[ad_1]
Mar 12, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) Discovering the very best methodology to ship chemotherapeutic medicine to tumor cells will be tough. Ideally, the therapies goal tumor cells whereas leaving wholesome cells alone.
Immunoliposomes might be the reply. They’ll effectively bind to antigens on tumor cell surfaces by their surface-targeting ligands, permitting tumor cells adequate time to take up the “poison.” The advantages of immunoliposomes in most cancers remedy have been extensively documented within the final 4 many years. Nevertheless, immunoliposomal medicine haven’t but made it to the market, though that they had been demonstrated in laboratories since 1981.
Why? One key barrier is the shortage of a large-scale, low-cost but possible manufacturing approach. Grafting concentrating on ligands onto plain liposomes to kind immunoliposomes entails a few half-dozen steps and may result in potential issues.
Yuan Wan, an affiliate professor at Binghamton College’s Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Utilized Science, not too long ago revealed analysis within the journal Nature Nanotechnology (“Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly”) outlining a one-step manufacturing course of for immunoliposome manufacturing. It doesn’t require any chemical conjugation and related chemical reagents, making it eco-friendly.
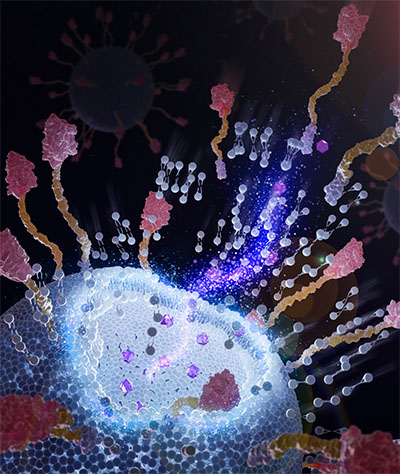
Chimeric nanobodies on the floor of immunoliposomes can connect to tumor cells and facilitate higher drug supply. (Picture: Courtesy of the researchers)
“The normal manufacturing strategy of immunoliposomes is comparatively advanced,” mentioned Wan, a school member within the Division of Biomedical Engineering. “It entails plenty of chemical conjugation and purification. Chemical conjugation and required reagents impair the steadiness and antigen binding of concentrating on ligands. The multistep course of results in payload leakage and product loss. So, immunoliposomes are much less enticing to industrial producers due to their low yield, excessive manufacturing prices and the excessive danger of batch-to-batch variation. These shortcomings hinder industrial manufacturing and medical use of immunoliposomes.”
What makes Wan’s analysis completely different is the addition of engineered chimeric nanobodies, which have a “sticky” finish. Greater than 2,500 nanobodies can combine on the surface of a single 100-nanometer liposome, which is about 1,000 occasions smaller than a human hair.
This methodology is simpler, quicker and cheaper than conventional strategies, and it permits for extra management over the ultimate product. The floor nanobodies additionally kind a protecting layer across the liposome, which could assist it keep away from being cleared by the physique too shortly and permit it to remain within the bloodstream longer.
One other large benefit is that this methodology doesn’t require harsh chemical compounds. Conventional strategies usually use a substance referred to as polyethylene glycol (PEG), which generally may cause issues for sufferers, even dying. Due to these considerations, the federal Meals and Drug Administration requires additional monitoring for medicine containing PEG.
“One thing actually fascinating we discovered is that when these chimeric nanobodies are inserted into the lipid bilayer, they really improve the rigidity and thermal stability of your entire immunoliposomes. So, the medicine packed inside can maintain up for 10 months with out apparent leaks,” Wan mentioned.
As a result of there are additionally round 20 plain liposomal medicine already in use, Wan is hopeful that — with additional analysis and medical trials —immunoliposomes might be manufactured and get federal approval for medical use.
“We’re additionally engaged on creating new chimeric nanobodies to ramp up manufacturing by at the very least 30 occasions. It should make the manufacturing price of those chimeric nanobodies a lot decrease.” Wan mentioned.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink



