[ad_1]

Genetic variations between people can have an effect on how they reply to medication.Credit score: Jekesai Njikizana/AFP/Getty
How an individual will reply to a drug is, partially, decided by their genetics. Africa holds the world’s most genetically various human inhabitants, and the United Nations estimates that, by 2050, the continent will probably be dwelling to just about 25% of the world’s folks. But pharmacogenomics analysis — research of how genetic variation performs into drug responses — is sorely missing in African populations.
Lower than 5% of the info within the pharmaco-genomics database PharmGKB are from African populations1. And of greater than 300 medication for which the US Meals and Drug Administration offers pharmacogenetic recommendation, solely 15 have been studied in African teams2.
Synthetic intelligence (AI) can assist to shut the hole. AI fashions skilled to determine pharmaco-genetic variants — DNA mutations which may have an effect on how a drug acts — are rising in lots of international locations within the world north. However a dearth of genetic information for African populations, together with an absence of coaching and infrastructure, is holding up using such fashions in Africa. Right here, we define methods to beat these hurdles.
Africa wants pharmacogenetics
Pharmacogenetic information have two key functions. First, they can be utilized to pick out one of the best medication for a person individual — for instance, folks with a pharmacogenetic mutation in an immune-response gene known as HLA-B are hypersensitive to the antiviral drug abacavir, and may subsequently be prescribed alternate options3. Second, such info can be utilized to refine the dose of present medication. As an illustration, a mutation within the gene CYP2C9, which encodes a cytochrome P450 enzyme concerned in drug metabolism, leads to lowered breakdown of the generally used blood thinner warfarin. Individuals who have this variant ought to be given a decrease dose of the drug to stop a build-up of unmetabolized warfarin within the physique that will enhance the chance of a haemorrhage4.

AI can assist to hurry up drug discovery — however provided that we give it the proper information
However pharmacogenetic info generated within the world north will not be at all times related to African populations, as a result of genetic variants are discovered at various frequencies in numerous ethnogeographical teams. Analysis into variants that particularly have an effect on drug responses in Africans residing in Africa, and the African diaspora, is crucial for a number of causes.
First, a reliance on medical information from the worldwide north can put the well being of Africans in danger. Take efavirenz. This promising HIV/AIDS drug was used efficiently in the US and Europe earlier than being launched as a first-line remedy in Zimbabwe in 2015. However the dosing suggestions for Zimbabweans didn’t bear in mind that Africans are extra probably than Europeans and Individuals to hold a mutation within the gene CYP2B6. This mutation is related to a variety of negative effects5. Whereas dizziness, irritability or headache had been generally reported negative effects in European and US sufferers6, many individuals in Zimbabwe skilled hallucinations, nervousness and suicidal ideation when taking efavirenz7.

A researcher analyses outcomes at a tuberculosis laboratory in Cotonou, Benin.Credit score: Yanick Folly/AFP/Getty
Second, the consequences of pharmacogenetic variants have to be thought of alongside a number of different elements that play out in a different way in Africa in contrast with different world areas. As an illustration, every year, the two.5 million individuals who contract tuberculosis in Africa are sometimes given the antimicrobial drug rifampicin, amongst different therapies. However rifampicin quickens the physique’s capacity to metabolize medication8, so if an individual is taking drugs for different situations, their dosages will in all probability have to be modified. Life-style elements akin to food plan, which varies between populations, additionally have an effect on drug metabolism, by altering the neighborhood of microorganisms in an individual’s intestine, which in flip impacts how the physique processes a drug. Analysis performed exterior Africa will in all probability fail to consider these complexities.
Third, there are business incentives. The African inhabitants, coupled with the diaspora, represents an enormous market share for medication. Dosing and prescription changes to make medication protected for these populations is prone to enhance uptake, and so enhance earnings for world pharmaceutical corporations.
AI on the horizon for Africa
Pharmacogenetic variants are exhausting to search out — it could take huge swathes of medical and genetic information to pinpoint a variant that’s related to a change in drug response. AI fashions are shifting the sector forwards by scouring the scientific literature for drug–gene connections that people have missed.

May Africa be the longer term for genomics analysis?
To determine extra variants, the following step — constructing on massive language fashions akin to GPT-4 and LLaMA — is to coach ‘basis’ AI fashions that deliver collectively a number of forms of information for evaluation. For pharmacogenetics, this info will embrace large-scale genetics assets akin to biobanks; digital well being information containing medical textual content and remedy responses; clinical-trial studies and drug labels that seize hostile drug reactions and prescription suggestions; and in vivo and in vitro information about genetics and drug exercise from the prevailing scientific literature.
Basis fashions are already being developed for medical science — for instance, to determine biomarkers of most cancers in imaging information9. We anticipate that an open-access basis mannequin with purposes in pharmacogenetics will probably be out there within the subsequent yr or two.
These basis fashions will probably be biased in direction of international locations within the world north, as a result of their coaching information will come primarily from folks of European descent (see ‘Knowledge bias’). However researchers in Africa can benefit from an method known as switch studying, by which a skilled basis mannequin is fine-tuned utilizing a smaller information set — on this case, info particular to African populations. Switch studying has been used efficiently for picture recognition, with a handful of labelled photographs permitting the mannequin to be taught new patterns10. We’re assured that there are already sufficient African information out there for switch studying to start to determine pharmacogenetic variants.
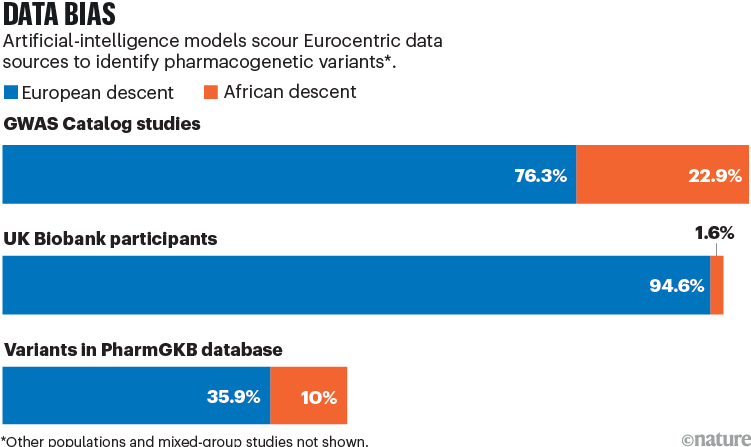
Sources: GWAS Catalog: https://go.nature.com/4CPZMJQ; UK Biobank: A. Fry et al. Am. J. Epidemiol. 186, 1026–1034 (2017); PharmGKB: https://go.nature.com/4A75YAX
4 steps to progress
African international locations principally rank low on the AI readiness index printed by the UK consultancy Oxford Insights, with sub-Saharan Africa the worst-scoring world area relating to how prepared governments are to implement AI in public providers11. The next modifications are wanted to make sure that the scientific neighborhood in Africa is able to harness switch studying — and future AI instruments for pharmacogenetic analysis (see additionally ‘The way forward for AI in pharmacogenetics’).
The way forward for AI in pharmacogenetics
Reducing-edge approaches in synthetic intelligence (AI) might sooner or later assist to tailor medication for Africa.
Strategy 1. Of all drug lessons, anticancer medication have essentially the most pharmacogenetic info out there. It is because anticancer medication are usually examined in vitro utilizing most cancers cells and ‘mini tumours’ grown in tradition dishes, with genetic info collected alongside myriad different organic information. AI fashions that harness this wealth of information are getting used to foretell how sufferers will reply to anticancer medication. An identical method that makes use of ‘mini livers’ and different in vitro fashions of how medication are metabolized may very well be helpful for pharmacogenetics past anti-cancer medication.
Strategy 2. AI fashions have gotten adept at predicting when ‘missense’ genetic variants (which modify one amino acid in a protein) will alter a protein’s structure12, and whether or not that change will forestall the protein from functioning usually. Use of those fashions to analyse variants which might be prevalent in Africa may very well be adopted by mechanistic simulations of how they may have an effect on the medication which might be most frequently prescribed there. This might assist researchers to determine variants of potential pharmacogenetic curiosity and so prioritize them for additional analysis.
Prepare African researchers. Scientists in Africa are greatest positioned each to leverage data of conventional drugs in Africa and to grasp illness epidemiology of their areas. Africans, subsequently, can greatest decide the analysis and information wanted for efficient drug discovery and drug tailoring on the continent.
Worldwide funders, analysis establishments and pharmaceutical corporations should put money into coaching African researchers in AI and pharmacogenetics. Partnering with African initiatives akin to Pharmacometrics Africa — a non-profit group that gives coaching in medical pharmacology — can assist institutes to construct native capability.
Hold gathering information. Though switch studying will probably be useful for figuring out pharmacogenetic variants which might be widespread throughout Africa, many extra genome sequences and centered clinical-trial outcomes are wanted to completely seize pharmacogenetic variations between African populations. Africa will not be homogeneous — totally different ethnogeographical teams ought to be thought of individually, in a lot the identical means as biomedical analysis considers totally different European populations. The variety of medical trials on the continent is rising; future trials should embrace various cohorts of individuals, spanning a number of ethnicities.
Researchers wishing to conduct medical trials throughout Africa at present want to use to the well being authorities of every nation, every of which has totally different authorized requirements, charges and response timelines. When the African Medicines Company turns into absolutely operational, clinical-trial regulation ought to change into harmonized throughout the continent. With the date of this unknown, till then researchers can get assist from the Medical Trials Neighborhood — a platform hosted by the medical software program firm Nuvoteq in Pretoria, South Africa, that gives up-to-date assets on the varied regulatory and ethics necessities for conducting medical trials in every nation in Africa.
Put money into infrastructure and gear. Genomics amenities are scarce in lots of African international locations. A bunch of internationally famend genomics researchers hopes to determine eight centres of excellence in genomics in Africa, every coordinated with a neighborhood tutorial unit and public-health facility. This initiative might deliver world-class genomics analysis to Africa, producing the info wanted to determine pharmacogenetic variants. To make this a actuality, sturdy coordination between worldwide funders, native governments and the Africa Centres for Illness Management and Prevention in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, is required to make sure that funding for the venture materializes.

Enable patents on AI-generated innovations — for the great of science
And genomics instruments akin to pharmacogenetics testing kits — which analyse organic samples for 1000’s of mutations in genes concerned in drug responses — should be tailor-made to Africans. This know-how might assist clinicians to adapt drug prescriptions to every affected person’s genetic traits, bringing personalised drugs to Africa. Corporations that make these instruments, such because the US biotechnology agency Illumina, ought to work with African scientists to drive the inclusion of Africa-relevant variants as they’re found.
Develop frameworks for information sharing and moral analysis. It’s unlikely {that a} single African establishment, metropolis and even nation may have all the required elements — human capability, analysis infrastructure and data-collection websites — to have the ability to conduct world-class pharmacogenetics analysis. Knowledge sharing is subsequently wanted.
However native researchers are involved that overtly sharing their information will put them at an obstacle in contrast with colleagues within the world north, who may need extra assets, infrastructure and expert personnel to analyse the info and publish their findings. This reluctance is exacerbated by the truth that acquiring moral approval to share and reuse samples is time-consuming — explaining and acquiring knowledgeable consent for genomics analysis typically entails translating consent varieties into native languages, as an example.
African scientists should construct trusted analysis networks for sharing of information. These efforts will profit from having continent-level authorized and ethics frameworks for information sharing, enabling cross-country collaborations.
An excellent instance of how information sharing throughout the continent can stimulate world-class analysis comes from the Pan-African Bioinformatics Community (H3ABioNet). This analysis consortium manages information storage and community infrastructure for the Human Heredity and Well being in Africa (H3Africa) initiative — the biggest effort to coordinate genomics analysis in Africa up to now. The community has amenities in a number of African international locations and well-defined data-submission and entry insurance policies for human genomics. It combines regionally led administration committees with coaching, good computational infrastructure and clear insurance policies about information high quality, permitting outcomes to be deposited in a shared databank and integrated into worldwide databases such because the European Genome–phenome Archive.
When sharing of open information is restricted — within the case of a affected person’s biomedical information, as an example — ‘decentralized’ AI algorithms can assist. These are skilled on information from quite a few institutes, however in a means that enables every institute to maintain its personal information non-public. Such cooperative algorithms have been piloted in reference centres and hospitals in Europe and the US for medical-imaging information.
The primary steps in direction of realizing pharmacogenetics analysis in Africa are being taken, and AI can play a pivotal half in shifting the sector forwards. With profitable capability constructing, folks in Africa will profit from safer and simpler therapies, lowering the price of well being care on the continent. With out it, the disease-eradication targets outlined by the World Well being Group for the present decade are unlikely to be met.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

