion to get aware of them, as they’re beginning to seem within the code of an increasing number of web sites and on-line demos.
For instance, you would possibly come throughout this:
p {
margin-block-start: 1em;
}
Until you’re aware of CSS logical properties, that most likely received’t imply a lot to you. In the event you learn on, you’ll quickly be a logical property ninja!
Obtain our useful logical properties PDF cheat sheet.
What Are Logical Properties?
Logical properties supply a brand new solution to declare properties like width and peak, padding, margin, border, border radius, place, float, textual content alignment, and overflow. Historically, these properties have been declared in relation to the bodily dimensions of a pc display — left, proper, prime and backside. Logical properties as a substitute are primarily based on the course of textual content.
Some languages run from left to proper, corresponding to English. Others run from proper to left, like Arabic. Others generally run from prime to backside, corresponding to Japanese. Many web sites have a number of variations in numerous languages, such because the BBC’s information website in English, Arabic and Chinese language, or Al Jazeera’s website in English, Arabic and Chinese language.
Having kinds linked to the course of textual content gives an a variety of benefits, as they’ll adapt to modifications in textual content course and thus apply throughout all variations of a website.
Understanding textual content course
To raised grasp the aim of logical properties, we actually want to grasp a couple of issues about textual content course.
We are able to specify the course of textual content in each HTML and CSS.
HTML has the dir attribute, which specifies whether or not textual content runs from left to proper throughout the web page (dir=”ltr”), proper to left (dir=”rtl”), or whether or not the browser ought to make up its personal thoughts primarily based on the language getting used (dir=”auto”). The dir attribute might be utilized to the entire doc (the norm if the entire doc makes use of the identical language) or to a person aspect.
As an alternative of utilizing the dir attribute in HTML, we will use the course property in CSS. To specify left-to-right textual content, use course: ltr, and for right-to-left textual content, use course: rtl.
It doesn’t actually matter whether or not we set textual content course in HTML or CSS, though it’s usually really helpful that we use the dir attribute in HTML, as that ensures textual content will run within the right course even when one thing goes improper with our fashion sheet.
We are able to additionally use CSS to specify that textual content runs from prime to backside. For vertical textual content that runs from left to proper, we use writing-mode: vertical-lr, and for vertical textual content that runs from proper to left, we use writing-mode: vertical-rl. (There’s no dir possibility for vertical textual content.)
On this article, we’ll take a look at a collection of demos that evaluate the consequences of bodily and logical CSS properties. These demos will illustrate the course of textual content utilizing a paragraph consisting of emojis — a form of common language!
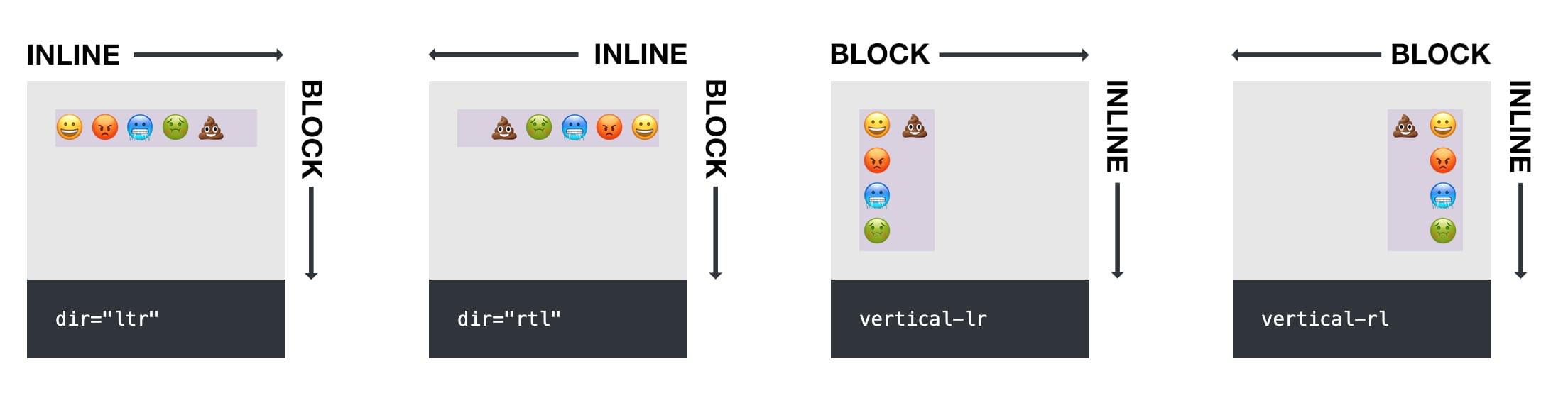
Within the Pen under, now we have 4 packing containers containing our emoji sentence. The primary is ready to dir=”ltr” (the browser default), the second to dir=”rtl”, the third to writing-mode: vertical-lr, and the fourth to writing-mode: vertical-rl.
On this demo, you possibly can see how the text-direction settings have an effect on the order of the characters within the paragraph.
Understanding block and inline in CSS
As CSS grows and develops, the main target is much less on issues that go left, proper, up and down on a display, and extra on the stream of content material. It’s possible you’ll be aware of the principle and cross axes in Flexbox, for instance, which fluctuate relying on the course during which textual content flows, as does the course of Grid content material.
The CSS block and inline properties are decided by the course of textual content. Within the picture under, block and inline course varies relying on the course of the textual content.
For a paragraph that runs left to proper, like this one, the inline course is left/proper, and the block course is up/down.
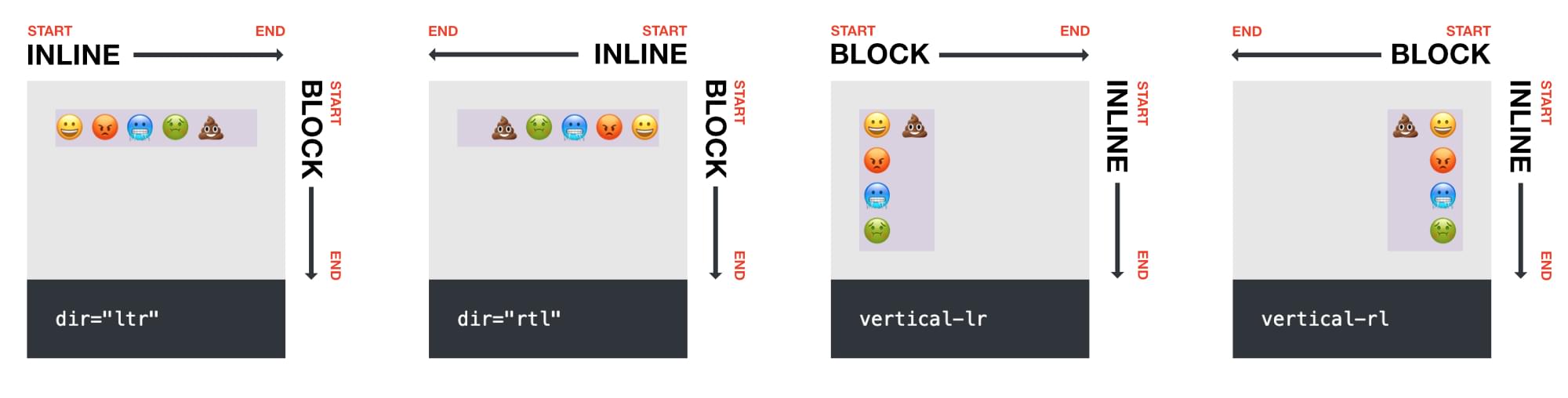
Logical properties are set when it comes to block and inline dimensions, which robotically swap round as textual content course modifications. This makes them way more adaptable than bodily properties.
Inline begin and finish are decided by the place textual content begins and ends, as are begin and finish within the block course.
Are logical properties just for multilingual websites?
Logical properties are helpful for all web sites. There are many conditions the place monolingual web sites would possibly profit from utilizing logical properties.
For instance, you would possibly end up altering the textual content course of a component whereas utilizing media or container queries. Think about a heading with a left pink border. On small screens, the heading is perhaps horizontal, above the next paragraphs. On broad screens, you would possibly set the heading to show vertically. The picture under reveals what would occur in case you used border-left: 5px stable pink on the heading.
As soon as the heading shows vertically, that left border stays on the left, once we most definitely need it at first of the textual content. Utilizing logical properties, we will as a substitute specify that the pink border seems on the inline begin of the heading (border-inline-start), it doesn’t matter what course it’s pointing in, producing the consequence pictured under.
(You possibly can try a stay demo of this on CodePen.)
This reveals how, with logical properties, our structure is extra adaptable to alter with out having so as to add additional CSS for various situations.
Along with this, we’ll additionally see that logical properties supply a lot of helpful shorthands that assist make CSS coding extra environment friendly for everybody — whether or not working with a number of languages or not.
Measurement (Width and Peak Dimensions)
As an alternative of width and peak, that are primarily based on the bodily display, logical properties use inline-size and block-size. To determine which to make use of to set width and peak, now we have to know what course the textual content will go in.
Within the demo under, the paragraphs within the first row have been given an block-size of 80px. In every case, the 80px is ready on the block course, whichever that could be.
Examine this with the second row of paragraphs, that are every set to peak: 80px. In every case, the peak is ready in relation to the display.
Different measurement properties embody:
max-inline-size
min-inline-size
max-block-size
min-block-size
See the cheat sheet for all measurement choices and the way to use them with every textual content course, together with browser assist data.
Margin
Utilizing logical properties, margin is ready with variations of margin-inline and margin-block.
For left-to-right languages, margin-inline-start: 40px will apply a margin at first of the textual content (on the left of the display). When utilized to a right-to-left language, that margin will seem on the proper of the display. For vertical textual content, the margin will seem on the prime, as proven within the demo under.
Examine the impact of margin-inline-start utilized to every paragraph within the first row with the margin-left: 40px utilized to every paragraph within the second row within the demo under.
Different margin properties embody:
margin-inline-end
margin-block-start
margin-block-end
margin-inline
margin-block
Be aware that margin-inline can be utilized as shorthand for margin-left and margin-right, which is available in very useful in numerous conditions — corresponding to margin-inline: auto.
See the cheat sheet for all margin choices and browser assist data.
Padding
Utilizing logical properties, padding is ready with variations of padding-inline and padding-block.
For left-to-right languages, padding-block-start: 40px will apply padding on the prime of the textual content (on the highest of the display). When utilized to a right-to-left language, that padding may even seem on the highest of the display. For vertical textual content, the padding will seem on the left or proper, relying on its horizontal course.
Examine the impact of padding-block-start within the first row with the padding-top: 40px utilized to every paragraph within the second row within the demo under.
Different padding properties embody:
padding-inline-start
padding-inline-end
padding-block-end
padding-inline
padding-block
Be aware that padding-inline can be utilized as shorthand for padding-left and padding-right.
See the cheat sheet for all padding choices, in every textual content course, together with browser assist particulars.
Inset (Positioned Parts)
Have you ever come throughout the very useful inset property? It’s used for positioning components (corresponding to once you’re utilizing place: absolute). For instance, inset: 0 is shorthand for prime: 0; proper: 0; backside: 0; left: 0;.
Let’s do that out in our emoji demo. The containing divs are set to place: relative and the paragraphs are set to place: absolute. The paragraphs within the first row are set to inset-block-end: 30px, whereas these within the second row are set bodily to backside: 30px.
Different properties for inset embody:
inset-block-start
inset-block
inset-inline-start
inset-inline-end
inset-inline
Be aware the useful shorthand inset-block and inset-inline, which can be utilized in simply two instructions. (inset-block: 20px is equal to inset: 20px auto. See a easy demo right here.)
View the complete checklist of inset properties and the way they work with textual content course within the cheat sheet.
Borders
We are able to set a border throughout a component with the border shorthand, corresponding to border: 5px stable pink. But when we simply wish to fashion explicit sides of a component, we’re all of the sudden coping with border-top, border-bottom, border-left and border-right, for which there are logical equivalents.
Borders are a bit of extra concerned, as a result of they contain three values — width (the thickness of the border), fashion (stable, dotted, and so forth), and coloration.
Let’s see what occurs once we apply border-inline-start: 5px stable pink to our paragraphs, and evaluate that with border-left: 5px stable pink;.
Different logical properties for border embody:
border-inline-end
border-block-start
border-block-end
border-inline
border-block
Discover that border-inline is a pleasant shorthand for border:left and border-right in left-to-right stream, and border-block for border-top and border-bottom.
We are able to drill down additional into border logical properties to focus on only a single worth. For width now we have these:
border-block-start-width
border-block-end-width
border-block-width
border-inline-start-width
border-inline-end-width
border-inline-width
For fashion now we have these:
border-block-start-style
border-block-end-style
border-block-style
border-inline-start-style
border-inline-end-style
border-inline-style
For coloration now we have these:
border-block-start-color
border-block-end-color
border-block-color
border-inline-start-color
border-inline-end-color
border-inline-color
Try the cheat sheet for all of the mixtures and permutations of those properties as they apply to every textual content course.
Border Radius
We are able to set a border radius to all corners of a component with the border-radius property. If we’re concentrating on particular person corners with bodily properties, we first contemplate whether or not it’s on the prime or backside of the aspect, after which whether or not it’s on the left or proper of the aspect. So the highest left nook is specified with border-top-left-radius.
When setting border radius with logical properties, as a substitute of prime/bottom-left/proper, we’d like to consider block[start/end]-inline[start-end].
That’s, to decide on the proper property for a selected nook, it’s a must to ask your self whether or not it’s at first or finish of the aspect’s block course and whether or not it’s at first or finish of the aspect’s inline course, giving 4 doable choices within the center:
-start-start-
-end-start-
-start-end-
-end-end-
Within the first row of the next demo, we’re setting a border radius of 20px at first of the block and inline textual content instructions with border-start-start-radius. Examine that with border-top-left-radius within the second row.
There aren’t any particular shorthands right here, so if you wish to spherical two corners, it’s a must to do one thing like this:
border-start-start-radius: 20px;
border-end-start-radius: 20px;
Oh properly! (See a demo of that right here.)
See the cheat sheet for all border radius choices and browser assist data. It took longer for border radius logical properties to be supported by browsers, however assist is now good in fashionable browsers.
Floating and Clearing
Logical properties for float and clear supply new choices for the way to float and clear a component. Earlier than logical properties, the one choices have been float: left and float: proper, clear: left, and clear: proper. The place textual content was vertical, there was no choice to float in the identical course because the textual content.
With logical properties, floating and clearing can now be performed particularly in relation to the inline stream of textual content, due to inline-start and inline-end.
Within the demo under, a span aspect is floated with the logical worth inline-start, in contrast with the bodily worth left within the second row.
The inline-start and inline-end values additionally apply to the clear property. (Right here’s a CodePen demo of that.)
There’s no want for a logical various for clear: each, as a result of it already clears in each inline instructions — which is kind of logical!
Textual content Alignment
We have already got textual content alignment values like left, proper, heart, and justify. Two logical values have now additionally been added: begin and finish. They can be utilized to align textual content alongside the inline axis, it doesn’t matter what course it runs in.
Within the demo under, the paragraphs within the first row have been set to text-align: finish. As you possibly can see, the emojis are all pushed to the far finish of the inline axis.
The cheat sheet reveals the way to apply begin and finish values to work with the varied textual content instructions.
Resizing
The resize property permits for resizing sure components in specified instructions, and now there are inline and block choices.
The demo under reveals the distinction between resize: inline and resize: horizontal. (There’s a tiny resize deal with on the backside proper nook of every field that you would be able to drag.)
(Within the demo above, the resizing for the right-to-left field is a bit wild as a result of dir=”rtl” isn’t being utilized to the entire doc however simply to the containing div.)
Overflow
The bodily properties of overflow-x and overflow-y now have logical enhances of overflow-inline and overflow-block.
Be aware that there’s little or no assist for these new properties on the time of writing (April 2024).
The overscroll-behavior property is a brand new one which refines how overflowing components scroll. We received’t delve into it right here, however you possibly can learn extra on MDN.
Suffice it to say that there are logical variations of those properties in addition to bodily. For instance, overscroll-behavior-x for left-to-right languages might be changed by overscroll-behavior-inline, and so forth. (See the cheat sheet for a full checklist of examples.)
Browser Assist
Browser assist for CSS logical properties superior quickly within the early 2020s, and logical properties at the moment are strongly supported throughout the foremost browsers.
Logical properties carry the identical weight as their bodily counterparts, so in case you’re apprehensive in regards to the expertise in older browsers, you possibly can declare two values, like so:
blockquote {
border-left: 5px stable pink;
border-inline-start: 5px stable pink;
}
Older browsers will use the primary declaration, whereas newer ones will use the second.
Nevertheless, it might be tedious to duplicate code like this all through a mode sheet, so in case you actually are apprehensive about older browsers, maybe go simple on logical properties for now.
Caniuse has an outline of logical property assist, and every part within the cheat sheet additionally has hyperlinks to assist for particular properties.
Conclusion
On this article, we’ve lined virtually each logical property that’s at present obtainable. (You can too try logical properties for caption-side and for measurement containment if you wish to go additional.)
If nothing else, it’s value understanding what logical properties are and the way to use them, even in case you select to not use them for now. A minimum of you’ll perceive the brand new CSS logical property code that’s showing all around the Internet now.
Logical properties do supply advantages, even in case you’re not engaged on multilingual websites. The varied shorthands like margin-inline are very helpful and are good instruments to have in your package.
In the event you’ve learn proper by this text, you need to be capable to acknowledge logical properties wherever they seem. (Look out for these block and inline key phrases!) Hopefully you’re additionally assured sufficient to make use of them often in your CSS — except you’ve been impressed to go full ninja!
Don’t neglect to obtain our useful logical properties PDF cheat sheet.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink