[ad_1]
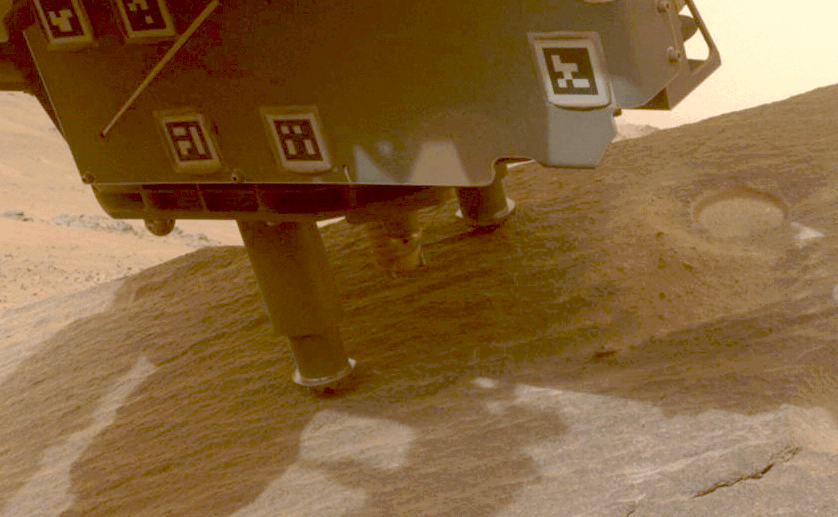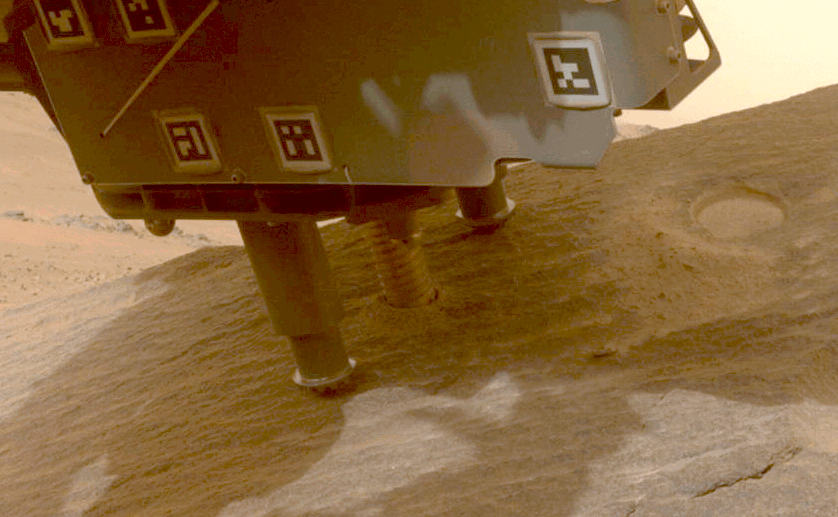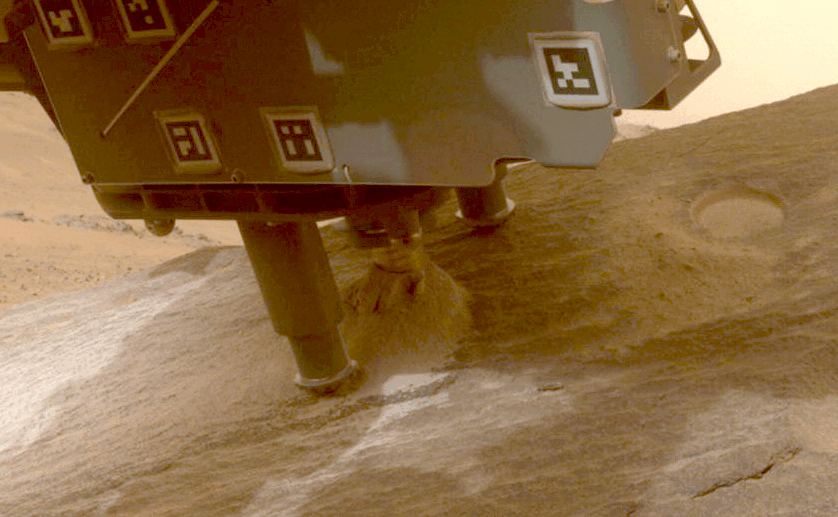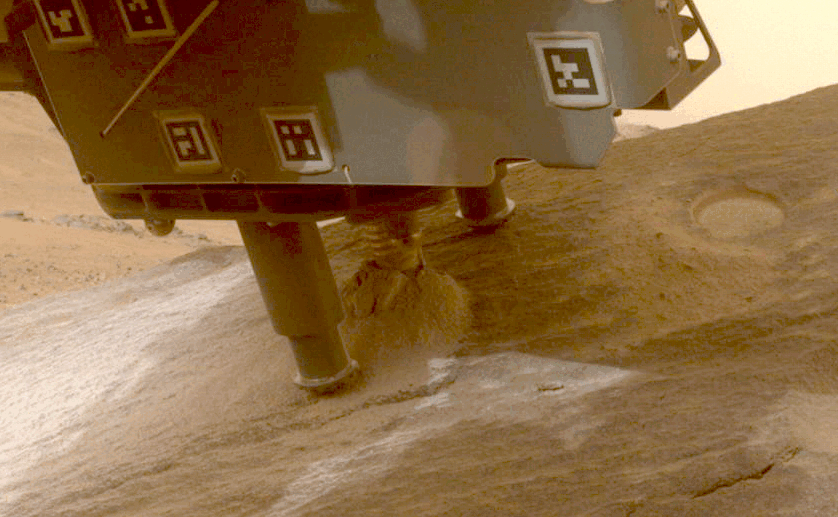
NASA’s Perseverance rover collects a pattern from a Martian rock utilizing a bit on the tip of its robotic arm.Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA introduced at this time that it’s abandoning its longstanding plan for ferrying rock and soil samples from Mars to Earth. As an alternative the company will search proposals for faster and cheaper methods to ship the samples to Earth.
An impartial overview board concluded final 12 months that NASA’s Mars pattern return mission may value as a lot as US$11 billion, greater than what it value to launch the James Webb House Telescope. In a report launched at this time, a separate NASA overview workforce concluded that even when the company spent that a lot cash, the dropoff of the samples on Earth can be delayed till 2040. The company had initially sought to land the samples on Earth within the early 2030s.
The $11 billion price ticket is “too costly,” stated NASA administrator Invoice Nelson at a press briefing, and “not returning the samples till 2040 is unacceptable.” Nelson stated the company “is dedicated to bringing at the least among the samples again” and later stated NASA would return “greater than 30” of the 43 deliberate samples.
Scaling again
NASA’s Perseverance rover has already collected greater than 20 rock samples from Jezero Crater, the place the rover landed in 2020. Scientists suppose that the crater was as soon as full of a lake of water, and samples from the crater and its environment may present a window into the planet’s historical past and, maybe, proof of previous life on the purple planet.
Within the company’s unique imaginative and prescient, a NASA spacecraft would have flown to Mars carrying a two-part retrieval system: a half-ton lander — which might have been probably the most large automobile to ever land on Mars — and a rocket to fly the lander and samples into Martian orbit. There they had been to satisfy a spacecraft launched by the European House Company that might fly the samples to Earth.
Now NASA plans to solicit proposals — from firms in addition to NASA centres — for a streamlined system, maybe one which makes use of a lighter lander, Nicky Fox, the affiliate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, stated on the briefing. The deadline for proposals is 17 Might, and the revised mission can be chosen later this 12 months. Fox didn’t reply on to reporters’ questions on when the samples will attain Earth beneath the brand new scheme.
NASA recommends spending $200 million of its planetary-science finances in 2025 on assessing various architectures for Mars pattern return, Fox stated. Dedicating any extra money to the mission threatened to “cannibalize” different planetary science missions, Nelson stated.
Again to the drafting board
Vicky Hamilton, a planetary scientist on the Southwest Analysis Institute in Boulder, Colorado, expressed disappointment that eight months after the impartial overview board launched its report, the company nonetheless lacks a strong plan for “a really useful science purpose.”
Returning these samples would additionally exhibit functionality for two-way journey to Mars earlier than we will ship astronauts, says Bethany Ehlmann, a planetary scientist on the California Institute of Expertise in Pasadena, California. “The pattern return expertise is right here, it exists,” she says. “It’s a matter of placing the items collectively.”
However scientists had been relieved by one announcement: Fox stated the revised timeline for pattern return won’t have an effect on the science objectives for Perseverance, together with plans for it to discover terrain past Jezero Crater.

NASA’s Mars rover makes ‘unbelievable’ discover in seek for previous life
Amongst samples collected exterior the crater can be “among the historic crust of Mars, representing rocks older than we’ve got seen but in Jezero Crater, a few of which can have been altered by near-surface water,” says Meenakshi Wadhwa, a planetary scientist at Arizona State College in Tempe and principal scientist for the Mars Pattern Return program.
To date, the one Mars samples that scientists have been capable of research on Earth are bits and items ejected from the purple planet that made it to Earth as meteorites. All identified Martian meteorites are “igneous” rocks, which means that they solidified from lava, and all are very outdated. Consequently, they supply useful timestamps for Mars’ geological evolution, however carry little details about how the planet’s floor was formed by the water that when flowed throughout it.
To realize the mission’s important purpose of looking for indicators of previous life, the actual treasures are layered sedimentary rocks fashioned by minerals and natural matter deposited over the aeons by water. Perseverance’s devices have already detected natural molecules in Martian samples, however whether or not these molecules are a marker of previous life can solely be decided by nearer scrutiny in laboratories on Earth.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

