[ad_1]
Local weather litigation is within the highlight once more after a landmark determination final week. The highest European human-rights court docket deemed that the Swiss authorities was violating its residents’ human rights via its lack of local weather motion. The case, introduced by greater than 2,000 older ladies, is certainly one of greater than 2,300 local weather lawsuits which were filed towards firms and governments all over the world (see ‘Local weather instances soar’).
However does authorized motion regarding local weather change make a distinction to nations’ and companies’ actions? Litigation is spurring on governments and firms to ramp up local weather measures, say researchers.

‘Actually historic’: How science helped youngsters win a landmark local weather trial
“There are a variety of notable local weather wins in court docket which have led to motion by governments,” says Lucy Maxwell, a human-rights lawyer and co-director of the Local weather Litigation Community, a non-profit group in London.
Nature explores whether or not lawsuits are making a distinction within the struggle towards world warming.
What have local weather court docket instances achieved?
One pivotal case that spurred on change was introduced towards the Dutch authorities in 2013, by the Urgenda Basis, an environmental group based mostly in Zaandam, the Netherlands, together with some 900 Dutch residents. The court docket ordered the federal government to cut back the nation’s greenhouse-gas emissions by a minimum of 25% by 2020, in contrast with 1990 ranges, a goal that the federal government met. Consequently, in 2021, the federal government introduced an funding of €6.8 billion (US$7.2 billion) towards local weather measures. It additionally handed a legislation to section out the usage of coal-fired energy by 2030 and, as pledged, closed a coal-production plant by 2020, says Maxwell.
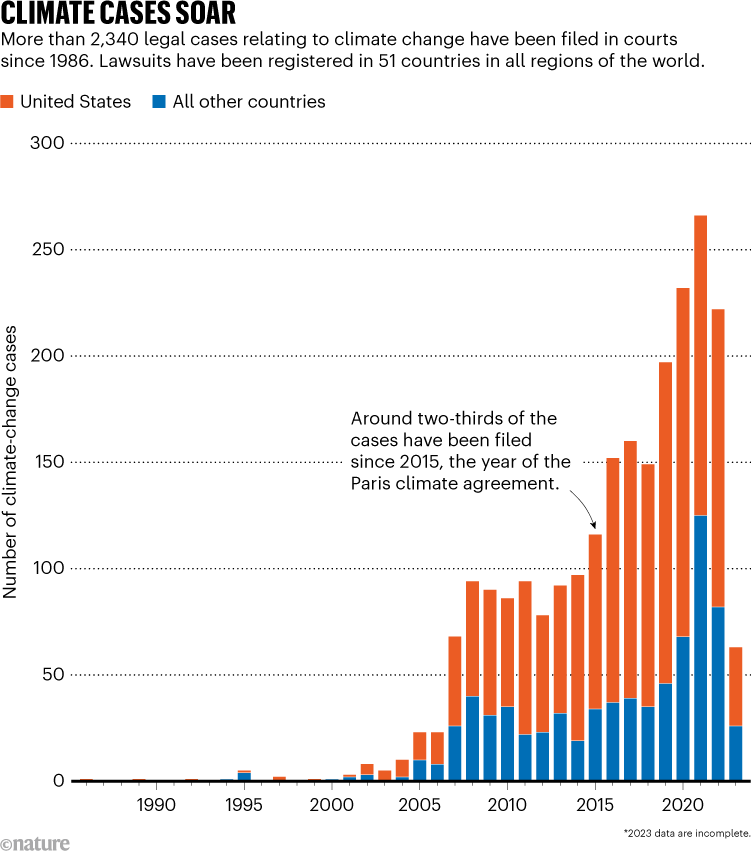
Supply: Grantham Analysis Institute/Sabin Middle for Local weather Change Legislation
In 2020, younger environmental activists in Germany, backed by organizations comparable to Greenpeace, gained a case arguing that the German authorities’s goal of lowering greenhouse-gas emissions by 55% by 2030 in contrast with 1990 ranges was inadequate to restrict world temperature rise to “nicely under 2 ºC”, the objective of the 2015 Paris local weather settlement. Consequently, the federal government strengthened its emissions-reduction goal to a 65% reduce by 2030, and set a objective to cut back emissions by 88% by 2040. It additionally introduced forwards a goal to succeed in ‘local weather neutrality’ — guaranteeing that greenhouse-gas emissions are equal to or lower than the emissions absorbed from the environment by pure processes — by 2045 as a substitute of 2050. “Within the Netherlands and Germany, motion was taken instantly after court docket orders,” says Maxwell.
In its 2022 report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change acknowledged for the primary time that local weather litigation could cause an “enhance in a rustic’s total ambition to sort out local weather change”.
“That was a giant second for local weather litigation, as a result of it did actually present the way it can affect states’ ambition,” says Maria Antonia Tigre, director of the Sabin Middle for Local weather Change Legislation at Columbia College in New York Metropolis.
What about instances that fail?
Instances that fail in court docket could be useful, says Joana Setzer on the Grantham Analysis Institute on Local weather Change and the Surroundings on the London Faculty of Economics and Political Science.
In a 2015 case known as Juliana v. United States, a bunch of younger folks sued the US authorities for not doing sufficient to decelerate local weather change, which they stated violated their constitutional proper to life and liberty. “It is a case that has confronted many authorized hurdles, that didn’t consequence within the court docket mandating coverage change. Nevertheless it has raised public consciousness of local weather points and helped different instances,” says Setzer.
One lawsuit that benefited from the Juliana case was gained final yr by younger folks in Montana, says Setzer. The court docket dominated that the state was violating the plaintiffs’ proper to a “clear and healthful setting”, by allowing fossil-fuel improvement with out contemplating its results on the local weather. The ruling signifies that the state should take into account local weather change when approving or renewing fossil-fuel initiatives.
What occurs when folks sue companies?
In a working paper, Setzer and her colleagues discovered that local weather litigation towards companies can dent the corporations’ share costs. The researchers analysed 108 local weather lawsuits filed between 2005 to 2021 towards public US and European companies. They discovered case filings and court docket judgments towards large fossil-fuel corporations, comparable to Shell and BP, noticed fast drops within the firms’ total valuations and share costs. “We discover that, particularly after 2019, there’s a extra important drop in share costs,” says Setzer. “This sends a robust message to buyers, and to the businesses themselves, that there’s a reputational harm that may consequence from this litigation,” she says.
In an evaluation of 120 local weather instances, to be revealed on 17 April by the Grantham Analysis Institute, Setzer’s crew discovered that local weather litigation can curb greenwashing in firms’ ads — this contains making deceptive statements about how climate-friendly sure merchandise are, or disinformation in regards to the results of local weather change. “With litigation being introduced, firms are undoubtedly speaking otherwise and being extra cautious,” she says.
What’s coming subsequent in local weather litigation?
Maxwell thinks that folks will carry extra lawsuits that demand compensation from governments and firms for loss and harm brought on by local weather change. And extra instances shall be centered on local weather adaptation — suing governments for not doing sufficient to organize for and regulate to the results of local weather change, she says. In an ongoing case from 2015, Peruvian farmer Saúl Luciano Lliuya argued that RWE, Germany’s largest electrical energy producer, ought to contribute to the price of defending his hometown from floods brought on by a melting glacier. He argued that planet-heating greenhouse gases emitted by RWE enhance the chance of flooding.
Extra instances shall be difficult an over-reliance by governments on carbon seize and storage (CCS) applied sciences — which take away carbon dioxide from the environment and retailer it underground — in reaching emissions targets, says Maxwell. However CCS applied sciences haven’t but proved to work at a big scale. As an example, in February, researchers criticized the European Union for relying an excessive amount of on CCS in its plans to chop greenhouse-gas emissions by 90% by 2040 in contrast with 1990 ranges.
“There’s a tendency now for firms and governments to say, we’ll use carbon seize, we’ll discover some expertise,” says Setzer. “Within the courts, we’ll begin seeing to what extent you possibly can rely on the longer term applied sciences, to what extent you actually have to start out appearing now.”
What about lower-income international locations?
There may also be extra local weather instances filed within the world south, which typically obtain much less consideration than these within the world north, says Antonia Tigre. “There may be extra funding now being channelled to the worldwide south for bringing these kind of instances,” she says. This month, India’s supreme court docket dominated that folks have a elementary proper to be free from the destructive results of local weather change.
Final week’s Swiss success demonstrates that folks can maintain polluters to account via lawsuits, say researchers. “Litigation permits stakeholders who typically do not get a seat on the desk to be concerned in pushing for additional motion,” says Antonia Tigre.
Maxwell thinks that the judgment will affect lawsuits worldwide. “It sends a really clear message to governments,” she says. “To adjust to their human rights obligations, international locations have to have science-based, speedy, formidable local weather motion.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

