[ad_1]
In keeping with Penn State researchers, a newly created “GPS nanoparticle” may be administered intravenously and goal most cancers cells to ship a genetic punch to the protein concerned in tumor improvement and dissemination.
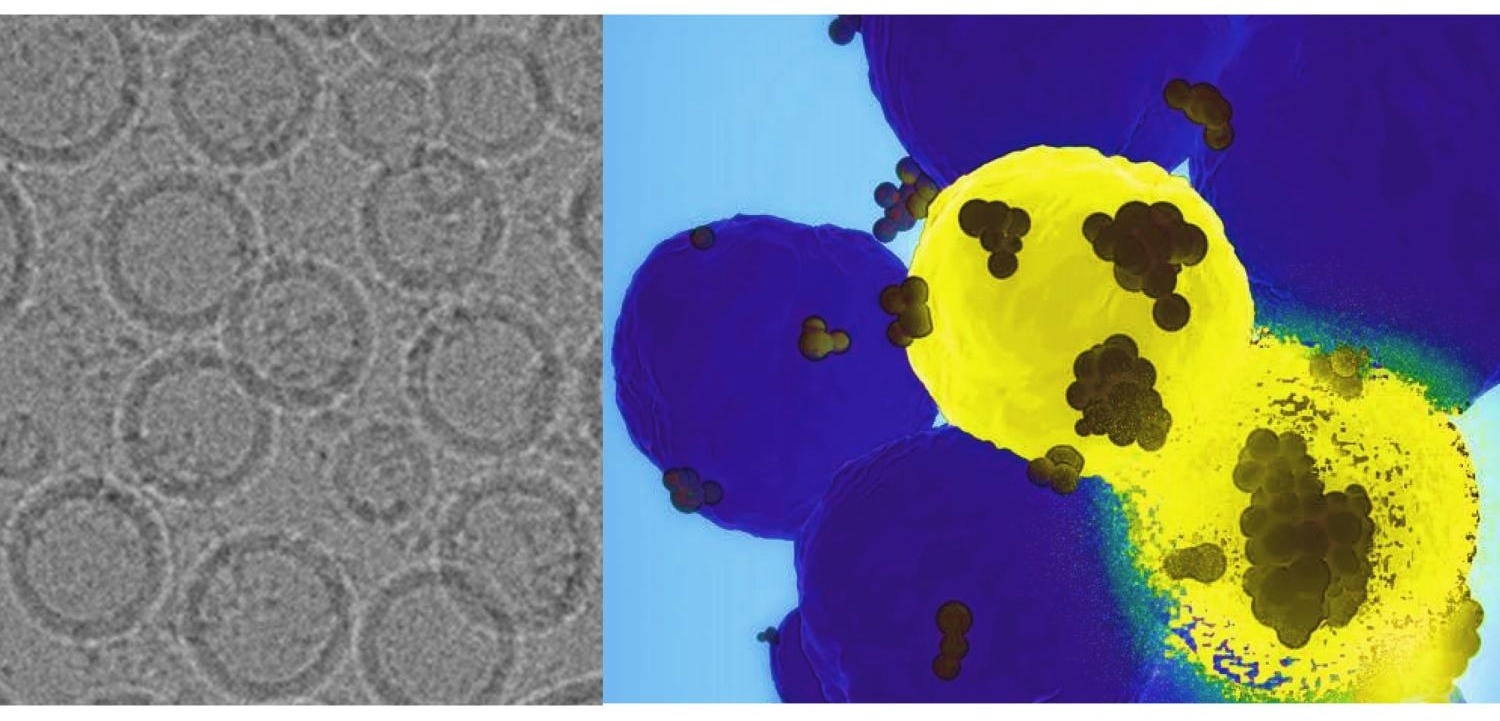
On the left is an electron microscopic picture of the nanoparticles designed by the staff led by Penn State researchers. On the correct, the nanoparticles, proven as black dots, discover the basal-like breast most cancers cells in yellow and ship the gene-editing instruments. The disintegrating cell demonstrates the damaging energy of the remedy delivered by the nanoparticle. Picture Credit score: Offered by Dipanjan Pan
Their technique to efficiently knock down a cancer-causing gene was evaluated in mice and human cell traces. They reported that the know-how may provide a extra correct and profitable remedy for basal-like breast tumors, that are recognized to be extraordinarily tough to remedy.
On March eleventh, 2024, their examine was printed in ACS Nano. Moreover, they submitted a provisional patent software for the approach included on this examine.
We developed a GPS nanoparticle that may discover the location the place it’s wanted. As soon as there — and solely there — it could possibly ship gene modifying proteins to stop the most cancers cells from spreading. It was a tough job, however we confirmed that the system works for basal-like breast cancers.
Dipanjan Pan, Dorothy Foehr Huck & J. Lloyd Huck Chair Professor in Nanomedicine, Pennsylvania State College
Although much less widespread than different breast cancers, basal-like tumors may be a lot more durable to deal with as a consequence of their lack of the three therapeutic targets current in different breast most cancers varieties, which is analogous to triple-negative breast cancers.
Additionally they often develop quickly, shedding cells that journey to different components of the physique and changing into aggressive tumors. This process, often known as metastasis, permits these cells to spawn new cancers.
Pan added, “Metastasis is a large problem, particularly with cancers like triple-negative and basal-like breast cancers. The most cancers may be arduous to detect and doesn’t present up throughout a routine mammogram, and it primarily impacts the youthful or African American inhabitants who will not be receiving preventative care but. The end result may be very, very poor, so there’s a clear unmet scientific want for simpler remedies when the most cancers isn’t caught early sufficient.”
The scientists created a Malicious program nanoparticle by overlaying it with specifically designed fatty molecules that resemble naturally occurring lipids and filling it with CRISPR-Cas9 molecules. These molecules can goal a cell’s genetic materials, establish a sure gene, and both knock it down or render it ineffective. On this situation, the system focused human forkhead field c1 (FOXC1), which is chargeable for metastasis.
Pan labeled the designer lipids as “zwitterionic,” which implies they’ve a near-neutral cost on the nanoparticle shell. This stops the physique’s immune system from combating the nanoparticle since it’s camouflaged as a non-threatening, regular molecule, and it could possibly assist launch the payload if the lipids detect the most cancers cell’s low pH surroundings.
To ensure that the lipids solely activated at that low pH, the researchers engineered them to cost positively as soon as they entered the extra acidic tumor microenvironment, prompting payload launch.
Nevertheless, given the scale of the physique, how may the researchers make sure that the CRISPR-Cas9 payload reached the supposed location? Moreover, scientists appended an epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), which is understood to hook up with basal-like breast most cancers cells, to ensure the nanoparticle would hyperlink to the right cells.
“Nobody has ever tried to focus on a basal-like breast-like most cancers cell with context-responsive supply system that may genetically knockdown the gene of curiosity. We’re the primary to point out that it may be carried out,” Pan famous.
Some researchers have created non-viral supply strategies that use nanoparticles in addition to viral supply programs that use a virus particle to ship medication to cells. The floor lipid in Pan’s staff’s methodology, he claimed, is exclusive in that it reacts solely within the goal surroundings, minimizing the potential of off-target supply and harm to wholesome cells.
Moreover, he said that there’s much less probability of an immune response because the physique doesn’t view lipids as a risk, some extent that their research supported.
To verify that the nanoparticle would launch the CRISPR/Cas9 system within the acceptable setting, the researchers initially examined the tactic on human triple-negative breast most cancers cells. In a mouse mannequin, they verified that the nanoparticle may find a tumor, activate the mechanism, and successfully destroy FOXC1.
Pan said that the researchers intend to check the nanoparticle platform additional sooner or later with the last word goal of utilizing it in human scientific settings.
Pan said, “We’re additionally exploring how else we’d apply the platform know-how. We will customise the molecules on the floor, the payload it carry, and use it to encourage therapeutic in different areas. There may be loads of potential with this platform.”
David Skrodzki, Matthew Molinaro, Nivetha Gunaseelan, all doctoral college students at Penn State; Dinabandhu Sar, College of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign; Teresa Aditya, postdoctoral researcher in nuclear engineering at Penn State; Dipendra Dahal and Priyanka Ray, each postdoctoral researchers in Pan’s laboratory at his earlier establishment of the College of Maryland Baltimore are the opposite authors.
This examine was supported by Penn State, the College of Maryland Baltimore College of Drugs, the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention, the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis, and the US Division of Protection Congressionally Directed Medical Analysis Program.
Journal Reference:
Moitra, P., et. al. (2024) Context-Responsive Nanoparticle Derived from Artificial Zwitterionic Ionizable Phospholipids in Focused CRISPR/Cas9 Remedy for Basal-like Breast Most cancers. ACS Nano. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c01400.
Supply: https://www.psu.edu/
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink




