[ad_1]
When Hurricane Otis hit Acapulco on the Pacific coast of Mexico on 25 October 2023, it had developed far more shortly and brought a special course than predicted. It broken an space protecting practically 700 hectares, dwelling to round 560,000 individuals (see go.nature.com/499dwgy). A preliminary evaluation means that reconstruction might price between US$14 billion and $21 billion (see go.nature.com/3pkbvav).
The hurricane’s influence uncovered a scarcity of readiness from the Mexican authorities’s Nationwide Civil Safety System, native authorities, emergency response companies and the personal sector (significantly the tourism trade); this lack of preparedness affected a big a part of the native inhabitants.
It additionally laid naked the structural and socio-economic vulnerabilities that prevail within the nation. Years of uneven improvement and territorial planning have led to the formation of settlements which are significantly in danger from pure hazards and through which the poorest communities are systematically probably the most weak. As excessive climate occasions improve in frequency and depth, so does the necessity for communities to be higher ready — and higher repaired.

Catastrophe early-warning programs are ‘doomed to fail’ — solely collective motion can plug the gaps
In 2023, we and others based the Mexican Community of Scientists for Local weather (REDCiC, for its acronym in Spanish) to construct bridges between these engaged on local weather points from totally different views. This consists of scientists and postgraduate college students from the nation at Mexican and worldwide private and non-private analysis establishments, in addition to journalists and outreach professionals. The community at present includes round 100 members, and is prone to double in dimension in a few years. By organizing actions resembling conferences and workshops, REDCiC facilitates scientific trade and data sharing, and seeks to make sure that local weather adaptation and mitigation insurance policies are rooted in strong knowledge and analyses. For instance, a workshop on Hurricane Otis led to a collaboration with the Mexican federal authorities’s Nationwide Council of Humanities, Sciences and Applied sciences (Conahcyt). And thru public campaigns, media publicity, outreach and training, REDCiC engages the general public in local weather actions and highlights the function of citizen science, native practices and Indigenous Data in addressing present and future environmental challenges.
Grounded on this interdisciplinary perspective, right here we set out three priorities for scientists and policymakers to sort out climate-driven hazards and assist scale back vulnerability.
Put money into modelling and forecasting
Disasters fuelled by the local weather disaster are on the rise globally. In 2023 alone, record-breaking floods hit a number of nations, together with the USA (see go.nature.com/3psmtaj), India and a number of other Mediterranean nations. In accordance with the worldwide catastrophe database EM-DAT, there have been distinguished episodes of intense droughts (go.nature.com/496q8uj), heatwaves1 and wildfires2 throughout the Northern Hemisphere, together with in Canada, the USA and Mexico. It’s important that fashions and practices replicate present local weather traits as precisely as attainable.
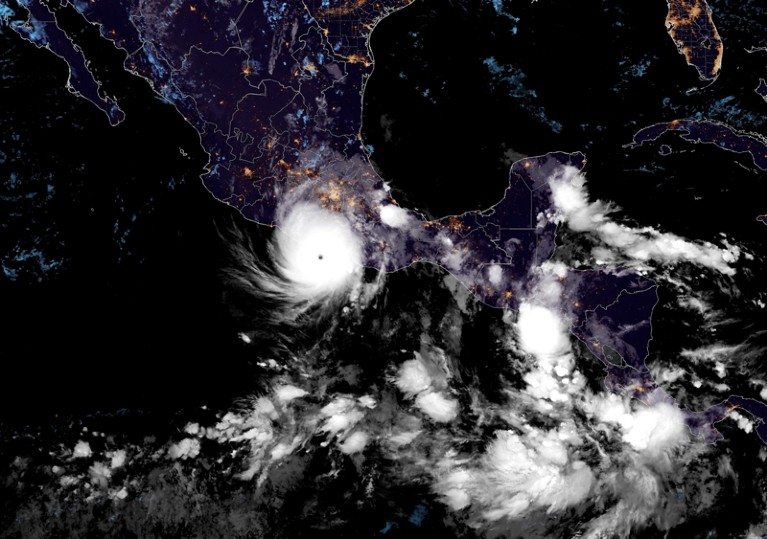
A satellite tv for pc picture of the class 5 Hurricane Otis over the west coast of Mexico.Credit score: GOES-East/NOAA/Alamy
Why did state-of-the-art fashions fail to forecast that Otis would attain the utmost depth (a class 5 hurricane), relatively than stay a tropical storm? Thorough analyses are required, but it surely appears to have stemmed partly from its fast improvement within the East Pacific area, the place data-collection factors are sparse. The restricted availability of ocean buoys, land observations, radars and hurricane hunters alongside the west coast of Mexico locations heavy reliance on satellite tv for pc imagery for forecasting, which, together with the annoying nature of local weather impacts, can result in less-accurate forecasts.

Flash floods: why are extra of them devastating the world’s driest areas?
Governments and funding companies should spend money on higher infrastructure and instrumentation, together with extra analysis into climate occasions. Many phenomena — together with how hurricanes intensify3 — are complicated and never properly understood. They continue to be troublesome to foretell regardless of appreciable advances in meteorological modelling and forecasting in current a long time4.
An overhaul of what’s thought of experience can also be required — Indigenous Data and native and conventional practices have sometimes been dismissed, however will help to enhance info high quality and knowledge availability for modelling and forecasting5. That is particularly essential for a rustic resembling Mexico, the place a big proportion of lands (together with a minimum of 60% of forests and tropical rainforests) are managed by Indigenous and native communities.
Construct resilience in weak communities
The results of Hurricane Otis additionally underscore the necessity to enhance early-warning programs — which is itself contingent on correct forecasts. As a result of catastrophe preparation turns into troublesome as soon as winds attain tropical storm power (sustained floor winds of 63–117 kilometres per hour), alerts must be issued between 36 and 48 hours earlier than the anticipated influence. That is consistent with the United Nations’ Early Warnings for All initiative, which goals to make sure everybody is protected against pure hazards by 2027.
To guard populations successfully, communication have to be fast and seamless between levels, from knowledge assortment and forecasting to the unfold of disaster-risk data and warnings to communities which are prone to be affected.
Furthermore, the response capability of a neighborhood comes into play. This facet is comparatively subjective and, in a way, is not only a coverage challenge however a political one, as a result of it includes defining what’s significant, fascinating and a precedence. Energy dynamics at native and nationwide ranges have lengthy led to the marginalization of Indigenous Peoples and native communities, which signifies that such teams have traditionally been excluded from decision-making processes.
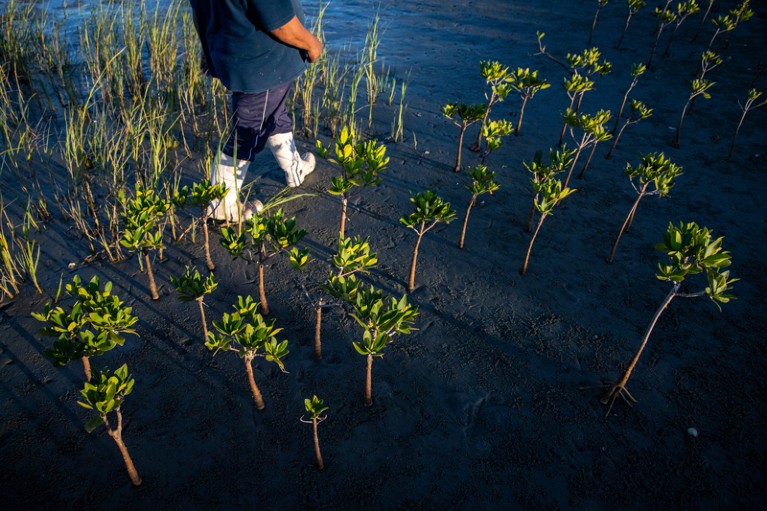

Mangrove saplings planted by a neighborhood reforestation undertaking in El Delgadito, Mexico.Credit score: Gemina Garland-Lewis
In making landfall in and round Acapulco, Otis hit an space identified for its long-standing stark inequalities and vulnerabilities, and its lack of inclusive mechanisms for planning, coordinating and implementing danger methods. Farther inland, the federal government of Mexico Metropolis has introduced the event of ‘neighborhood brigades’ to handle these points. Teams of skilled volunteers assist to lead disaster-risk prevention and responses of their communities, though the undertaking continues to be within the developmental section.

With the arrival of El Niño, put together for stronger marine heatwaves
In addition to being disproportionately affected by the consequences of local weather change, low- and middle-income nations typically encounter vital boundaries to implementing long-term local weather methods. Though worldwide local weather justice and loss-and-damage mechanisms are essential, so are formidable nationwide and regional actions. A sturdy adaptation framework includes reshaping city and rural improvement methods, re-evaluating constructing codes and development practices for effectivity, circularity and resilience, and reconceptualizing reconstruction efforts to include ecosystemic, social and cultural variety. This will succeed provided that the framework is put in place by native and nationwide governments working with native communities, as a result of it isn’t sufficient to only swiftly and pragmatically disburse loss-and-damage funding. Native wants, challenges and priorities should be thought of.
Traditionally, low- and middle-income nations have been assigned the function of useful resource suppliers. These prevailing dynamics of worldwide manufacturing, consumption and commerce have to be re-evaluated. Every nation should assess the extent to which it could actually decouple useful resource extraction from financial development, by decreasing reliance on linear fashions of manufacturing and consumption, and enhancing useful resource effectivity and circularity. Equally, nations should discover methods to decouple financial development from total prosperity and high quality of life. This features a re-evaluation of the importance of personal, public and social property, which might play a key half in useful resource demand. For instance, prioritizing investments in public infrastructure and concrete utilities can alleviate useful resource demand. Somewhat than selling personal facilities resembling swimming swimming pools, which are sometimes an inefficient use of land and sources, emphasis must be positioned on public alternate options resembling open areas and public leisure areas.
Work with native communities
In Mexico, investing in and implementing mid- and long-term adaptation insurance policies and plans has proved difficult, although these have been formulated by the federal authorities, a lot of the state governments and some municipal governments. That is largely as a result of greater than one-third of the nation’s inhabitants lives in poverty, in line with CONEVAL (the Nationwide Council for the Analysis of Social Growth Coverage). Towards this background, addressing primary pressing wants inside a framework of short-term targets has essentially been prioritized over future local weather adaptation plans, although this inhabitants group is prone to be most affected by long-term local weather results.
Past poverty and insufficient primary providers and infrastructure, nevertheless, local weather motion is hindered by weak governance, restricted funding, restricted human capability on the native stage and a scarcity of belief and involvement of Indigenous and native communities.

Meet the scientists planning for disasters
Instruments resembling danger atlases, territorial and hydrological planning and constructing requirements have to be tailored and robustly up to date to take local weather dangers and systemic vulnerabilities into consideration. For this to occur, it’s important for the scientific neighborhood, practitioners, authorities companies and, definitely, Indigenous and native communities to achieve a consensus on probably the most appropriate standards, whereas contemplating variety (spatial, social and cultural). A participatory and inclusive consensus ought to allow improvement of significant metrics to evaluate vulnerability and consider the effectiveness of actions taken.
This kind of consensus-building observe led to the profitable reforestation of mangroves within the El Vizcaíno Biosphere Reserve in Mexico. The mangroves shield the native coastal neighborhood of El Delgadito from hurricanes, storms and floods; present habitats for fish and shellfish — a key supply of livelihood — and function carbon dioxide sinks. Since 2017, nevertheless, it has been recorded that mangroves have suffered dryness and uprooting, which is attributed to local weather change.
In response, in 2019, the area people initiated a reforestation effort in partnership with scientists at Mexican establishments, the US–Mexican non-governmental group WILDCOAST and the Mexican authorities’s Nationwide Fee of Pure Protected Areas (CONANP). This enabled the reintroduction of greater than 60,000 vegetation in 4 years6. Girls and younger individuals of any gender are actively concerned in planting, upkeep and monitoring actions. Youngsters are additionally inspired to take part, fostering environmental consciousness and training in the neighborhood.
The REDCiC community goals to advertise progress alongside all three priorities outlined. It fosters interactions within the scientific neighborhood — from local weather, environmental and social sciences to public well being; helps communication between scientists, related establishments and the general public; and promotes the inclusion of Indigenous and native communities in any respect ranges of the discourse.
These collaborations are essential for constructing a climate-resilient society, significantly in contexts which are characterised by constrained capacities and escalating wants, as in Mexico. Worldwide organizations, native and regional governments, scientific establishments, organized civil society, the personal sector and the media ought to help networks resembling this one — in Mexico and elsewhere — by funding but in addition by participating with their members and actions to speed up transformational, relatively than merely incremental, local weather motion.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink

