[ad_1]
Apr 03, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) A global workforce led by Australian analysis centre ASTRO 3D experiences that age is the driving power in altering how stars transfer inside galaxies.
Galaxies begin life with their stars rotating in an orderly sample however in some the movement of stars is extra random. Till now, scientists have been unsure about what causes this – probably the encompassing setting or the mass of the galaxy itself.
A brand new research, printed in a paper in Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (“The SAMI Galaxy Survey: galaxy spin is extra strongly correlated with stellar inhabitants age than mass or setting”), has discovered that a very powerful issue is neither of these items. It exhibits the tendency of the celebrities to have random movement is pushed largely by the age of the galaxy – issues simply get messy over time.
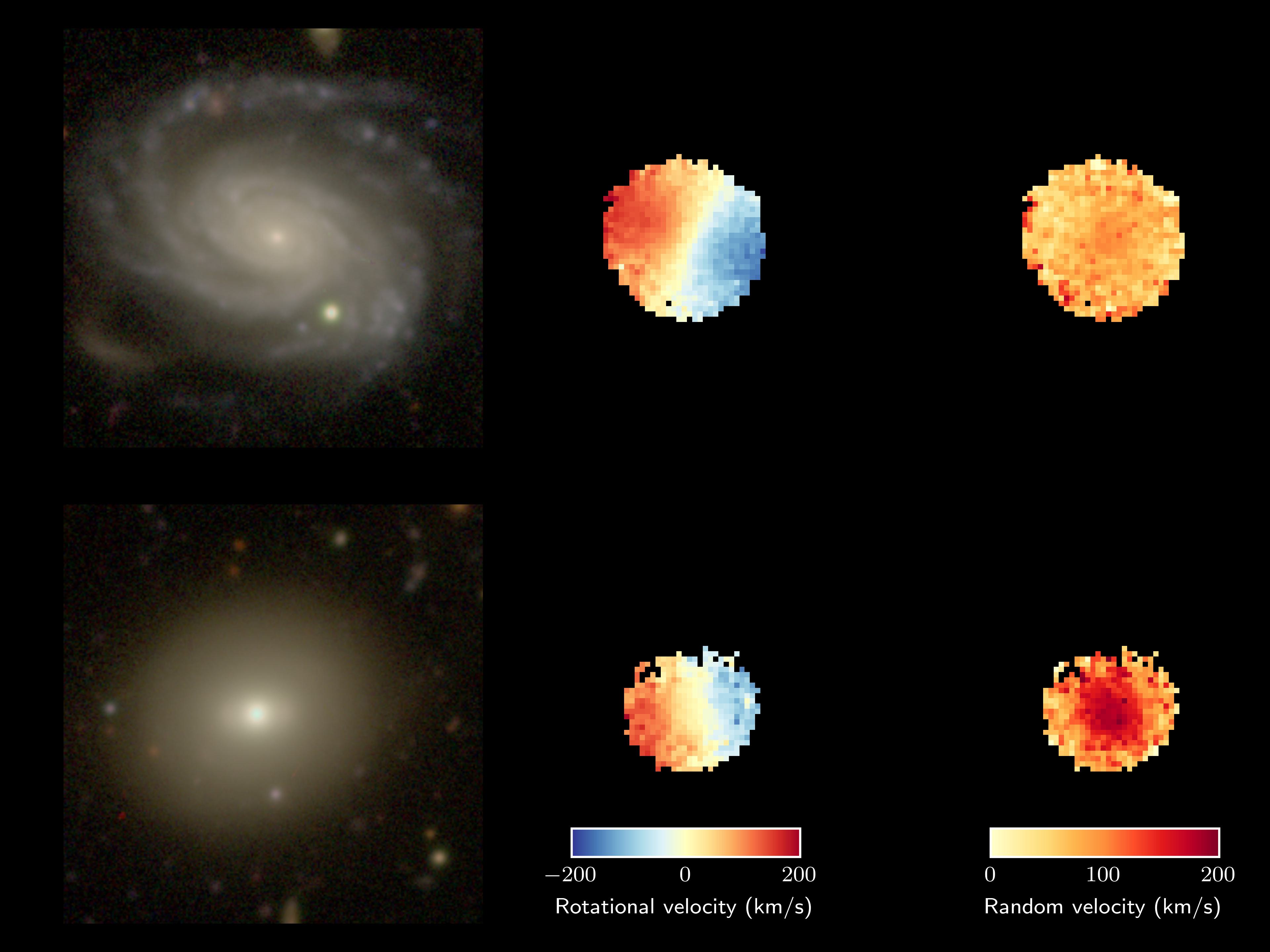
Comparability of a younger (high) and outdated (backside) galaxy noticed as a part of the SAMI Galaxy Survey. Panels on the left are common optical photographs from the Subaru Telescope. Within the center are rotational velocity maps (blue coming in the direction of us, pink going away from us) from SAMI. On the suitable are maps measuring random velocities (redder colors for higher random velocity). Each galaxies have the identical whole mass. The highest galaxy has a median age of two billion years, excessive rotation and low random movement. The underside galaxy has a median age of 12.5 billion years, slower rotation and far bigger random movement. (Picture: Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program)
“After we did the evaluation, we discovered that age, persistently, whichever method we slice or cube it, is all the time a very powerful parameter,” says first creator Prof Scott Croom, an ASTRO 3D researcher on the College of Sydney.
“When you account for age, there’s primarily no environmental pattern, and it’s comparable for mass.
“In case you discover a younger galaxy it will likely be rotating, no matter setting it’s in, and in case you discover an outdated galaxy, it can have extra random orbits, whether or not it’s in a dense setting or a void.”
The analysis workforce additionally included scientists from Macquarie College, Swinburne College of Know-how, the College of Western Australia, the Australian Nationwide College, the College of New South Wales, the College of Cambridge, the College of Queensland, and Yonsei College within the Republic of Korea.
The research updates our understanding from earlier research which have variously recommended setting or mass as extra vital elements. However the earlier work is just not essentially incorrect, says second creator Dr Jesse van de Sande.
Younger galaxies are star-forming super-factories, whereas in older ones, star formation ceases.
“We do know that age is affected by setting. If a galaxy falls right into a dense setting, it can are inclined to shut down the star formation. So galaxies in denser environments are, on common, older,” Dr van de Sande says.
“The purpose of our evaluation is that it’s not residing in dense environments that reduces their spin, it’s the truth that they’re older.”
Our personal galaxy, the Milky Method, nonetheless has a skinny star forming disk, so remains to be thought of a excessive spin rotational galaxy.
“However once we take a look at the Milky Method intimately, we do see one thing known as the Milky Method thick disk. It’s not dominant, by way of mild, however it’s there and people look to be older stars, which can nicely have been heated from the skinny disk at earlier instances, or born with extra turbulent movement within the early Universe,” Prof Croom says.
The analysis used information from observations made below the SAMI Galaxy Survey. The SAMI instrument was inbuilt 2012 by the College of Sydney and the Anglo-Australian Observatory (now Astralis). SAMI makes use of the Anglo-Australian Telescope, at Siding Spring Observatory, close to Coonabarabran, New South Wales. It has surveyed 3000 galaxies throughout a wide range of environments.
The research permits astronomers to rule out many processes when attempting to grasp galaxy formation and so fine-tune fashions of how the Universe has developed.
The following steps will likely be to develop simulations of galaxy evolution with extra granular element.
“One of many challenges of getting simulations proper is the excessive decision you want in to foretell what is going on on. Typical present simulations are based mostly on particles which have the mass of perhaps 100,000 stars and you may’t resolve small-scale constructions in galaxy disks,” Prof. Croom says.
The Hector Galaxy Survey will assist Prof Croom and his workforce increase this work utilizing a brand new instrument on the Anglo-Australian Telescope.
“Hector is observing 15,000 galaxies however with larger spectral decision, permitting the age and spin of galaxies to be measured even in a lot decrease mass galaxies and with extra detailed environmental info,” says Professor Julia Bryant, lead of the Hector Galaxy Survey, College of Sydney.
Professor Emma Ryan-Weber, Director of ASTRO 3D, says, “These findings reply one of many key questions posed by ASTRO 3D: how does mass and angular momentum evolve within the Universe? This cautious work by the SAMI workforce reveals that the age of a galaxy determines how the celebrities orbit. This crucial piece of knowledge contributes to a clearer big-picture view of the Universe.”
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

